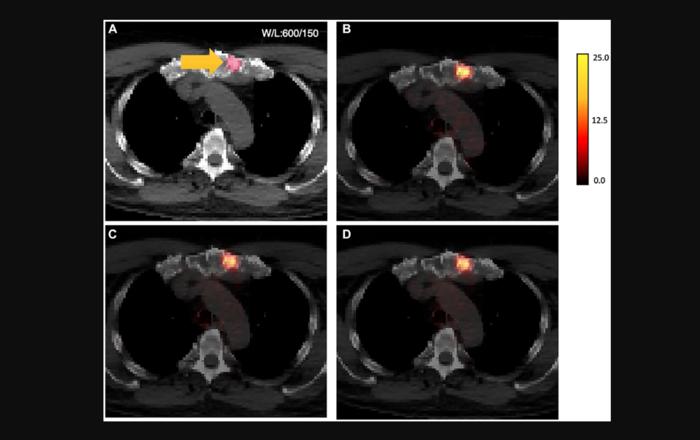
“We have developed a Pix-2-Pix GAN model to perform attenuation correction on whole-body PSMA [prostate-specific membrane antigen] PET images with 18F-DCFPyL.”
Credit: 2024 Ma et al.
“We have developed a Pix-2-Pix GAN model to perform attenuation correction on whole-body PSMA [prostate-specific membrane antigen] PET images with 18F-DCFPyL.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 9, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 15 on May 7, 2024, entitled, “Deep learning-based whole-body PSMA PET/CT attenuation correction utilizing Pix-2-Pix GAN.”
The sequential PET/CT studies oncology patients can undergo during their treatment follow-up course is limited by radiation dosage. In this new study, researchers Kevin C. Ma, Esther Mena, Liza Lindenberg, Nathan S. Lay, Phillip Eclarinal, Deborah E. Citrin, Peter A. Pinto, Bradford J. Wood, William L. Dahut, James L. Gulley, Ravi A. Madan, Peter L. Choyke, Ismail Baris Turkbey, and Stephanie A. Harmon from the National Institutes of Health’s National Cancer Institute proposed an artificial intelligence (AI) tool to produce attenuation-corrected PET (AC-PET) images from non-attenuation-corrected PET (NAC-PET) images to reduce need for low-dose CT scans.
“AI-generated PET images has clinical potential for reducing the need for CT scans for attenuation correction while preserving quantitative markers and image quality in prostate cancer patients.”
Methods: A deep learning algorithm based on 2D Pix-2-Pix generative adversarial network (GAN) architecture was developed from paired AC-PET and NAC-PET images. 18F-DCFPyL PSMA (prostate-specific membrane antigen) PET-CT studies from 302 prostate cancer patients, split into training, validation, and testing cohorts (n = 183, 60, 59, respectively). Models were trained with two normalization strategies: Standard Uptake Value (SUV)-based and SUV-Nyul-based. Scan-level performance was evaluated by normalized mean square error (NMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), structural similarity index (SSIM), and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR). Lesion-level analysis was performed in regions-of-interest prospectively from nuclear medicine physicians. SUV metrics were evaluated using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), repeatability coefficient (RC), and linear mixed-effects modeling.
Results: Median NMSE, MAE, SSIM, and PSNR were 13.26%, 3.59%, 0.891, and 26.82, respectively, in the independent test cohort. ICC for SUVmax and SUVmean were 0.88 and 0.89, which indicated a high correlation between original and AI-generated quantitative imaging markers. Lesion location, density (Hounsfield units), and lesion uptake were all shown to impact relative error in generated SUV metrics (all p < 0.05).
“The Pix-2-Pix GAN model for generating AC-PET demonstrates SUV metrics that highly correlate with original images. AI-generated PET images show clinical potential for reducing the need for CT scans for attenuation correction while preserving quantitative markers and image quality.”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28583
Correspondence to: Stephanie A. Harmon
Email: [email protected]
Keywords: deep learning, PSMA PET, attenuation correction
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
- X, formerly Twitter
- YouTube
- Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Street., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
Journal
Oncotarget
DOI
10.18632/oncotarget.28583
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Deep learning-based whole-body PSMA PET/CT attenuation correction utilizing Pix-2-Pix GAN
Article Publication Date
7-May-2024




