Cilia play critical roles in sending and receiving signals from distant sites through mechano- and chemosensation and now through small extracellular vesicles known as ectosomes
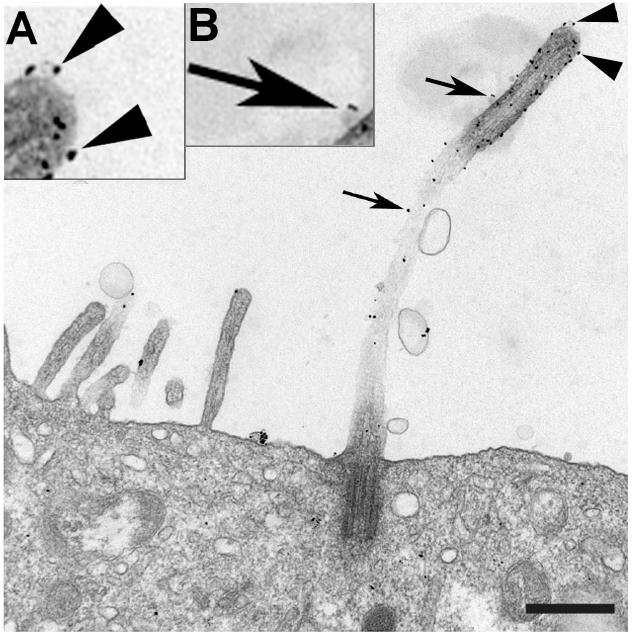
Credit: This image was previously published at low magnification in Molecular Biology of the Cell (Zuo, X., Guo, W., Lipschutz, J.H. 2009. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 20:2522-2529) and is…
Although the cilium has been known to scientists for more than 100 years, it is only recently that it has been acknowledged to play important roles in physiology. Virtually every cell has a primary cilium that functions to senses fluid flow, transmits chemical signals to other cells and controls cell growth. Defects in the function of cilia lead to a class of diseases called ciliopathies, which include polycystic kidney disease, primary ciliary dyskinesia and Bardet-Biedl syndrome.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), membrane-bound carriers with complex cargos that include proteins, lipids and nucleic acids, function in long-distance cellular communication, but how cilia contribute to EV production was previously unclear to the scientific community. New work from researchers at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC), published online on Nov. 6 by the Journal of Biological Chemistry, shows that primary cilia generate approximately 60% of the small EVs produced by renal tubule cells and that manipulation of cilium length affects the production of EVs. Furthermore, the protein content of EVs is very different depending on the length of the cilia.
“For many years, people thought EVs represented a garbage disposal system – a way for the cell to get rid of things it didn’t need. But I think it is pretty clear that small (50-150nm) EVs represent one of the main signaling mechanisms of the cell,” says Joshua H. Lipschutz, M.D., the Arthur V. Williams Chair and director of the Division of Nephology at MUSC. “This is the first real demonstration in mammalian cells that ectosomes, EVs produced by primary cilia as opposed to exosomes, which are EVs that are similar in size but form in the multivesicular bodies of the cell, are so prominent.”
One of the key components of ciliogenesis – the process of generating a cilium – is the exocyst, an eight-protein complex that is highly conserved and was first discovered in yeast. Previous work has shown that loss of exocyst complex component 5 (EXOC5), one of the eight proteins that make up the exocyst, causes very short or no cilia to be produced. Conversely, increased expression of EXOC5 causes the cilia to lengthen.
In their current work, Lipschutz and colleagues took these data one step further and examined the contribution of the exocyst to EV production. They compared three groups of cells: normal kidney cells, kidney cells that have lost EXOC5 and kidney cells that make more EXOC5 than normal. All three of these groups were significantly different from one another. The cells that lost EXOC5 had very short or absent cilia and also produced fewer EVs. On the other hand, cells that made more EXOC5 had longer cilia and produced significantly more EVs. Analysis of the protein content of the EVs that were made under these various conditions showed dramatic differences, which suggests that the capacity for these EVs to signal to other cells was different in each condition.
The researchers then expanded their work. They generated kidney cells that had lost expression of intraflagellar transport protein 88 (IFT88), a protein that is also required for proper cilium formation. These cells again showed a reduction in EV production like that seen under conditions where EXOC5 was reduced. Finally, the researchers made a mouse with EXOC5 depleted specifically in proximal tubule kidney cells and showed that EVs isolated from the urine of these mice had a different protein content than the EVs of normal mice, with many of the same changes observed in the cell lines.
“The exciting and surprising thing is that so many of the small EVs appear to be ectosomes because the cilia make up just 0.2% of the cell membrane yet are one of the main drivers of EV production,” says Lipschutz.
In summary, Lipschutz and colleagues have linked the presence and length of mammalian primary cilia to EV production. Loss of EXOC5 or IFT88 resulted in shorter cilia that produced fewer EVs, while the presence of more EXOC5 resulted in longer cilia that produced more EVs. Importantly, the proteins that were found in these various EVs were very different. This has important implications for intercellular communication that is not limited to the kidney.
“These ectosomes are not only in the urine, but they’re also likely in the blood and may play a role in the biology of many systems, including cancer,” says Lipschutz.
Because most cells have a primary cilium, defects in cilia can affect many different tissue types. In the future, Lipschutz plans to work with other researchers at MUSC to examine EVs in other tissues with impaired cilia, including eye and heart tissues.
“These organelles, which 20 years ago people were writing were evolutionary holdovers, like the appendix of organelles, not only are mechano- and chemosensors but are also involved in making a significant portion of the EVs that are centrally involved in cell signaling,” says Lipschutz. “I think we’re finding out more and more things that cilia, which contain between 500 and 1000 proteins, do and how important they are.”
###
About MUSC
Founded in 1824 in Charleston, MUSC is the oldest medical school in the South, as well as the state’s only integrated, academic health sciences center with a unique charge to serve the state through education, research and patient care. Each year, MUSC educates and trains more than 3,000 students and 700 residents in six colleges: Dental Medicine, Graduate Studies, Health Professions, Medicine, Nursing and Pharmacy. The state’s leader in obtaining biomedical research funds, in fiscal year 2018, MUSC set a new high, bringing in more than $276.5 million. For information on academic programs, visit http://musc.
As the clinical health system of the Medical University of South Carolina, MUSC Health is dedicated to delivering the highest quality patient care available while training generations of competent, compassionate health care providers to serve the people of South Carolina and beyond. Comprising some 1,600 beds, more than 100 outreach sites, the MUSC College of Medicine, the physicians’ practice plan and nearly 275 telehealth locations, MUSC Health owns and operates eight hospitals situated in Charleston, Chester, Florence, Lancaster and Marion counties. In 2019, for the fifth consecutive year, U.S. News & World Report named MUSC Health the No.1 hospital in South Carolina. To learn more about clinical patient services, visit http://muschealth.
Media Contact
Heather Woolwine
[email protected]
843-792-7669
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




