Credit: Tohoku University
The Japanese now have their own reference genome thanks to researchers at Tohoku University who completed and released the first Japanese reference genome (JG1).
Their study was published in the journal Nature Communications on January 11, 2021.
“JG1 can aid with the clinical sequence analysis of Japanese individuals with rare diseases as it eliminates the genomic differences from the international reference genome,” said Jun Takayama, co-author of the study.
Back in 2003, the Human Genome Project, through a gargantuan global effort, cracked the code of life and mapped all the genes of the human genome.
Since then, more accurate versions of the human reference genome have been realized. Aiding this has been the advancement in next-generation sequencing technologies that allow for short read of approximately several hundred bases in a massively parallel way, reducing the costs and time to sequence DNA and RNA.
The international reference genome is based on an individual of African-European descent. This hampers investigating genetic variants or rare disease and cancer driving genes in Japanese owing to natural genomic difference reflective in different populations.
Associate professor Takayama and professor Gen Tamiya from Tohoku University’s Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization (ToMMo) and the Advanced Research Center for Innovations in Next-Generation Medicine (INGEM) and colleagues from Tohoku University School of Medicine, School of Information Sciences, RIKEN AIP Center, and Miyagi Cancer Research Institute developed JG1 as the first part of the Japanese Reference Genome Assembly (JRGA) project.
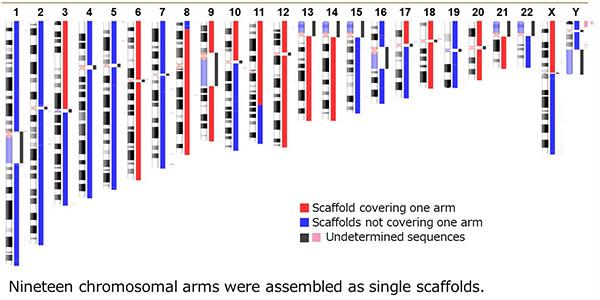
This high-precision reference sequence is applicable to the whole human genome analysis and was constructed by analyzing the genomes of three Japanese individuals using high-coverage, long-read next-generation sequencing technologies.
Researchers can efficiently investigate the causal genetic variants of rare diseases and cancer driver genes with JG1.
“JG1 may be applicable to other populations, especially those from Asia. In addition, with the JG1, the accuracy of the Japanese allele frequency and haplotype reference panels gets improved,” added Takayama.
###
Media Contact
Fuji Nagami
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




