image: Article Graphical Abstract
view more
Credit: Lucas P. Kwiyukwa, Geradius Deogratias, Fidele Ntie-Kang, Lucas Paul.
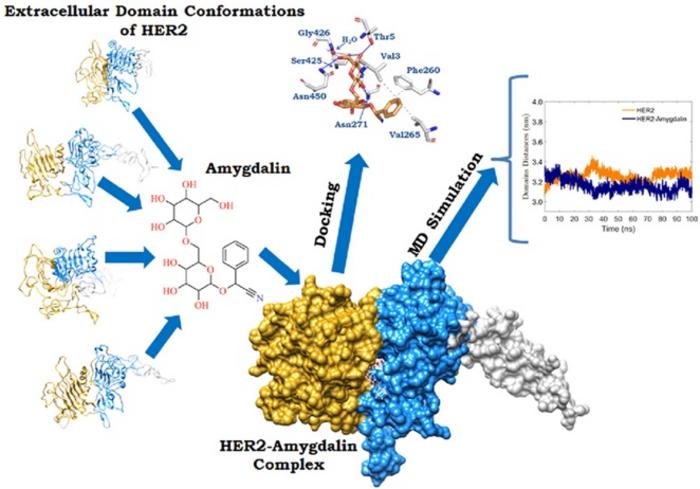
This study investigates the potential of amygdalin, a natural compound found in almonds, peaches, and apples, as a therapeutic agent for HER2-positive breast cancer. HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) is overexpressed in a significant percentage of aggressive breast cancer cases and is associated with poor prognosis. The researchers aimed to explore whether amygdalin could effectively bind to and stabilize the HER2 protein, which could suppress its cancer-promoting activity.
To do this, the study employed a variety of computational tools. Molecular docking was used to determine how strongly amygdalin could bind to HER2, and results showed favorable binding energies, especially when water molecules were included in the simulation. Molecular dynamics simulations over a 100-nanosecond period revealed that amygdalin binding induced structural changes in the HER2 protein, particularly reducing the flexibility of the dimerization arm and decreasing interdomain distances—features associated with an inactive HER2 conformation. The binding was shown to be energetically favorable, primarily driven by van der Waals forces, as revealed by MMPBSA energy calculations.
Finally, the study identified key amino acids within HER2 that contributed most to the binding interaction, and the presence of water was shown to enhance the stability and tightness of the binding. The authors conclude that while these computational results are promising and show that amygdalin could interfere with HER2 activity, further in vitro and clinical studies are needed to validate its effectiveness as a treatment option. Nonetheless, the findings offer a strong foundation for future drug development targeting HER2 in breast cancer.
Journal
LabMed Discovery
DOI
10.1016/j.lmd.2025.100070
Method of Research
Experimental study
Article Title
Binding affinity and structural dynamics of amygdalin-HER2 interactions: An investigation for breast cancer therapy
Article Publication Date
16-May-2025
Media Contact
Bowen Li
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Journal Center
Office: 021-62800059
Journal
LabMed Discovery
DOI
10.1016/j.lmd.2025.100070
Journal
LabMed Discovery
DOI
10.1016/j.lmd.2025.100070
Method of Research
Experimental study
.adsslot_PGy72agLiH{width:728px !important;height:90px !important;}
@media(max-width:1199px){ .adsslot_PGy72agLiH{width:468px !important;height:60px !important;}
}
@media(max-width:767px){ .adsslot_PGy72agLiH{width:320px !important;height:50px !important;}
}
ADVERTISEMENT Article Title
Binding affinity and structural dynamics of amygdalin-HER2 interactions: An investigation for breast cancer therapy
Article Publication Date
16-May-2025
Keywords
/Health and medicine/Diseases and disorders/Cancer/Breast cancer
bu içeriği en az 2000 kelime olacak şekilde ve alt başlıklar ve madde içermiyecek şekilde ünlü bir science magazine için İngilizce olarak yeniden yaz. Teknik açıklamalar içersin ve viral olacak şekilde İngilizce yaz. Haber dışında başka bir şey içermesin. Haber içerisinde en az 12 paragraf ve her bir paragrafta da en az 50 kelime olsun. Cevapta sadece haber olsun. Ayrıca haberi yazdıktan sonra içerikten yararlanarak aşağıdaki başlıkların bilgisi var ise haberin altında doldur. Eğer yoksa bilgisi ilgili kısmı yazma.:
Subject of Research:
Article Title:
News Publication Date:
Web References:
References:
Image Credits:
Keywords
Tags: almond-derived compounds in medicineamygdalin and HER2 bindingbreast cancer therapy researchcancer prognosis and HER2computational drug design techniquescomputational methods in oncologyHER2-positive breast cancermolecular docking studiesnatural compounds for cancer treatmentprotein stabilization in cancer therapystabilizing effects of amygdalintherapeutic agents for aggressive cancer