The study is led by Xiaojun Han (School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology).
Credit: Beijing Zhongke Journal Publising Co. Ltd.
The study is led by Xiaojun Han (School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology).
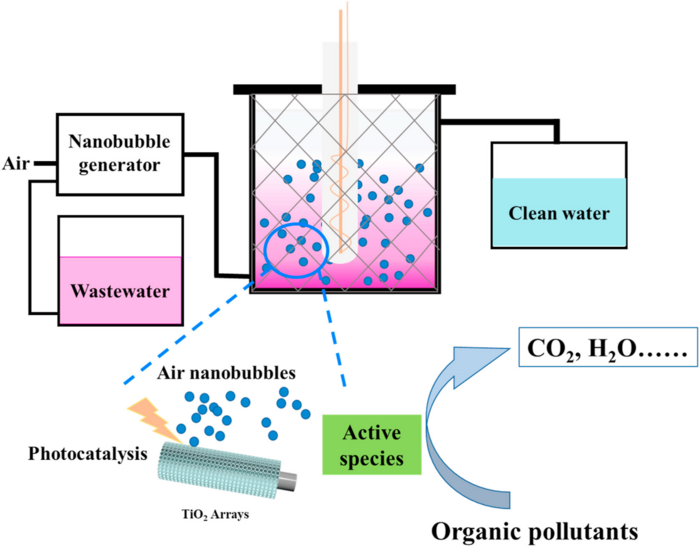
With the rapid development of urbanization and industrialization, environmental problems became increasingly serious. Dye wastewater is considered to be one of the biggest challenges due to its high toxicity. Organic dyes have mutagenic, teratogenic, and carcinogenic properties, and threaten the health and life of humans while hindering plant photosynthesis, which brings risks to the ecosystem. Traditional organic pollutant treatment methods include the physical method, biological method, and chemical method. These methods have drawbacks such as poor efficiency, high energy consumption, and incomplete treatment, so it is necessary to develop new sewage treatment methods. In 1972, Fujishima performed the pioneering work of photocatalytic decomposition of water to produce hydrogen using TiO2 as a photocatalyst. After that, photocatalytic technology was developed to be applied in sewage treatment due to its advantages of superior mineralization ability, fast reaction rate, and no secondary pollution. TiO2 is a common photocatalytic material because of its high catalytic activity, non-toxicity, excellent chemical stability, and low cost. In order to convert TiO2 photocatalytic technology from the experimental research stage to practical application, it is essential to design a photocatalytic reactor with a simple structure, convenient assembly, and outstanding treatment performance.
In recent years, photocatalytic technology has been coupled with various advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) to improve photocatalytic performance. TiO2-based photocatalytic technology coupling with classical AOPs such as Fenton oxidation, plasma oxidation, and ozone oxidation was reported to improve the treatment of organic pollutants. Nanobubbles (NBs) are extremely small gas bubbles with unique physical properties, which make nanobubbles a superior aeration method for many applications. Nanobubbles have been widely used in wastewater treatment due to their long residence time, large specific surface area, and free radicals generation ability. Yu et al. designed a UV/NBs/P25-TiO2 photocatalytic reactor to degrade methyl orange in water. The results showed that the photocatalytic performance of TiO2 coupling with nanobubbles is enhanced by 11.6% compared with that without bubbles. However, the TiO2 photocatalyst needs to be re-separated and recovered after photocatalytic degradation, which was unfavorable to the design of the photocatalytic reactor. Therefore, the fixed photocatalyst was required for assembling the photocatalytic reactor.
Herein, a photocatalytic reactor was assembled using a Ti mesh coated with TiO2 nanotube array to degrade organic pollutants. The reactor coupling with nanobubbles technology showed outstanding photocatalytic degradation ability, with a degradation efficiency of Rhodamine B (RhB) of 95.39% after irradiation treatment. The other organic pollutants including methylene blue, tetracycline, and oxytetracycline hydrochloride were all photodegradable using this photocatalytic reactor, with degradation efficiencies of 74.23%, 68.68%, and 64.10%, respectively. Therefore, this work provides a strategy to develop a coupling technology of photocatalysis and nanobubbles to treat wastewater.
See the article:
Degradation of Rhodamine B in the photocatalytic reactor containing TiO2 nanotube arrays coupled with nanobubbles
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asems.2023.100054
Journal
Advanced Sensor and Energy Materials
DOI
10.1016/j.asems.2023.100054
Article Title
Degradation of Rhodamine B in the photocatalytic reactor containing TiO2 nanotube arrays coupled with nanobubbles
Article Publication Date
7-Mar-2023




