Credit: Haruka Omachi
A new, cheaper method easily and effectively separates two types of carbon nanotubes. The process, developed by Nagoya University researchers in Japan, could be up-scaled for manufacturing purified batches of single-wall carbon nanotubes that can be used in high-performance electronic devices. The findings were published in the journal Applied Physics Express.
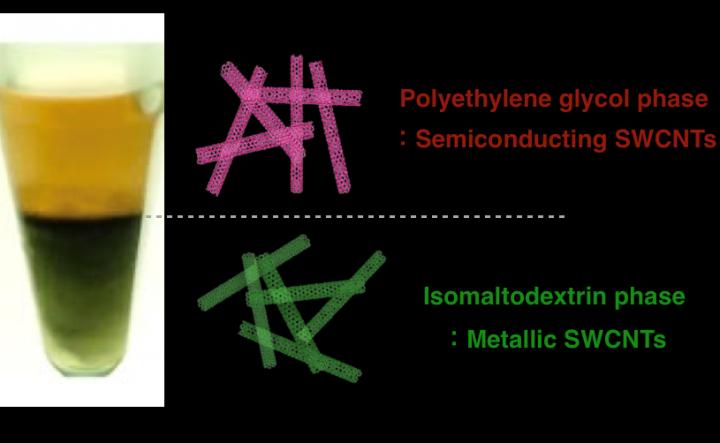
Single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) have excellent electronic and mechanical properties, making them ideal candidates for use in a wide range of electronic devices, including the thin-film transistors found in LCD displays. A problem is that only two-thirds of manufactured SWCNTs are suitable for use in electronic devices. The useful semiconducting SWCNTs must be separated from the unwanted metallic ones. But the most powerful purification process, known as aqueous two-phase extraction, currently involves the use of a costly polysaccharide, called dextran.
Organic chemist Haruka Omachi and colleagues at Nagoya University hypothesized that dextran’s effectiveness in separating semiconducting from metallic SWCNTs lies in the linkages connecting its glucose units. Instead of using dextran to separate the two types of SWCNTs, the team tried the significantly cheaper isomaltodextran, which has many more of these linkages.
A batch of SWCNTs was left for 15 minutes in a solution containing polyethylene glycol and isomaltodextrin and then centrifuged for five minutes. Three different types of isomaltodextrin were tried, each with a different number of linkages and a different molecular weight. The team found that metallic SWCNTs separated to the bottom isomaltodextrin part of the solution, while the semiconducting SWCNTs floated to the top polyethylene glycol part.
The type of isomaltodextrin with high molecular weight and the most linkages was the most (99%) effective in separating the two types of SWCNTs. The team also found that another polysaccharide, called pullulan, whose glucose units are connected with different kinds of linkages, was ineffective in separating the two types of SWCNTs. The researchers suggest that the number and type of linkages present in isomaltodextrin play an important role in their ability to effectively separate the carbon nanotubes.
The team also found that a thin-film transistor made with their purified semiconducting SWCNTs performed very well.
Isomaltodextrin is a cheap and widely available polysaccharide produced from starch that is used as a dietary fibre. This makes it a cost-effective alternative for the SWCNT extraction process. Omachi and his colleagues are currently in discussions with companies to commercialize their approach. They are also working on improving the performance of thin-film transistors using semiconducting SWCNTs in flexible displays and sensor devices.
###
The article, “Aqueous two-phase extraction of semiconducting single-wall carbon nanotubes with isomaltodextrin and thin-film transistor applications,” was published in Applied Physics Express at DOI: 10.7567/1882-0786/ab369e
Authors: Haruka Omachi, Tomohiko Komuro, Kaisei Matsumoto, Minako Nakajima, Hikaru Watanabe, Jun Hirotani, Yutaka Ohno, and Hisanori Shinohara
For more information, contact:
Associate Professor Haruka Omachi
Research Center for Materials Science, Nagoya University
Email: [email protected]
Media Contact
Haruka Omachi
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




