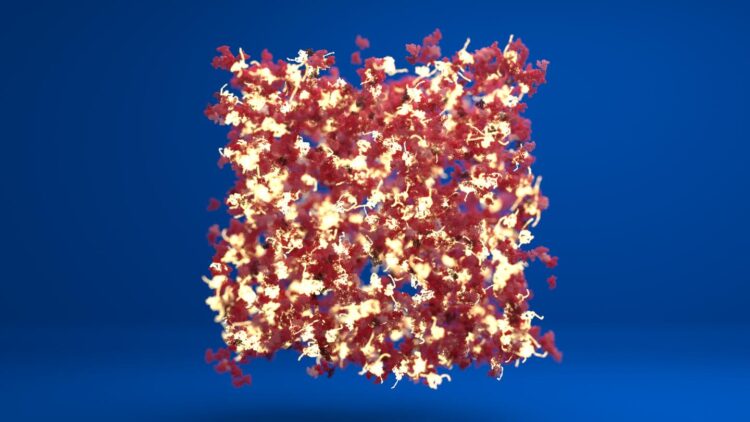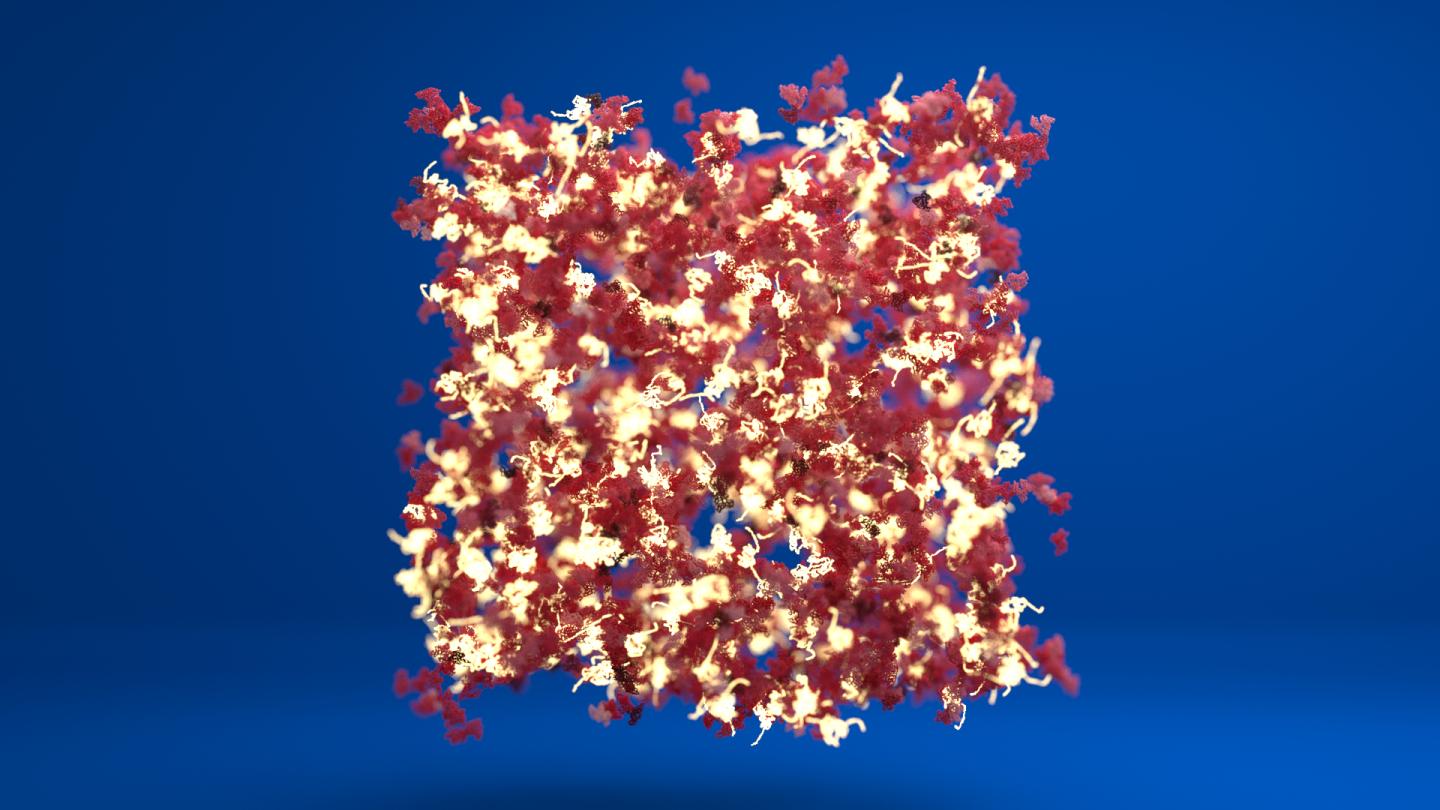
Credit: Lorna Dougan/Phospho Animations
Scientists at the University of Leeds have developed an approach that could help in the design of a new generation of synthetic biomaterials made from proteins.
