Credit: ©Science China Press
The directly catalytic oxidation of alkanes has high atomic economy and application value to form corresponding chemical organic products such as alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acid. It is challenging to achieve efficient and selective oxidation of alkane under mild conditions due to the inert C-H bonds of alkanes.
Many researchers have developed a series of supported iron based catalysts to simulate the alkane biological monooxygenase with iron center atoms. However, traditional methods, such as impregnation method, ion exchange method, etc., are difficult to control the dispersion and the deposition position of iron species on the catalyst support.
Generally, iron species can easily replace the H+ of Brønsted acid sites to reduce the number of Brønsted acid sites, and many types of iron species will be formed on other different potential sites of ZSM-5 (Lewis acid sites and defect sites, etc.). The coexistence of multiple active centers on the catalyst is one of the main reasons for the low selectivity.
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is an advanced thin film technology by single-layer chemisorption and reaction of vapor precursors on the surface of substrates with atomic and molecular control precision.
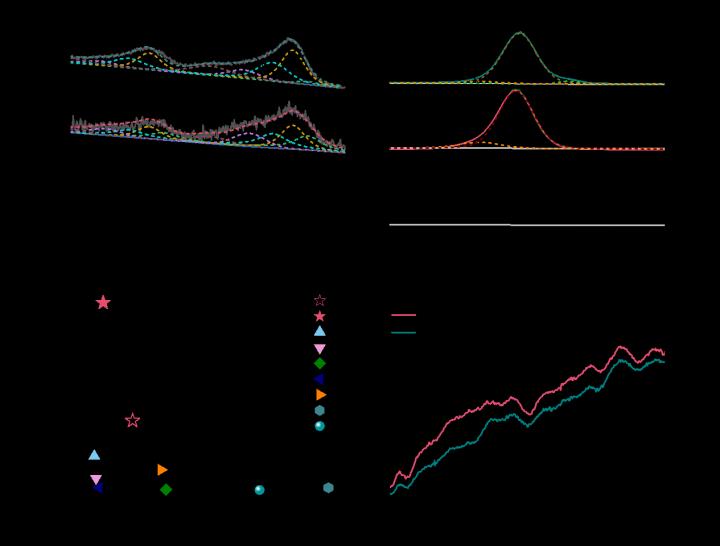
Recently, Dr. Bin Zhang and colleagues in the Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, report a general strategy to selectively deposit high-dispersed Fe species into the micropores of ZSM-5 to prepare FeOx/ZSM-5 catalysts.
The obtained FeOx/ZSM-5 catalysts perform high selectivity of cyclohexanone (92%-97%), and the catalyst activity is significantly higher than those of the iron-based catalysts reported in the literature. Ferrocene (Fe(Cp)2) is used as a precursor for the deposition since its kinetic diameter is smaller than the pore size of ZSM-5. The framework of ZSM-5 and the Brønsted acid sites are intact during ALD, and the Fe species are selectively deposited onto the defect and Lewis acid sites of ZSM-5. The loading, size and surface electronic state of FeOx species can be precisely controlled by merely changing ALD cycles. The Fe content in the FeOx/ZSM-5 catalyst increases linearly with the increase of ALD cycles. Fe-O-Si bonds are dominantly formed over FeOx/ZSM-5 with a low loading of Fe, while FeOx nanoparticles are generated at a high Fe loading. Compared with the FeOx nanoparticles, the Fe-O-Si species performs higher turnover frequency and stability in the oxidation reaction.
###
See the article: Zhai LM, Zhang B*, Liang HJ, Wu HB, Yang XC, LuoG, Zhao SC, Qin Y. The selective deposition of Fe species inside ZSM-5 for the oxidation of cyclohexane to cyclohexanone. Sci. China Chem., 2021, DOI:10.1007/s11426-020-9968-x.
http://engine.
Media Contact
Bin Zhang
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




