Credit: © Institut Pasteur
The major challenge facing physicians treating Alzheimer's is the ability to detect markers of the disease as early as possible. These markers, located in the brain, are difficult to access, hampering diagnosis. Using two types of llama antibody capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier, scientists from the Institut Pasteur, Inserm, the CNRS, the CEA, Pierre & Marie Curie and Paris Descartes Universities and Roche* have developed a non-invasive approach to reach brain cells in a mouse model of the disease. Once in the brain, these llama antibodies can specifically mark and show amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, the two types of lesions that characterize Alzheimer's disease. These results were published in the Journal of Controlled Release on October 7, 2016.
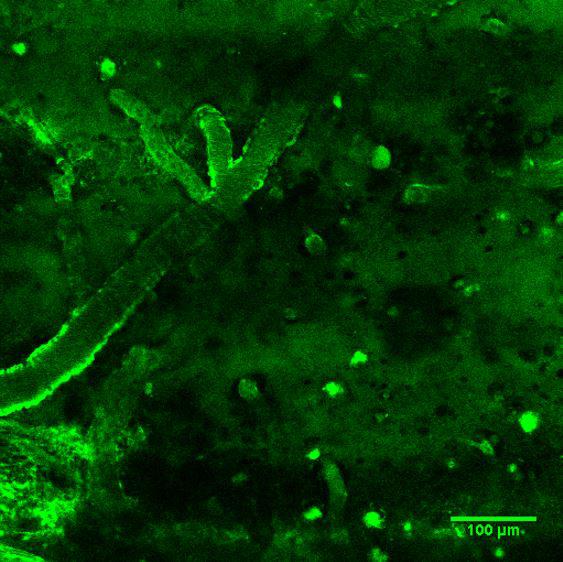
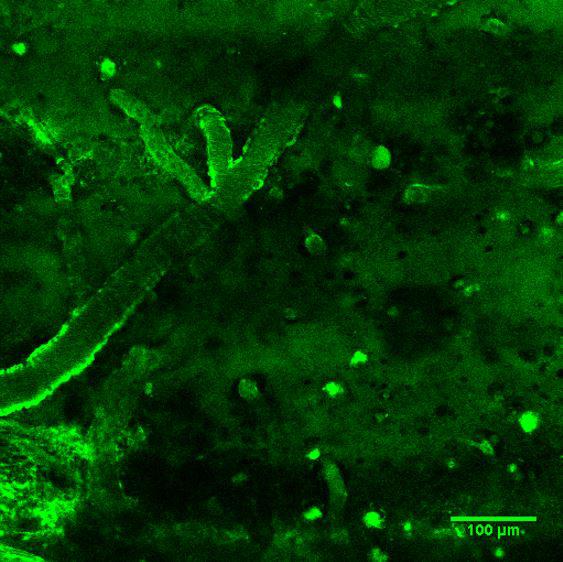
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by two types of cerebral lesion: amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Amyloid beta peptide (Aβ), naturally present in the brain, builds up over the years as a result of genetic and environmental factors until it forms amyloid plaques. This build-up is toxic for nerve cells: it leads to a loss of neuronal structure and to what is known as "neurofibrillary" tangles (abnormal aggregation of the tau protein), which in turn results in cell death.
In this study, the team led by Pierre Lafaye, Head of the Antibody Engineering Platform in the Citech at the Institut Pasteur, in collaboration with the Chemistry of Biomolecules and Integrative Neurobiology of Cholinergic Systems Units from the Institut Pasteur and the CNRS, developed two new types of antibody capable of detecting the extracellular and intracellular targets (respectively amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles) that are characteristic of Alzheimer's disease. To achieve this, they turned their attention to camelids, specifically llamas, since their small antibodies are easy to use. They used the variable region of the antibody, known as VHH or nanobodiesTM, to specifically recognize the markers of Alzheimer's.
These antibodies have the rare ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, which generally protects the brain from microbial attacks but also prevents potential therapeutic molecules from reaching it.
This collaborative research project, jointly conducted by scientists from the Institut Pasteur, Inserm, the CNRS, the CEA, Pierre & Marie Curie and Paris Descartes Universities and the Roche Group, led to the development of anti-Aβ and anti-tau protein antibodies that specifically detect amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. These antibodies were subsequently tested in vitro on the brain tissue of Alzheimer's patients.
The antibodies were then tested in vivo in two mouse models, each with one of the two characteristic lesions associated with Alzheimer's disease. These antibodies, labeled with a green fluorochrome, were injected intravenously and crossed the blood-brain barrier, binding to the two targets the scientists were aiming to identify: amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. This made the signs of the disease visible in the brain using two-photon microscopy. The scientists involved in this collaborative project are currently working on the development of an MRI imaging technique to observe the lesions. In the long term this could be applied to humans.
"Being able to diagnose Alzheimer's at an early stage could enable us to test treatments before the emergence of symptoms, something we were previously unable to do," explained Pierre Lafaye. These VHH antibodies could be used in combination with therapeutic molecules so that the molecules can be delivered in a targeted way to the brain.
Patents have been filed for these VHH antibodies and for their use based on their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and bind to amyloid plaques and tau proteins.
###
This research was partly funded by the Roche Institute, the France Alzheimer Foundation and the Georges Pompidou Foundation.
Media Contact
Myriam Rebeyrotte
[email protected]
http://www.pasteur.fr