The biomaterials could eventually have applications in joint repair or wound healing as well as other fields of healthcare and food production.
But one of the fundamental challenges is to control and fine tune the way protein building blocks assemble into complex protein networks that form the basis of biomaterials.
Scientists at Leeds are investigating how changes to the structure and mechanics of individual protein building blocks – changes at the nanoscale – can alter the structure and mechanics of the biomaterial at a macro level while preserving the biological function of the protein network.
In a paper published by the scientific journal ACS Nano, the researchers report that they were able to alter the structure of a protein network by removing a specific chemical bond in the protein building blocks. They called these bonds the “protein staples”.
With the protein staples removed, the individual protein molecules unfolded more easily when they connect together and assemble into a network. This resulted in a network with regions of folded protein connected by regions containing the unfolded protein resulting in very different mechanical properties for the biomaterial.
Professor Lorna Dougan, from the School of Physics and Astronomy at Leeds, who supervised the research, said: “Proteins display amazing functional properties. We want to understand how we can exploit this diverse biological functionality in materials which use proteins as building blocks.
“But to do that we need to understand how changes at a nano scale, at the level of individual molecules, alters the structure and behaviour of the protein at a macro level.”
Dr Matt Hughes, also from the School of Physics and Astronomy and lead author of the paper, said: “Controlling the protein building block’s ability to unfold by removing the “protein staples” resulted in significantly different network architectures with markedly different mechanical behaviour and this demonstrates that unfolding of the protein building block plays a defining role in the architecture of protein networks and the subsequent mechanics.”
The researchers used facilities at the Astbury Centre for Structural Molecular Biology and School of Physics and Astronomy at Leeds and the ISIS Neutron Muon Source facility at the STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory in Oxfordshire. Using beams of neutrons, it allowed them to identify critical changes to the protein network’s structure when the nano-staples where removed.
In conjunction with the experimental work, Dr Ben Hanson, a Research Associate in the School of Physics and Astronomy at Leeds, modelled the structural changes taking place. He found that it was specifically the act of protein unfolding during network formation, that was crucial in defining the network architecture of the protein hydrogels.
Professor Dougan added: “The ability to change the nanoscale properties of protein building blocks, from a rigid, folded state to a flexible, unfolded state, provides a powerful route to creating functional biomaterials with controllable architecture and mechanics.”
###
The research was conducted with assistance from Professor David Brockwell and Sophie Cussons, Research Technician, at the Astbury Centre for Structural Molecular Biology at Leeds.
Further information
Top image shows a schematic visualisation of a network of proteins where some of the protein staples have been removed. Unfolded protein building blocks are colourd yellow and they are connected with folded protein building blocks. Image credit: Lorna Dougan and Phospho animations.
The paper – Control of Nanoscale in situ Protein Unfolding Defines Network Architecture and Mechanics of Protein Hydrogels – has been published online at ACS Nano: https:/
The project was supported by a grant from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EP/P02288X/1). For further details, please contact David Lewis in the media office at the University of Leeds: [email protected].
Media Contact
David Lewis
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.