Energy-saving benefits expected in a wide variety of devices through substituting magnetic steel sheets
Credit: Tohoku Magnet Institute
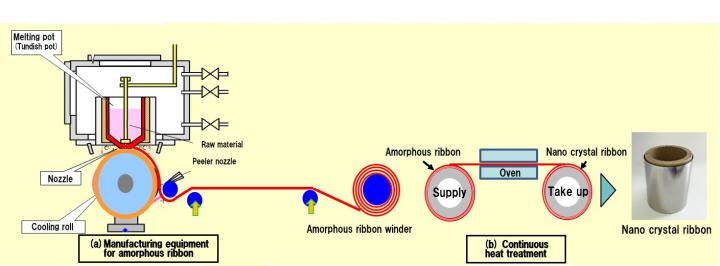
JST announces that enterprise-led development of production equipment for ultra-low loss nano crystal (*1) ribbon, supported through the NexTEP-B type phase of the agency’s “Adaptable and Seamless Technology Transfer Program through Target-driven R&D” (A-STEP) program (*2), has succeeded in its goal of creating mass production equipment. This equipment should allow for the mass production of 250mm-width nano crystal ribbon, an industry first. JST’s evaluation revealed that the program achieved its targeted results. The R&D challenge was consigned to Tohoku Magnet Institute (TMI) Co. Ltd., a company established around research performed by Professor Akihiro Makino and others at Tohoku University’s New Industry Creation Hatchery Center. The company performed practical development between April 2017 and March 2019.
TMI developed process technologies and standard equipment for the mass commercial production of ultra-low loss nano crystal ribbon, a technology initially developed by Tohoku University. The ribbon is a new material that minimizes electrical energy loss.
Ultra-low loss nano crystal ribbon has superb features such as minimal iron loss (excellent energy efficiency) and high saturated magnetic flux density (allowing for miniaturization). The development project aimed to establish technologies and produce equipment for the production of ribbon with a product sheet thickness of 35 micrometers (μm, 1μm being one-millionth of a meter) and a sheet width of 250 millimeters (mm). The project also involved the joint development of techniques to dramatically improve the durability of production equipment such as melting pots, nozzles, and cooling rolls.
Test production resulted in widths of 245mm and thicknesses of 30μm.
At levels of mass production that took stable production into consideration, TMI succeeded in creating ribbon with widths of 127mm and thicknesses of 27μm.
TMI will begin production and sales of this nano crystal ribbon and perform ongoing testing relating to improvements in quality, cost, and stability of production. The company is aiming for the ribbon to be broadly adopted as a substitute for magnetic steel sheets. TMI’s results are expected to have a wide range of practical uses, such as in electric vehicle motors, with worldwide market volume expected to be approximately 1 trillion yen.
###
(*1) Ultralow loss nano crystal
An ultra-low loss nano crystal magnetic material with a high iron concentration of between 93 – 94% by mass. Its structure consists of ~10-nanometer α-iron nano crystals surrounded by an amorphous magnetic layer. The amorphous magnetic layer consists of popular materials such as silicon (Si), boron (B), phosphorus (P), and copper (Cu).
(*2) “Adaptable and Seamless Technology Transfer Program through Target-driven R&D” (A-STEP) supports the transfer of scientific technologies important to the national economy that has been produced from research performed at universities and public research institutes. The technologies the program supports are in the R&D phase, and the program aims to put them to practical use. A-STEP’s NexTEP-B type phase is enterprise-led. It aims to support the practical development of technology seeded from institutes such as universities by small and medium enterprises that are engaged in R&D.
Media Contact
Akira Takara
[email protected]
81-227-969-731
Original Source
https:/




