CHICAGO – COVID-19 infection is associated with increased liver stiffness, a sign of possible long-term liver injury, according to the results of a new study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Credit: RSNA and Firouzeh Heidari, M.D.
CHICAGO – COVID-19 infection is associated with increased liver stiffness, a sign of possible long-term liver injury, according to the results of a new study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“Our study is part of emerging evidence that COVID-19 infection may lead to liver injury that lasts well after the acute illness,” said Firouzeh Heidari, M.D., a post-doctorate research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
Liver stiffness is a marker of liver damage, such as inflammation or fibrosis. Fibrosis is the buildup of scar tissue in the liver. Over time, healthy liver tissue diminishes, and the liver can no longer function properly. Progressive fibrosis can lead to liver cancer and liver failure.
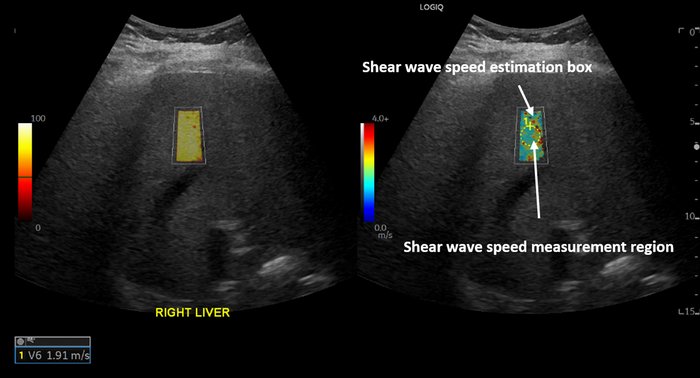
In the retrospective study, the researchers compared liver stiffness of patients with a history of COVID-19 infection to two control groups. All patients underwent ultrasound shear wave elastography between 2019 and 2022 at Massachusetts General Hospital. Shear wave elastography is a specialized technique that uses sound waves to measure the stiffness of tissue.
The patients were categorized into one of three groups based on when they underwent elastography and whether they tested positive for COVID-19. The COVID-19 positive group contained 31 patients who had a positive COVID-19 PCR test result at least 12 weeks before the elastography exam. The pandemic control group consisted of a random sample of 50 patients who underwent elastography during the COVID-19 pandemic and had a history of only negative COVID-19 PCR test results. The pre-pandemic control group consisted of a random sample of 50 patients who underwent an elastography exam prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The mean age was 53.1 years for the COVID-positive patients, 55.2 years for the pandemic control group and 58.2 years for the pre-pandemic control group. Of the total cohort, 67 were women. In the COVID-positive group, elastography exams were performed an average of 44 weeks after a positive PCR test result.
After controlling for age, sex and time period, a statistical analysis of the elastography results revealed that COVID-positive patients had a statistically significant higher liver stiffness than the control patients.
COVID-positive patients had a higher median live stiffness (7.68 kPa) than pandemic control patients (5.99 kPa).
Unexpectedly, the pre-pandemic control group also had a higher median stiffness (7.01) compared to pandemic control group. The reason for this finding is not yet understood but is believed to be a result of changing referral patterns during the pandemic. Additionally, patients referred for elastography before the pandemic were noted to be older than patients referred after the start of the pandemic.
“We don’t yet know if elevated liver stiffness observed after COVID-19 infection will lead to adverse patient outcomes,” Dr. Heidari said. “We are currently investigating whether the severity of acute COVID-related symptoms is predictive of long-term liver injury severity. We hope to enrich our existing database with additional patient data and a broader scope of co-variates to better understand the post-acute effects of COVID-19 within the liver.”
Co-authors are Theodore Pierce, M.D., Anthony Samir, M.D., M.P.H., Arinc Ozturk, M.D., Madhangi Parameswaran, M.B.B.S., M.Res., Marian Martin, M.D., M.P.H., and Hannah Edenbaum, M.S.
###
Note: Copies of RSNA 2022 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press22.
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on elastography, visit RadiologyInfo.org.




