Larger fishes are more likely to experience oxygen deficiency in warming water than smaller species. The same applies to fish with large cells, note researchers at Radboud University in their latest study. In addition, marine fishes are less tolerant of oxygen-depleted water than freshwater fishes. Based on these insights, the researchers ultimately aim to predict which aquatic species are at risk due to changes in their habitat caused by global warming and human activities. The study will be published in the journal Global Change Biology on 25 July.
Credit: Radboud University
Larger fishes are more likely to experience oxygen deficiency in warming water than smaller species. The same applies to fish with large cells, note researchers at Radboud University in their latest study. In addition, marine fishes are less tolerant of oxygen-depleted water than freshwater fishes. Based on these insights, the researchers ultimately aim to predict which aquatic species are at risk due to changes in their habitat caused by global warming and human activities. The study will be published in the journal Global Change Biology on 25 July.
Declining dissolved oxygen levels represent a major problem for fish and other aquatic organisms. Oxygen levels decline because the water is heating up due to climate change and because it is becoming more polluted. General biological rules can tell us which fish attributes are beneficial or detrimental when environmental conditions change. “Once we have identified these rules for fish,” says researcher Wilco Verberk, “we can ultimately predict which fish species are most at risk from environmental change.”
Large and small cells
There is a lively debate among biologists on the role of oxygen in the sensitivity of fish to water subject to warming. “Many oxygen hypotheses are being fiercely debated. The problem is that the various effects are lumped together. For example, some studies look at how fish respond to oxygen levels in the water but do not account for the temperature of the water or the size of the fish. As a result, the reported patterns are variable,” Verberk explains.
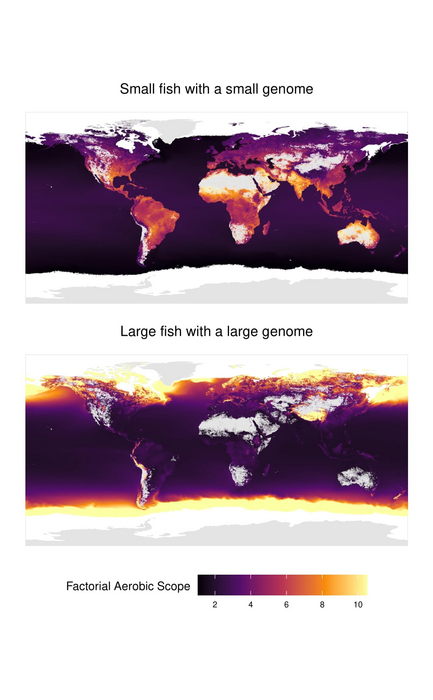
Verberk and colleagues have systematically separated the various effects and compiled data on tolerance to deficiency oxygen from 195 fishes to resolve this discussion. When analysing the data, they saw that larger fishes are more sensitive to oxygen stress, but only in warm water. When the water is cold, the effect is reversed.
The researchers saw a similar effect for fish that have relatively large cells. “Many people think that all animal species have the same cell size, but some animals have large cells, and some have small cells, even within the same species. There are many advantages to having small cells, especially in warm water. For example, small cells have relatively more membrane area, which is needed to absorb oxygen from their surrounding environment.”
Fresh water and saltwater
In addition, the researchers found differences between freshwater fish and marine fish. “Far too often, scientific studies only compare marine and terrestrial life. Indeed, freshwater species are sometimes lumped with terrestrial species. It is a missed opportunity because taking these differences into account can greatly increase our understanding of the environmental impacts of climate change.”
According to the study by Verberk and colleagues, freshwater fishes appear to be more tolerant of oxygen-depleted water than marine fishes. “The explanation probably involves different selection pressures on freshwater fish during their evolutionary history. In the ocean, the temperature is relatively stable, but in fresh water the fish are more often confronted with higher temperatures. Fluctuations in oxygen levels are also larger in rivers and especially in lakes, for example, due to the presence of algae.”
Journal
Global Change Biology
DOI
10.1111/GCB.16319
Article Title
Body mass and cell size shape the tolerance of fishes to low oxygen in a temperature-dependent manner
Article Publication Date
25-Jul-2022




