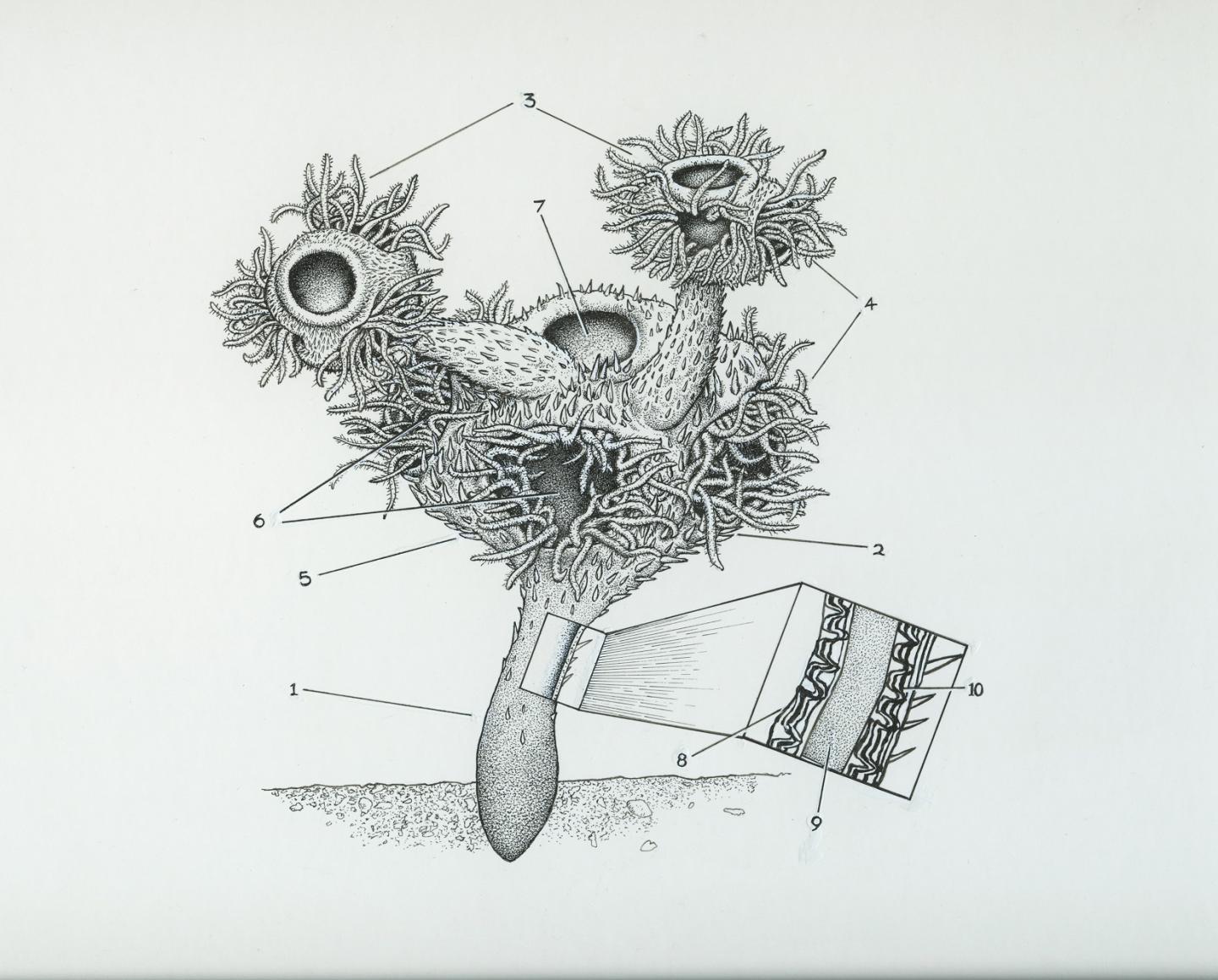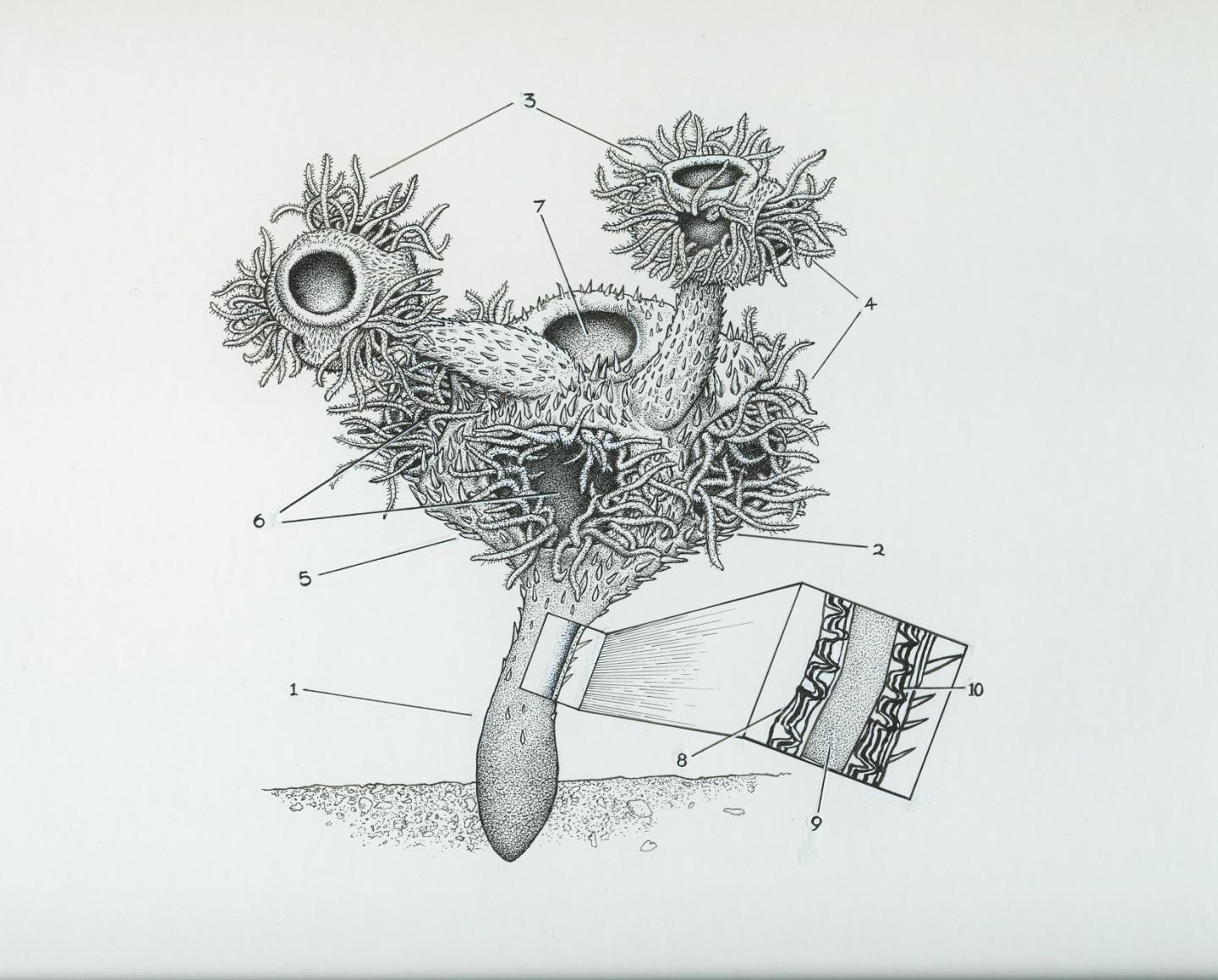
The first animals to have complex skeletons existed about 550 million years ago, fossils of a tiny marine creature unearthed in Namibia suggest.
The find is the first to suggest the earliest complex animals on Earth – which may be related to many of today's animal species – lived millions of years earlier than was previously known.
Until now, the oldest evidence of complex animals – which succeeded more primitive creatures that often resembled sponges or coral – came from the Cambrian Period, which began around 541 million years ago. Scientists had long suspected that complex animals had existed before then but, until now, they had no proof.
Genetic family tree data suggested that complex animals – known as bilaterians – evolved prior to the Cambrian Period. The finding suggests that bilaterians may have lived as early as 550 million years ago, during the late Ediacaran Period.
The study suggests that complex animals existed long before a period in the planet's history – known as the Cambrian explosion – during which most major animal groups evolved.
The team studied fossils of an extinct marine animal – known as Namacalathus hermanastes – which was widespread during the Ediacaran Period. The fossils are remarkably well preserved and reveal that the species possessed a rigid skeleton made of calcium carbonate – a hard material from which the shells of marine animals are made. The complex skeletal structures are similar to those of living creatures that dwell at the bottom of the sea, the team says.
The study, published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, was funded by the Natural Environment Research Council. The research was carried out in collaboration with Lomonosov Moscow State University.
Professor Rachel Wood, of the University of Edinburgh's School of GeoSciences, who led the study, said: "This fossil has been known for a long time, and was assumed to have been a primitive animal, such as a sponge or coral. This study suggests that it was, in fact, more advanced. We have suspected that these complex animals were present in the Ediacaran, but this study provides the first proof."
###