A paper saw light in Catalysts.
Credit: Kazan Federal University
Ashalcha oilfield in Tatarstan is one of the most popular locations to study the extraction of heavy oils. In particular, Kazan Federal University’s In-Situ Combustion Lab has been working there for a few years.
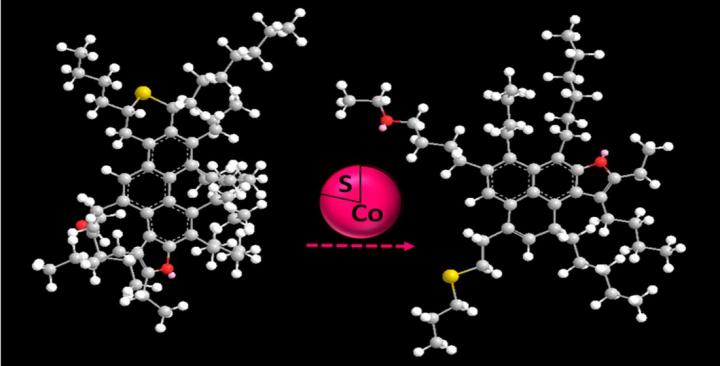
Senior Research Associate Irek Mukhamatdinov explains, “On average, there are one sulfur and one nitrogen atom and five oxygen atoms per resin molecule. In the course of transformation under the action of a catalytic agent and a hydrogen donor, the content of heteroatoms (sulfur, nitrogen and oxygen) in a much larger number of structural blocks of resin molecules decreases. Resin molecules are mainly represented by mono- and two-block structures with a predominance of aromatic rings over naphthenic ones, with long paraffin chains.”
His co-author, Head of the In-Situ Combustion Lab Alexey Vakhin adds, “As a result of thermal steam treatment with a catalyst and a hydrogen donor, the fraction of atoms in paraffinic and naphthenic fragments decreases, while in aromatic fragments it increases, which confirms the fact that an increase in the aromaticity and a decrease in the aliphaticity of oil take place during its hydrothermal transformations.”
During the study, scientists were able to identify the distribution of resin fractions. These fractions were obtained by liquid-adsorption chromatography, extracted with individual solvents and their binary mixtures in various ratios. The results of MALDI spectroscopy revealed a decrease in the molecular weight of all resin fractions after catalytic treatment, mainly with a hydrogen donor.
“Elemental analysis data indicate a decrease in the H / C ratio for resin fractions as a result of the removal of alkyl substituents in resins and asphaltenes. The data of 1H NMR spectroscopy of resin fractions indicate an increase in the aliphatic hydrogen index during catalytic aquathermolysis in the high-molecular part of resins R3 and R4,” says Mukhamatdinov.
One of the advantages of this particular technology is its relative cost effectiveness. New catalysts are planned for use in Ashalcha soon.
###
Media Contact
Yury Nurmeev
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




