In the realm of pediatric medicine, the evaluation of lymphadenopathies remains a pivotal subject, frequently encountered yet complex in diagnosis and management. A comprehensive understanding of ultrasound evaluation in this context unveils not just the diagnostic patterns but also the inherent pitfalls that practitioners must navigate. With an increasing reliance on ultrasound as a first-line imaging modality in the assessment of lymph node enlargement, the advancements in imaging technology offer substantial benefits, yet they come with challenges that require astute awareness and understanding.
The research led by Sideris et al. emphasizes the importance of recognizing these diagnostic patterns while adhering to a systematic approach. The authors meticulously outline the various presentations of lymphadenopathies, which can significantly affect the decision-making process in pediatric patients. Ultrasound has emerged as a non-invasive, real-time imaging technique that provides valuable insights into the morphology and characteristics of lymph nodes. These features are instrumental in differentiating benign from malignant processes, ultimately guiding the clinical pathway for the patient.
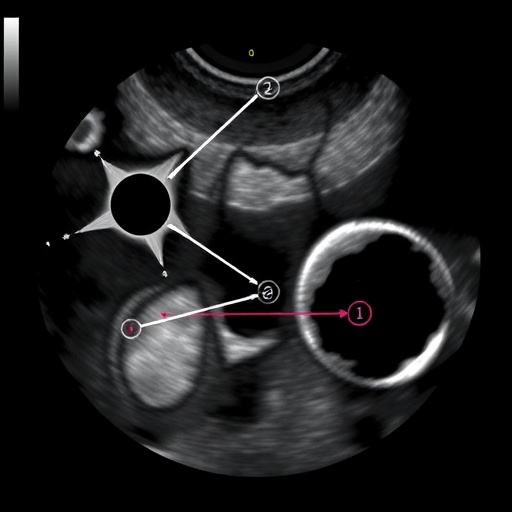
Ultrasound allows for the assessment of lymph nodes based on size, shape, echogenicity, and vascularity. For instance, characteristic features commonly observed in normal lymph nodes include an oval shape, a thin cortex, and a central echogenic area known as the hilum. In contrast, suspicious nodes may exhibit irregular borders, hypoechoic characteristics, and increased vascular flow. These nuanced differences are critical for radiologists and clinicians alike when determining the likelihood of neoplastic conditions versus reactive hyperplasia due to infection or inflammation.
Understanding the infectious causes of lymphadenopathy is equally essential. Viral, bacterial, and even fungal infections can lead to lymph node enlargement, often presenting as a hallmark sign of the body’s immune response. However, distinguishing between lymphadenopathy caused by an infectious etiology and one driven by malignancy can pose a significant diagnostic challenge. This conundrum is where the detailed patterns outlined in Sideris et al. serve an essential role, shedding light on which ultrasound features correlate with specific infectious agents.
Moreover, the article addresses the potential pitfalls associated with ultrasound evaluation. A common misunderstanding is the reliance solely on size criteria for lymph node assessment. While size can be an important factor, it is not an absolute determinant of pathology. Some malignant lymph nodes may be smaller than expected, while large nodes can be entirely benign. A thorough diagnostic approach necessitates considering patient history, clinical examination, and imaging findings together rather than in isolation.
The implications of inaccurately diagnosing lymphadenopathy can be profound. In cases where malignancy is overlooked or misdiagnosed, a delay in appropriate treatment can lead to dire consequences. Conversely, unnecessary invasive procedures may result from misinterpretation of benign processes as malignant. The delicate balance in making an accurate diagnosis can be daunting for healthcare providers. Hence, this study plays a crucial role in potentially reshaping educational efforts surrounding the evaluation of pediatric lymphadenopathies.
Furthermore, the authors propose a refined algorithm that could assist practitioners in navigating the complexities of pediatric lymphadenopathy assessment. This algorithm emphasizes integrating clinical findings with ultrasound characteristics to arrive at an accurate diagnosis. It enhances patient care by promoting efficiency and accuracy in evaluation, while reducing the likelihood of unnecessary biopsies and interventions.
In conclusion, the insights shared by Sideris et al. represent a significant contribution to pediatric radiology and the broader field of pediatric medicine. The implementation of structured diagnostic pathways and an awareness of the pitfalls surrounding lymphadenopathy is crucial to improving outcomes. As ultrasound technology continues to evolve, embracing these advancements, along with a comprehensive understanding of lymph node evaluation, will ensure that pediatric patients receive the best possible care.
As this research highlights, the journey towards diagnosis is multifaceted, involving the collaboration of radiologists, pediatricians, and other healthcare professionals. Ongoing education and an emphasis on shared experiences within the medical community are imperative as we strive for excellence in pediatric diagnostic imaging. The analysis and subsequent findings presented by Sideris and colleagues pave the way for better practices and understanding in the challenges posed by pediatric lymphadenopathies.
In an era where precision medicine is becoming the gold standard, it is vital to foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptation amongst healthcare providers. By embracing the findings of this study and actively applying them in clinical practice, we can work collectively towards the goal of enhanced diagnostic accuracy, ultimately benefiting the pediatric population we serve.
With the landscape of pediatric healthcare constantly evolving, researchers such as Sideris et al. are at the forefront of illuminating the intricacies of diagnostic imaging. Their work serves not only as a timely reminder of the complexities inherent in lymphadenopathy evaluation but also as a call to action for physicians to remain vigilant and informed.
The collaboration of multidisciplinary teams in elucidating the patterns and pitfalls of lymphadenopathy is paramount as we look towards the future of pediatric care. Learning from one another’s experiences and insights will be indispensable in overcoming the challenges that lie ahead in diagnostic imaging.
Through educational initiatives, case discussions, and research efforts, we can fortify our understanding of pediatric lymph node evaluation, paving the way for innovative approaches that harness the power of modern imaging technologies to improve patient outcomes.
As 2025 unfolds, we anticipate that the insights provided in this study will not only impact clinical practices in pediatric radiology but will also spark further inquiries and discussions within the medical community. The critical role of ultrasound in evaluating lymphadenopathies is undeniable, and as we continue to refine our approaches and methodologies, we can improve the lives of countless children facing the same hurdles.
Ultimately, the advancement of pediatric healthcare is a collective endeavor, demanding unwavering commitment to research, education, and collaboration. As we strive to comprehend the intricacies of lymphadenopathy in children, the findings of Sideris and his team will undoubtedly be a cornerstone of our ongoing collective efforts.
With the expanding body of literature on the subject, there is hope that future advancements will lead to even greater accuracy in diagnosis and management, benefitting the pediatric population across the globe.
Subject of Research: Ultrasound evaluation of pediatric lymphadenopathies
Article Title: Ultrasound evaluation of pediatric lymphadenopathies: diagnostic patterns and pitfalls
Article References: Sideris, G.A., Stever, M., Khubchandani, M. et al. Ultrasound evaluation of pediatric lymphadenopathies: diagnostic patterns and pitfalls. Pediatr Radiol (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-025-06490-1
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: 10.1007/s00247-025-06490-1
Keywords: Pediatric lymphadenopathy, ultrasound evaluation, diagnostic patterns, imaging pitfalls, pediatric radiology
Tags: advancements in pediatric ultrasound technologychallenges in lymphadenopathy assessmentdiagnostic patterns in lymphadenopathydistinguishing benign from malignant lymphadenopathylymph node enlargement diagnosislymph node morphology characteristicsnon-invasive imaging techniques for childrenpediatric lymphadenopathy evaluationreal-time ultrasound insightssystematic approach to lymphadenopathyultrasound features of lymph nodesultrasound imaging in pediatrics