A research team based in Kumamoto University (Japan) has created complex 3D kidney tissue in the lab solely from cultured mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells. These organoids could lead the way to better kidney research and, eventually, artificial kidneys for human transplant.
Credit: Dr. Shunsuke Tanigawa
A research team based in Kumamoto University (Japan) has created complex 3D kidney tissue in the lab solely from cultured mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells. These organoids could lead the way to better kidney research and, eventually, artificial kidneys for human transplant.
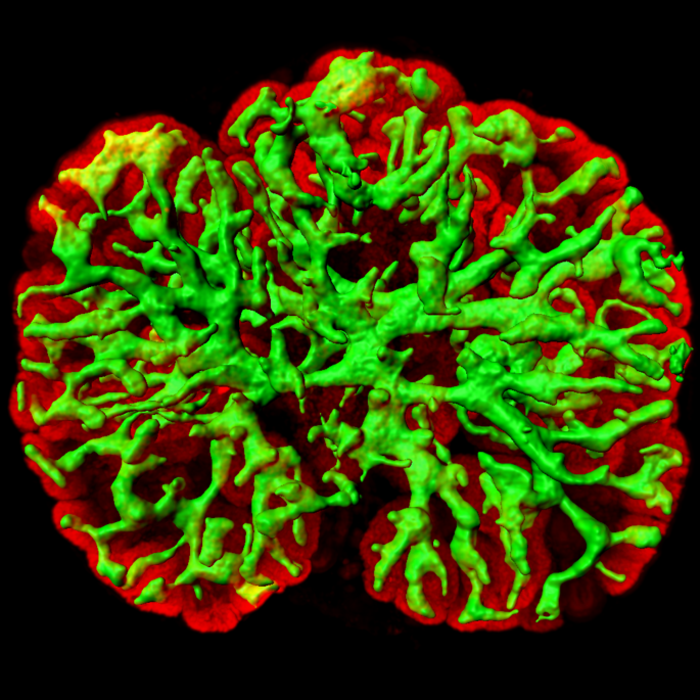
By focusing on an often-overlooked tissue type of organoid generation research, a type of organ tissue made up of various support and connective tissues called the stroma, Dr. Ryuichi Nishinakamura and his team were able to generate the last of a three-part puzzle that they had been working on for several years. Once the three pieces were combined, the resulting structure was found to be kidney-like in its architecture. The researchers believe that their work will be used to advance kidney research and even lead to a transplantable organ in the future.
The kidney is a very important organ for continued good health because it acts as a filter to extract waste and excess water from blood. It is a complex organ that develops from the combination of three components. Protocols have already been established by various research teams, including Dr. Nishinakamura’s team at the Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics (IMEG) at Kumamoto University, to induce two of the components (the nephron progenitor and the ureteric bud) from mouse ES cells.
In this, their most recent work, the IMEG team has developed a method to induce the third and final component, kidney-specific stromal progenitor, in mice. Furthermore, by combining these three components in vitro, the researchers were able to generate a kidney-like 3D tissue, consisting of extensively branched tubules and several other kidney-specific structures.
The researchers believe that this is the first ever report on the in-lab generation of such a complex kidney structure from scratch. The IMEG team has already succeeded in inducing the first two components from human iPS cells. If this last component can also be generated from human cells, a similarly complex human kidney should be achievable.
“We are now working very hard to generate a fully functional human kidney,” said Dr. Nishinakamura. “We hope to use our developments to screen drugs for various diseases, and for transplantation in the long run.”
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-022-28226-7
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Lab-produced tissue samples
Article Title
Generation of the organotypic kidney structure by integrating pluripotent stem cell-derived renal stroma
Article Publication Date
1-Feb-2022
COI Statement
The authors declare no competing interests.




