“We expect DNAmFitAge will be a useful biomarker for quantifying fitness benefits at an epigenetic level and can be used to evaluate exercise-based interventions.”
Credit: 2023 McGreevy et al.
“We expect DNAmFitAge will be a useful biomarker for quantifying fitness benefits at an epigenetic level and can be used to evaluate exercise-based interventions.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 7, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 10, entitled, “DNAmFitAge: biological age indicator incorporating physical fitness.”
Physical fitness is a well-known correlate of health and the aging process and DNA methylation (DNAm) data can capture aging via epigenetic clocks. However, current epigenetic clocks did not yet use measures of mobility, strength, lung, or endurance fitness in their construction.
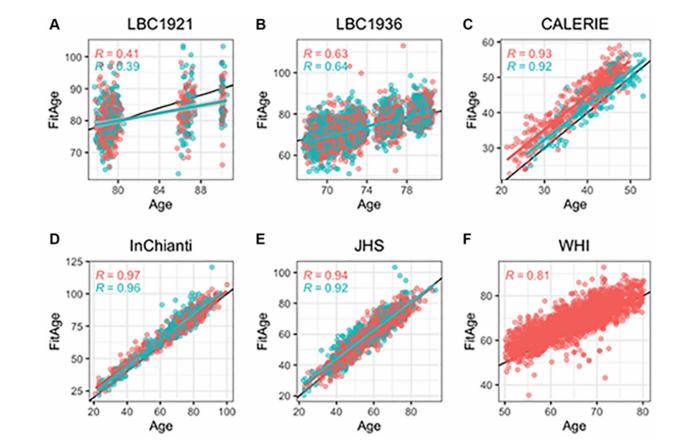
In this new study, researchers Kristen M. McGreevy, Zsolt Radak, Ferenc Torma, Matyas Jokai, Ake T. Lu, Daniel W. Belsky, Alexandra Binder, Riccardo E. Marioni, Luigi Ferrucci, Ewelina Pośpiech, Wojciech Branicki, Andrzej Ossowski, Aneta Sitek, Magdalena Spólnicka, Laura M. Raffield, Alex P. Reiner, Simon Cox, Michael Kobor, David L. Corcoran, and Steve Horvath from the University of California Los Angeles, University of Physical Education, Altos Labs, Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, University of Hawaii, University of Edinburgh, National Institute on Aging, Jagiellonian University, Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin, University of Łódź, Central Forensic Laboratory of the Police in Warsaw, Poland, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, University of Washington, and University of British Columbia develop blood-based DNAm biomarkers for fitness parameters including gait speed (walking speed), maximum handgrip strength, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) which have modest correlation with fitness parameters in five large-scale validation datasets (average r between 0.16–0.48).
“These parameters were chosen because handgrip strength and VO2max provide insight into the two main categories of fitness: strength and endurance [23], and gait speed and FEV1 provide insight into fitness-related organ function: mobility and lung function [8, 24].”
The researchers then used these DNAm fitness parameter biomarkers with DNAmGrimAge, a DNAm mortality risk estimate, to construct DNAmFitAge, a new biological age indicator that incorporates physical fitness. DNAmFitAge was associated with low-intermediate physical activity levels across validation datasets (p = 6.4E-13), and younger/fitter DNAmFitAge corresponds to stronger DNAm fitness parameters in both males and females.
DNAmFitAge was lower (p = 0.046) and DNAmVO2max is higher (p = 0.023) in male body builders compared to controls. Physically fit people had a younger DNAmFitAge and experienced better age-related outcomes: lower mortality risk (p = 7.2E-51), coronary heart disease risk (p = 2.6E-8), and increased disease-free status (p = 1.1E-7). These new DNAm biomarkers provide researchers a new method to incorporate physical fitness into epigenetic clocks.
“Our newly constructed DNAm biomarkers and DNAmFitAge provide researchers and physicians a new method to incorporate physical fitness into epigenetic clocks and emphasizes the effect lifestyle has on the aging methylome.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204538
Corresponding Authors: Kristen M. McGreevy, Zsolt Radak, Steve Horvath
Corresponding Emails: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Keywords: epigenetics, aging, physical fitness, biological age, DNA methylation
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204538
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud
- YouTube
- LabTube
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.204538
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
DNAmFitAge: biological age indicator incorporating physical fitness
Article Publication Date
31-May-2023




