Scientists have accurately analysed the tough barrier layer of the skin giving the most detailed molecular map of its structure that will help in the development of new skin products and treatments.
Credit: University of Nottingham
Scientists have accurately analysed the tough barrier layer of the skin giving the most detailed molecular map of its structure that will help in the development of new skin products and treatments.
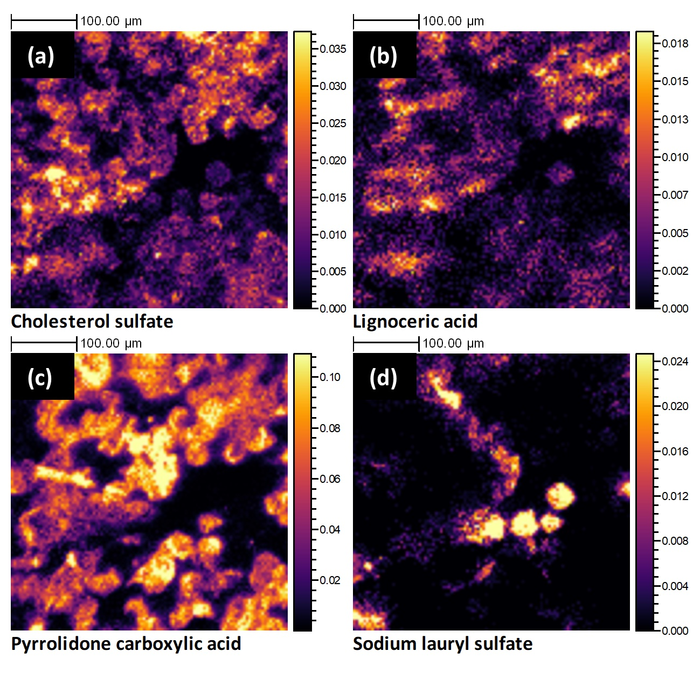
Researchers from the University of Nottingham used the latest three-dimensional mass spectrometry imaging technique to analyse human skin tissue from the stratum corneum to reveal its molecular chemistry in unprecedented detail. These new findings provide increased fundamental understanding in skin biology and enable the development of new skin products and treatments. These research findings have been published today in PNAS.
The University of Nottingham was the first University in the world to own and operate the 3D OrbiSIMS instrument used in this research. The technology facilitates an unprecedented level of molecular analysis for a range of materials including biological tissues, such as human skin. Importantly, its high mass resolving power, chemical specificity and high sensitivity allow it to be used to analyse in situ human skin samples to accurately map the molecular structure of the skin.
Researchers used ex vivo full-thickness human skin tissue samples and a single gas cluster ion beam to both sputter through the skin and generate secondary ions, which were analysed using the OrbitrapTM to generate a depth profile. This process showed the range of chemistries and 3D distributions within the stratum corneum and indicate how these relate to fundamental biological processes such as the cholesterol sulphate cycle.
David Scurr, Principal Research Fellow in the School of Pharmacy, led the research and said: “This research gives the chemical structure detail of the stratum corneum never seen before. The information we were able to gather on the complex chemistry of this tough barrier layer has the potential to benefit research into fundamental biological processes, such as those associated with ageing and disease in addition to improving the efficacy of topical delivery.”
This research is part of a collaboration with No7 Beauty Company and the analysis done as part of this study has also shown the penetration profile of the stratum corneum. The team were able to accurately track the penetration of No7’s peptide blend Super Matrixyl 3000 Plus™ (a trademark of Sederma) following topical application to the skin surface and detected the peptides responsible for targeting invisible photo-damage that occurs early in the ageing process.
Mike Bell, Head of Science Research at No7 Beauty Company said: “Commercially this research is very significant as this technique can offer an improved understanding of topical delivery and therefore lead to the development of more effective peptide based anti-ageing products.”
Journal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
DOI
10.1073/pnas.2114380119
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Human tissue samples
Article Title
Elucidating the molecular landscape of the stratum corneum
Article Publication Date
14-Mar-2022




