They look like storm clouds that could fit on the head of a pin: Organoids are three-dimensional cell cultures that play a key role in medical and clinical research. This is thanks to their ability to replicate tissue structures and organ functions in the petri dish. Scientists can use organoids to understand how diseases occur, how organs develop, and how drugs work. Single-cell technologies allow researchers to drill down to the molecular level of the cells. With spatial transcriptomics, they can observe which genes in the organoids are active and where over time.
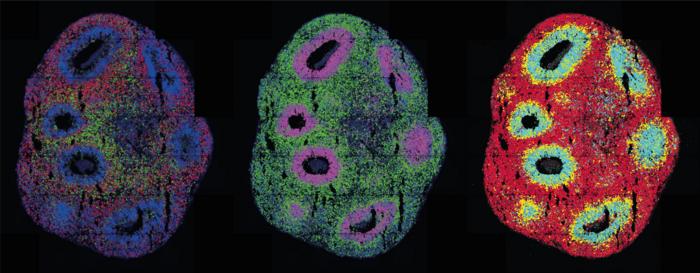
Credit: Ivano Legnini, Agnieszka Rybak-Wolf, Max Delbrück Center
They look like storm clouds that could fit on the head of a pin: Organoids are three-dimensional cell cultures that play a key role in medical and clinical research. This is thanks to their ability to replicate tissue structures and organ functions in the petri dish. Scientists can use organoids to understand how diseases occur, how organs develop, and how drugs work. Single-cell technologies allow researchers to drill down to the molecular level of the cells. With spatial transcriptomics, they can observe which genes in the organoids are active and where over time.
The miniature organs are usually derived from stem cells. These are cells that haven’t differentiated at all, or only minimally. They can become any kind of cell, such as heart or kidney cells, muscle cells, or neurons. To make stem cells differentiate, scientists “feed” them with growth factors and embed them in a nutrient solution. There, the cells bunch together in tiny clumps and begin functioning and interacting as if they were in a real tissue. Previously, it was almost impossible to control this process. But now researchers led by Professor Nikolaus Rajewsky, Director of the Berlin Institute for Medical Systems Biology of the Max Delbrück Center (MDC-BIMSB), have published a paper in Nature Methods describing the technology they used to both initiate and control the process, and observe it across time and space. “We combined spatial transcriptomics with optogenetics,” says lead author Dr. Ivano Legnini. “This allows us to both control gene expression in living cells and observe their behavior.”
Using light sensors to activate or block genes
In optogenetics, natural or artificial “light sensors” are inserted into cells. If light reaches the sensors, they activate or block genes in the cells, depending on how they’re programmed. Legnini installed these light sensors in stem cell-derived neuronal precursor cells that would come together to form neural organoids. He worked on this with the Organoid Technology Platform team led by Dr. Agnieszka Rybak-Wolf, and with the Systems Biology of Neural Tissue Differentiation Lab led by Dr. Robert Patrick Zinzen. The researchers wanted to find out how the nervous system develops in the human embryo. Molecules known as morphogens play a key role in the process. They signal to neuronal progenitors whether they should become neurons that function in the front of the brain or the rear part of the spinal cord for example. The combination of these molecules produces typical patterns of gene expression during development.
The researchers used light to activate a morphogen called Sonic Hedgehog. Their subsequent spatially resolved single-cell analyses showed that the cells responded by arranging themselves into stereotypically patterned organoids. The researchers created the light in two ways: using either a laser microscope or a digital micromirror device, which Rajewsky’s group developed in collaboration with Dr. Andrew Woehler. At the time, Dr. Woehler was leading the Systems Biology Imaging Platform at the Max Delbrück Center. Since November 2022, he has been leading the Janelia Experimental Technology facility at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute in Ashburn, Virginia, USA. The micromirror microscope is fitted with a chip holding several hundred thousand tiny mirrors. These can be programmed so the microscope can – unlike a laser, which only hits a single point – produce complex light patterns on a sample.
Accurate – with room for improvement
“Our method allows us to very accurately reproduce, in the petri dish, processes that are connected to gene expression in tissue,” says Legnini. In March this year, he began setting up his own working group at the Human Technopole in Milan, Italy. His plans for the group include improving the technology’s spatial and temporal resolution and making it usable for other organoids.
Rajewsky also wants to refine the method: “I’m really looking forward to working with optogenetics experts to further improve the technology and to apply it to clinically relevant human organoid models.”
Max Delbrück Center
The Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (Max Delbrück Center) is one of the world’s leading biomedical research institutions. Max Delbrück, a Berlin native, was a Nobel laureate and one of the founders of molecular biology. At the locations in Berlin-Buch and Mitte, researchers from some 70 countries study human biology – investigating the foundations of life from its most elementary building blocks to systems-wide mechanisms. By understanding what regulates or disrupts the dynamic equilibrium of a cell, an organ, or the entire body, we can prevent diseases, diagnose them earlier, and stop their progression with tailored therapies. Patients should benefit as soon as possible from basic research discoveries. The Max Delbrück Center therefore supports spin-off creation and participates in collaborative networks. It works in close partnership with Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin in the jointly run Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH) at Charité, and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK). Founded in 1992, the Max Delbrück Center today employs 1,800 people and is funded 90 percent by the German federal government and 10 percent by the State of Berlin.
Journal
Nature Methods
DOI
10.1038/s41592-023-01986-w
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Lab-produced tissue samples
Article Title
Spatiotemporal, optogenetic control of gene expression in organoids
Article Publication Date
21-Sep-2023




