Researchers identify gene that helps plants sense heat
Credit: Meng Chen/UCR
By 2050 global warming could reduce crop yields by one-third. UC Riverside researchers have identified a gene that could put the genie back in the bottle.
Warmer temperatures signal to plants that summer is coming. Anticipating less water, they flower early then lack the energy to produce more seeds, so crop yields are lower. This is problematic as the world’s population is expected to balloon to 10 billion, with much less food to eat.
“We need plants that can endure warmer temperatures, have a longer time to flower and a longer growth period,” said UCR botany and plant sciences professor Meng Chen. “But, to be able to modify plants’ temperature responses, you first have to understand how they work. So, that’s why identifying this gene that enables heat response is so important.”
The work that Chen and his colleagues did to uncover the heat-sensing gene was published this week in the journal Nature Communications. It is the second gene they’ve found involved in temperature sensing.
They located the first gene, called HEMERA, two years ago. Then they did an experiment to see if they could identify other genes involved in controlling the temperature-sensing process.
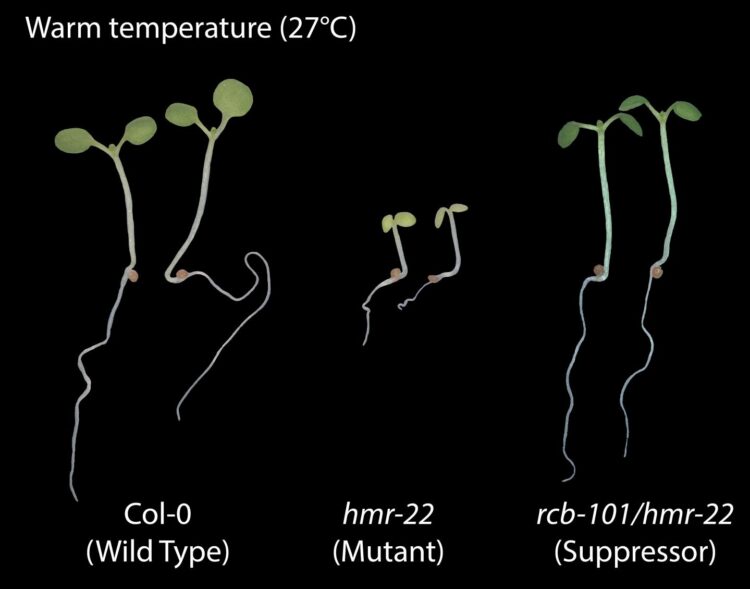
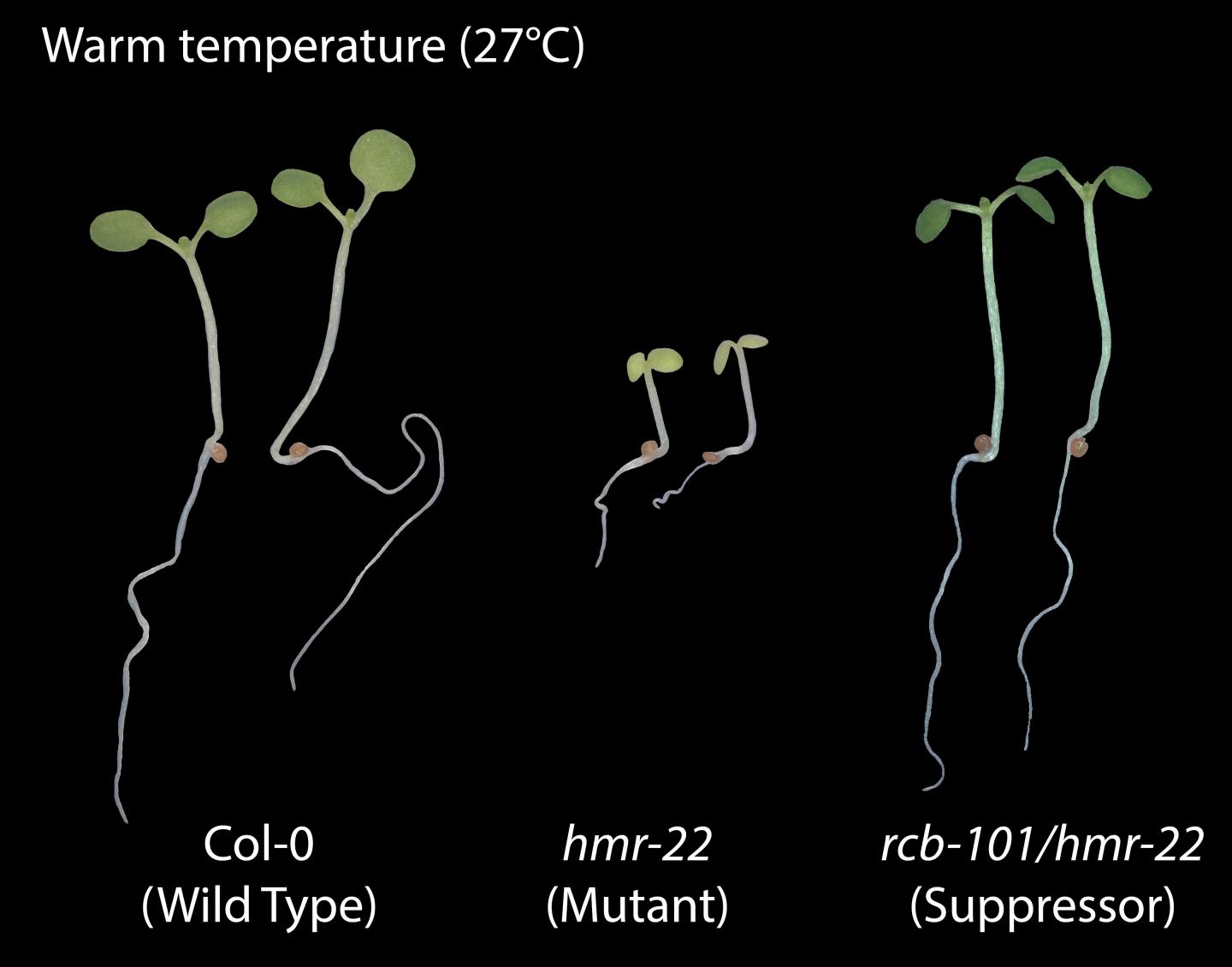
Ordinarily, plants react to shifts of even a few degrees in weather. For this experiment, the team began with a mutant Arabidopsis plant completely insensitive to temperature, and they modified it to once again become reactive.
Examining the genes of this twice-mutated plant revealed the new gene, RCB, whose products work closely with HEMERA to stabilize the heat-sensing function. “If you knock out either gene, your plant is no longer sensitive to temperature,” Chen said.
Both HEMERA and RCB are required to regulate the abundance of a group of master gene regulators that serve multiple functions, reacting to temperature as well as light, and turning plants green. These proteins are distributed to two different parts of plant cells, the nucleus as well as organelles called chloroplasts.
Going forward, Chen says his laboratory will focus on understanding how these two parts of the cell communicate and work together to achieve growth, greening, flowering, and other functions.
“When you change light or temperature, genes in both the nucleus and chloroplasts change their expression. We think HEMERA and RCB are involved coordinating gene expression between these two cell compartments,” Chen said.
Ultimately, the goal is to be able to modify temperature response to ensure the future of our food supply.
“We were excited to find this second gene,” Chen said. “It’s a new piece of the puzzle. Once we understand how it all works, we can modify it, and help crops cope better with climate change.”
###
Media Contact
Jules Bernstein
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.