Mother to fetus transfer of OH-PCBs in the Japanese macaque: Extrapolation of Exposure Scenarios for Humans
Credit: Center for Marine Environmental Studies (CMES), Ehime University
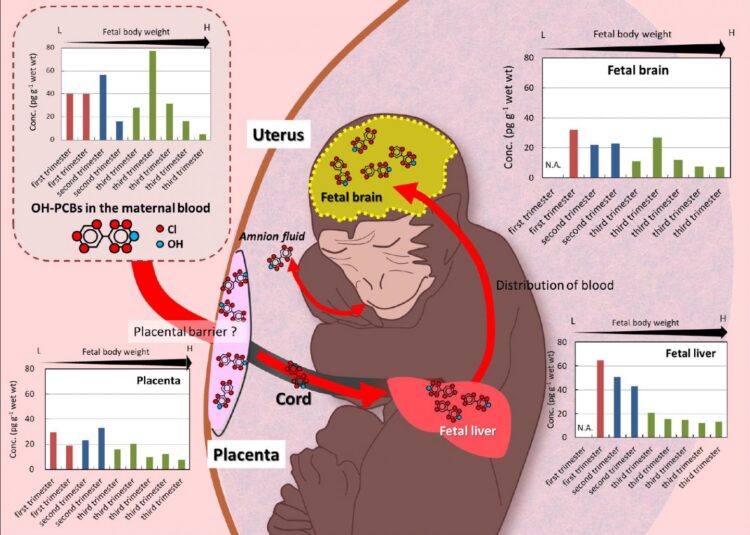
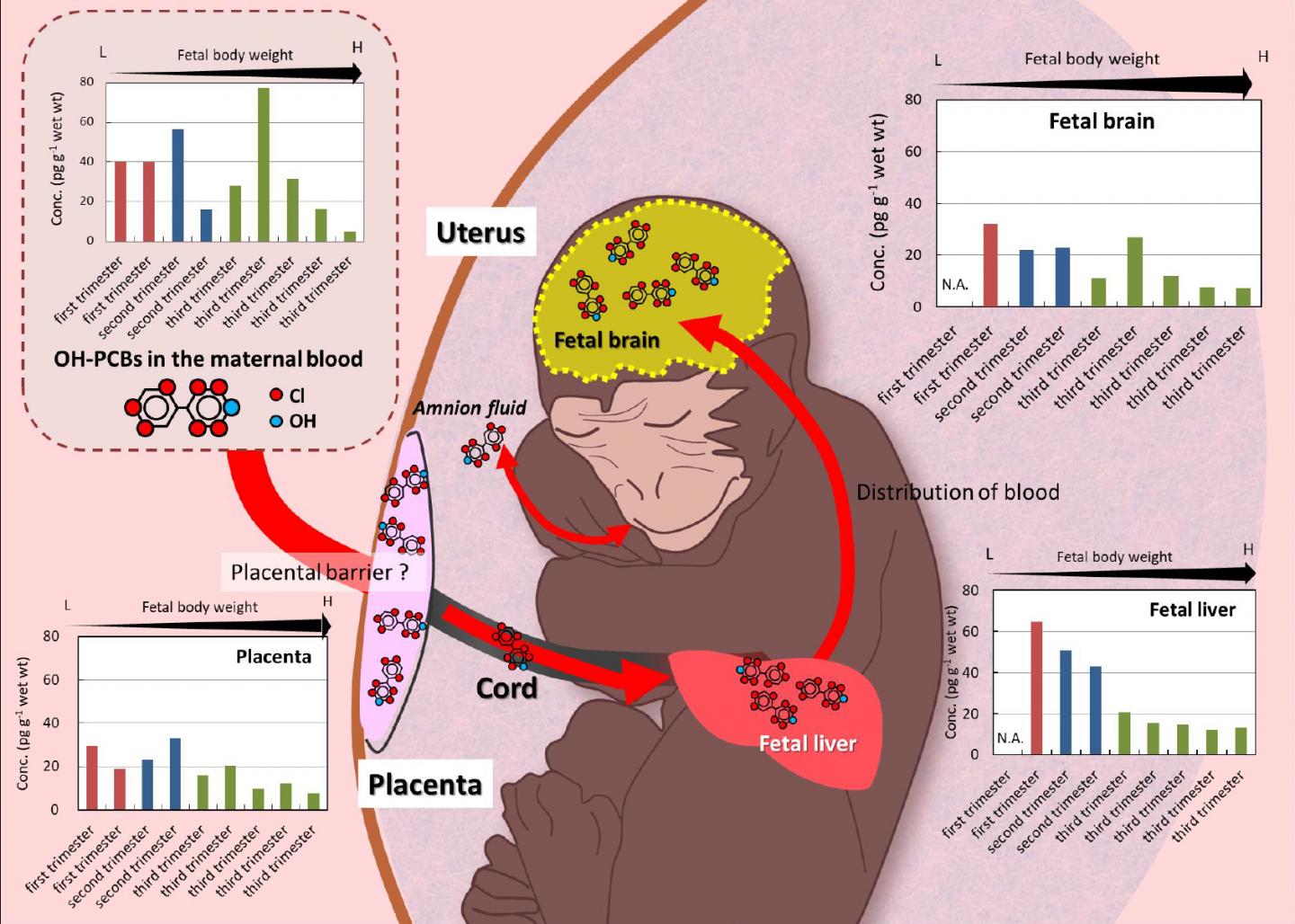
Hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyls (OH-PCBs) are metabolites of PCBs and known endocrine disruptors in humans. Of particular concern regarding this kind of effect has been the disruption of the thyroid hormone homeostasis by OH-PCBs. Some OH-PCB congeners are involved in disrupting TH transport by competitive binding to the thyroid hormone transport protein, transthyretin (TTR) in mammalian blood. Prenatal OH-PCBs exposure may disrupt fetal brain development during the critical period of thyroid hormone action. Congenital hypothyroidism causes cretinism and mental retardation, and an insufficient thyroid hormone signaling has been suggested as one of the causes of attention deficit/hyper activity disorder (ADHD). However, there have been limited studies on the OH-PCBs transfer to the fetal brain, particularly in primates.
In this study, we selected the Japanese macaque (Macaca fuscata) as a model animal for the fetal transfer of OH-PCBs in humans, and revealed OH-PCB concentrations and their relationships in maternal and fetal blood, liver, and brain. L-thyroxine (T4)-like OH-PCBs, including 4OH-CB187 as a major congener in humans, were found in high proportions in the blood, liver, brain, and placenta of pregnant Japanese macaques. OH-PCBs were detected in the fetal brain (7.2 ~ 32 pg/g wet wt.), indicating their transfer to the brain in early pregnancy. 4OH-CB187 and 4OH-CB202 of OH-PCB congeners were the major congeners found in the fetal brain, indicating that these T4-like OH-PCBs are transported from maternal blood to the fetal brain via the placenta. These results are important as a potential model for further assessing and understanding of the ability of OH-PCBs to alter neurodevelopment in the human fetus.
In this study, OH-PCBs concentrations in the fetal brains of the Japanese macaques were comparable to the levels that suppressed the T3-induced transcriptional activation of the thyroid hormone receptor and caused neurodevelopmental abnormalities in cerebellar Purkinje cells of mice in a previous study. The brain of the human fetus may be exposed to higher PCB contamination levels than the Japanese macaque fetus; OH-PCB concentrations may thus exceed the levels that induce adverse effects on neurodevelopment. Considering the chronic exposure to PCBs in humans, further studies on the effects of their long-term exposure on fetal brain function are needed.
###
Media Contact
Public Relations Division
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.