DENVER, May 23, 2022 – Lurking beneath the ocean’s surface, marine mammals use sound for navigation, prey detection, and a wide range of natural behaviors. Passive acoustic data from underwater environments can provide valuable information on these animals, such as their presence or absence within an area, their density and abundance, and their vocal response to anthropogenic noise sources.
Credit: Ferguson
DENVER, May 23, 2022 – Lurking beneath the ocean’s surface, marine mammals use sound for navigation, prey detection, and a wide range of natural behaviors. Passive acoustic data from underwater environments can provide valuable information on these animals, such as their presence or absence within an area, their density and abundance, and their vocal response to anthropogenic noise sources.
As the size and number of acoustic datasets increase, accurately and quickly matching the bioacoustics signals to their corresponding sources becomes more challenging and important. This is especially difficult in noisy, natural acoustic environments.
Elizabeth Ferguson, from Ocean Science Analytics, will describe how DeepSqueak, a deep learning tool, can classify underwater acoustic signals at the 182nd Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America during her presentation, “Development of deep neural networks for marine mammal call detection using an open-source, user friendly tool.” The session will take place May 23 at 11:25 a.m. Eastern U.S. as part of the conference at the Sheraton Denver Downtown Hotel.
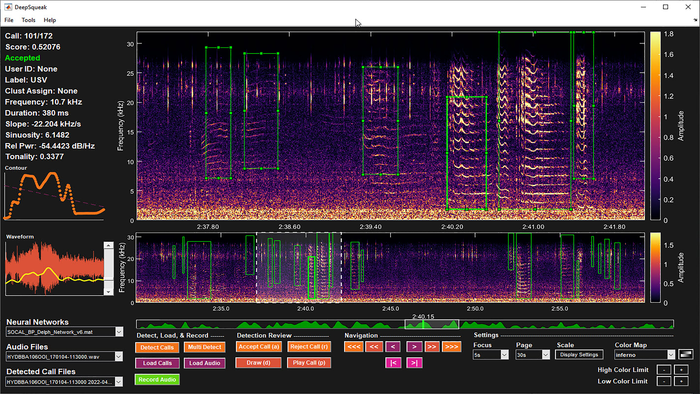
Spectrograms show how acoustic signals of different frequencies vary with time. They look like heat maps, with brighter regions indicating higher sound intensity at that frequency and time. DeepSqueak uses deep neural network image recognition and classification methods to determine the important features within spectrograms, then match those features to specific sources.
“Although we used DeepSqueak to detect underwater sounds, this user-friendly, open source tool would be useful for a variety of terrestrial species,” said Ferguson. “The capabilities of call detection extend to frequencies below the ultrasonic sounds it was originally intended for. Due to this and the capability of DeepSqueak to detect variable call types, development of neural networks is possible for many species of interest.”
DeepSqueak was originally developed to classify ultrasound signals from rodents, but its neural network framework allows the technique to adapt to detect sounds at other frequencies. Ferguson and her team used the method and data from hydrophones on the Ocean Observatories Initiative’s Coastal Endurance Array to detect humpback whales, delphinids, and fin whales, which have highly variable calls with a wide range of frequencies.
###
———————– MORE MEETING INFORMATION ———————–
USEFUL LINKS
Main meeting website: https://acousticalsociety.org/asa-meetings/
Technical program: https://eventpilotadmin.com/web/planner.php?id=ASASPRING22
Press Room: https://acoustics.org/world-wide-press-room/
WORLDWIDE PRESS ROOM
In the coming weeks, ASA’s Worldwide Press Room will be updated with additional tips on dozens of newsworthy stories and with lay language papers, which are 300 to 500 word summaries of presentations written by scientists for a general audience and accompanied by photos, audio and video. You can visit the site during the meeting at http://acoustics.org/world-wide-press-room/.
PRESS REGISTRATION
We will grant free registration to credentialed journalists and professional freelance journalists. If you are a reporter and would like to attend, contact AIP Media Services at [email protected]. For urgent requests, staff at [email protected] can also help with setting up interviews and obtaining images, sound clips, or background information.
ABOUT THE ACOUSTICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA
The Acoustical Society of America (ASA) is the premier international scientific society in acoustics devoted to the science and technology of sound. Its 7,000 members worldwide represent a broad spectrum of the study of acoustics. ASA publications include The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America (the world’s leading journal on acoustics), JASA Express Letters, Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics, Acoustics Today magazine, books, and standards.
###




