At the first sign of cognitive trouble, people often worry Alzheimer’s disease is forthcoming. But poor cognition can be part of the spectrum of normality in older age, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Credit: Kocagoncu et al., JNeurosci 2022
At the first sign of cognitive trouble, people often worry Alzheimer’s disease is forthcoming. But poor cognition can be part of the spectrum of normality in older age, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
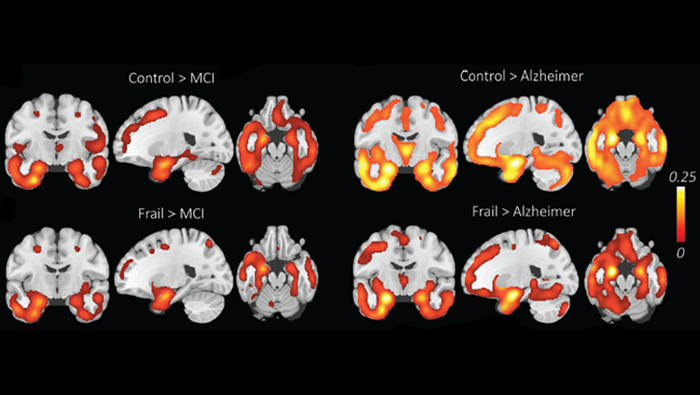
Kocagoncu et al. compared the brains of cognitively frail adults — people with reduced cognitive function who haven’t noticed memory issues — to those of adults with a mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and healthy controls. They recruited healthy and cognitively frail adults from the Cambridge Centre for Ageing and Neuroscience study. Researchers measured participants’ cognition with a battery of tests, their brain structure with MRI, and their brain activity with EEG and MEG.
Cognitively frail adults performed like adults with MCI on the cognitive tests — both worse than controls. But their brain structure and activity resembled those of the healthy controls: the atrophy in regions like the hippocampus typical in adults in AD did not appear in cognitively frail adults. Impaired cognition can be part of the range of normal aging and is not always an early sign of Alzheimer’s disease. Cognitive frailty may instead hinge on lifestyle factors — many of which are reversible and modifiable — like physical activity, stress, education, and cardiovascular health.
###
Paper title: Neurophysiological and Brain Structural Markers of Cognitive Frailty Differ From Alzheimer’s Disease
Please contact [email protected] for the full-text PDF and to join SfN’s journals media list.
About JNeurosci
JNeurosci, the Society for Neuroscience’s first journal, was launched in 1981 as a means to communicate the findings of the highest quality neuroscience research to the growing field. Today, the journal remains committed to publishing cutting-edge neuroscience that will have an immediate and lasting scientific impact, while responding to authors’ changing publishing needs, representing breadth of the field and diversity in authorship.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world’s largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 37,000 members in more than 90 countries and over 130 chapters worldwide.
Journal
JNeurosci
DOI
10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0697-21.2021
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Neurophysiological and Brain Structural Markers of Cognitive Frailty Differ from Alzheimer’s Disease
Article Publication Date
10-Jan-2022




