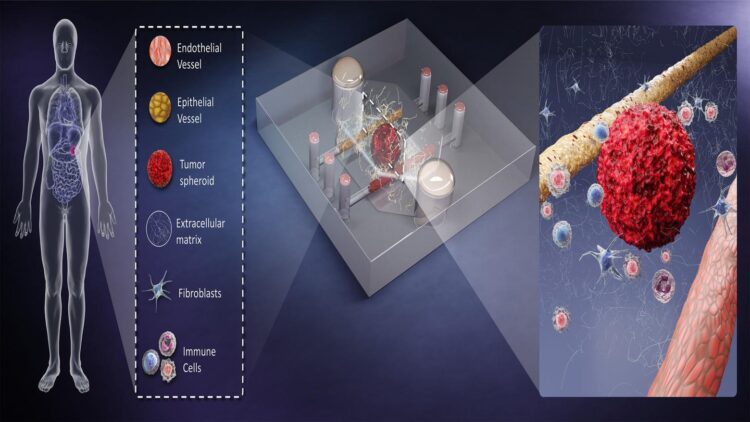
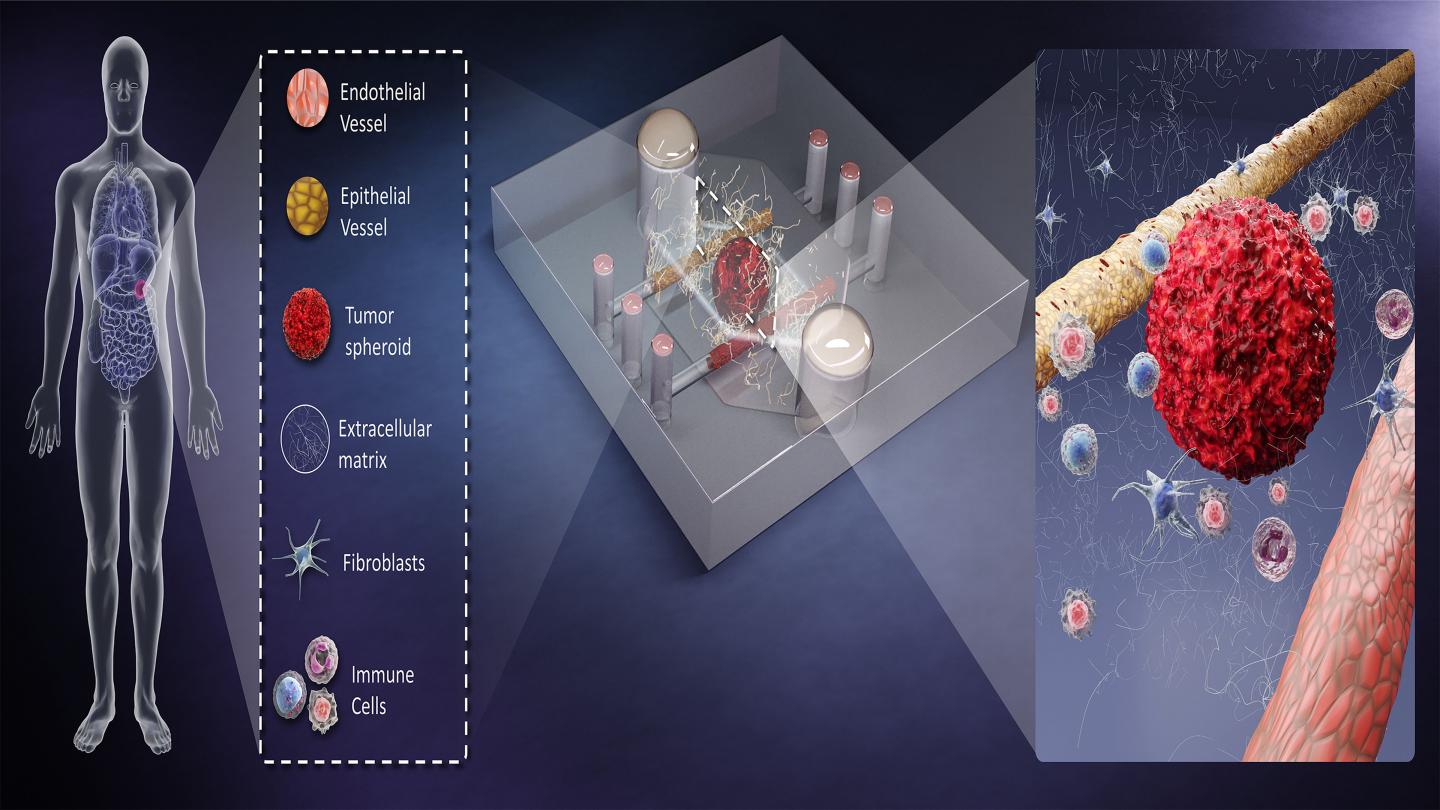
Tiny devices use samples taken directly from patients to combine in vivo and in vitro testing.
Credit: Terry Juang
WASHINGTON, January 21, 2021 — Despite cancer being a leading cause of death worldwide, treatment options for many types of cancers remain limited. This is partly due to the in vitro tools used to model cancers, which cannot adequately predict the behavior of a cancer or its sensitivity to drugs.
Further, animal models, like mice, biologically differ from humans in ways that play a critical role in immunotherapy, and results from animal studies do not always translate well to human disease.
These shortcomings point to a clear need for a better, patient-specific model to improve the understanding of cancer cells and their impacts.
Researchers from the University of Wisconsin and the University of California, San Francisco suggest bioengineered microscale organotypic models (BMOMs) can address this need. They discuss the advantages and capabilities of this technique, as well as its challenges, in the journal APL Bioengineering, from AIP Publishing.
Due to their very small size, BMOMs require only a tiny patient-derived biopsy sample to monitor biological processes. This reduces any concern about the translatability of findings, since all the associated models are developed directly from human material. In addition, BMOMs can be integrated with microscopes and miniaturized sensors to watch the response of the cell culture to test treatments in high resolution and real time.
“BMOMs attempt to merge the best of in vivo and in vitro models,” said David Beebe, one of the authors. “These models place human cells in a more realistic environment context, where they are more likely to respond to treatment in a way more reflective of the patient response.
“The 3D and multicellular attributes of BMOMs capture more of the myriad and complex cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions that regulate treatment response.”
Though promising, these devices have several limitations. They are difficult to fabricate in large quantities, and they require specialized training to use. Beyond these hurdles, BMOMs are also restricted in their capacity to consider human behavioral responses and fall short in modeling the interactions that occur between multiple organs in complex diseases.
With additional research and clinical trials, the authors are optimistic about the applications of BMOMs. Their use with primary cells taken directly from patient tissue can help with patient-specific cancer treatments and drug testing.
###
The article “Towards improved in vitro models of human cancer” is authored by Jose M. Ayuso, Keon-Young Park, María Virumbrales-Muñoz, and David J. Beebe. The article appears in APL Bioengineering (DOI: 10.1063/5.0026857) and can be accessed at https:/
See also: Personalizing cancer care with improved tumor models at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.