Credit: Graphic by Gopikrishna J. Pillai, Scientific Illustrator
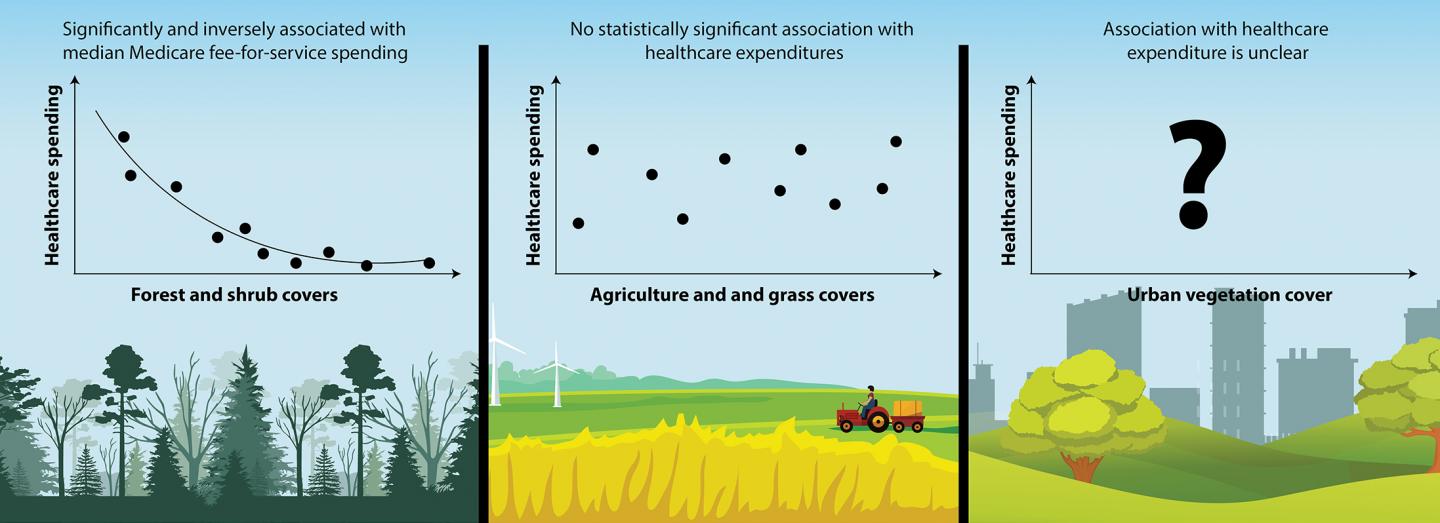
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study finds that Medicare costs tend to be lower in counties with more forests and shrublands than in counties dominated by other types of land cover. The relationship persists even when accounting for economic, geographic or other factors that might independently influence health care costs, researchers report.
The analysis included county-level health and environmental data from 3,086 of the 3,103 counties in the continental U.S.
Urban and rural counties with the lowest socioeconomic status appeared to benefit the most from increases in forests and shrubs, said University of Illinois graduate student Douglas A. Becker, who led the new research with Matt Browning, a professor of recreation, sport and tourism at the U. of I.
“At first, I was surprised by this,” Becker said. “But then it occurred to me that low-income communities are getting the biggest bang for their buck because they probably have the most to gain.”
The findings, reported in the journal Urban Forestry and Urban Greening, are observational and do not prove that having more trees and shrubs directly lowers health care costs, Becker said. But the study adds to a growing body of evidence linking green space – in particular, forested areas – to better health outcomes for those living nearby.
“Previous studies have looked at any health outcomes people think might be linked to nature: depression, cardiovascular disease, physical activity levels, even recovery from surgery,” Becker said.
Several studies report no association between access to green space and health, he said.
“But there is also a lot of work – including experimental work, which we consider to be the strongest – showing a link between exposure to green space and beneficial health effects,” Becker said.
For example, studies have shown that people in intensive care units recover more quickly and have fewer complications after surgery if their hospital rooms look out over trees rather than parking lots. Other studies have found that forest walks can influence potentially health-promoting hormone levels or anti-cancer immune cells in the blood.
For the current study, the team turned to the National Land Cover Database, which divides each county into 30-meter-square plots and identifies the environmental composition of each plot. Categories include urban developed or open space, forest, grassland, shrubs and agricultural cover.
“We took the average of different types of land cover and the per capita Medicare spending in a county and compared these two while controlling for several socioeconomic and demographic factors like age, sex, race, median household income, health care access and health behaviors,” Becker said.
The Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services adjust the Medicare expenditure data to reflect differences in health care costs and health-risk profiles in different regions of the U.S., he said.
The analysis revealed that each 1 percent of a county’s land that was covered in forest was associated with an average Medicare expenditure savings of $4.32 per person per year, Becker said.
“If you multiply that by the number of Medicare fee-for-service users in a county and by the average forest cover and by the number of counties in the U.S., it amounts to about $6 billion in reduced Medicare spending every year nationally,” he said.
Adding the effects of shrublands increases the estimated savings to $9 billion annually.
As a follow-up to these findings, Becker, Browning and their colleagues are looking at individual health and environmental data in a collaboration with Kaiser Permanente in California.
###
The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s U.S. Forest Service and the National and Urban Community Forestry Advisory Council supported this research.
Editor’s notes:
To reach Douglas Becker, call 847-431-0504; email [email protected].
To reach Matthew Browning, call 217-300-3496; email [email protected].
The paper “Is green land cover associated with less health care spending? Promising findings from county-level Medicare spending in the continental United States” is available online or from the U. of I. News Bureau.
Media Contact
Diana Yates
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




