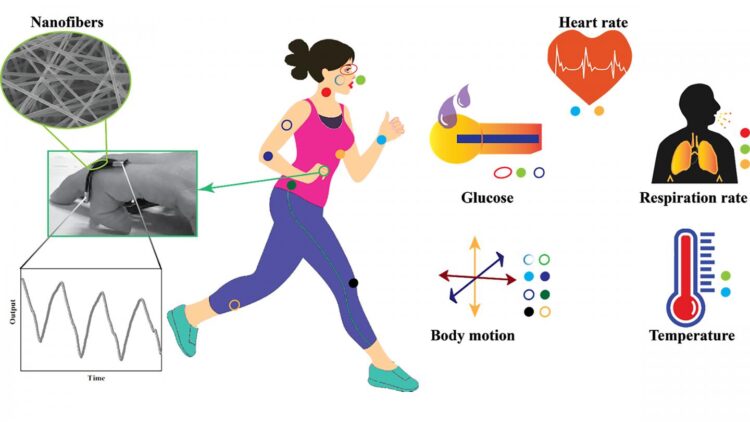
Emerging wearable technology uses tiny fibers that can track your blood pressure, heart rate, and more
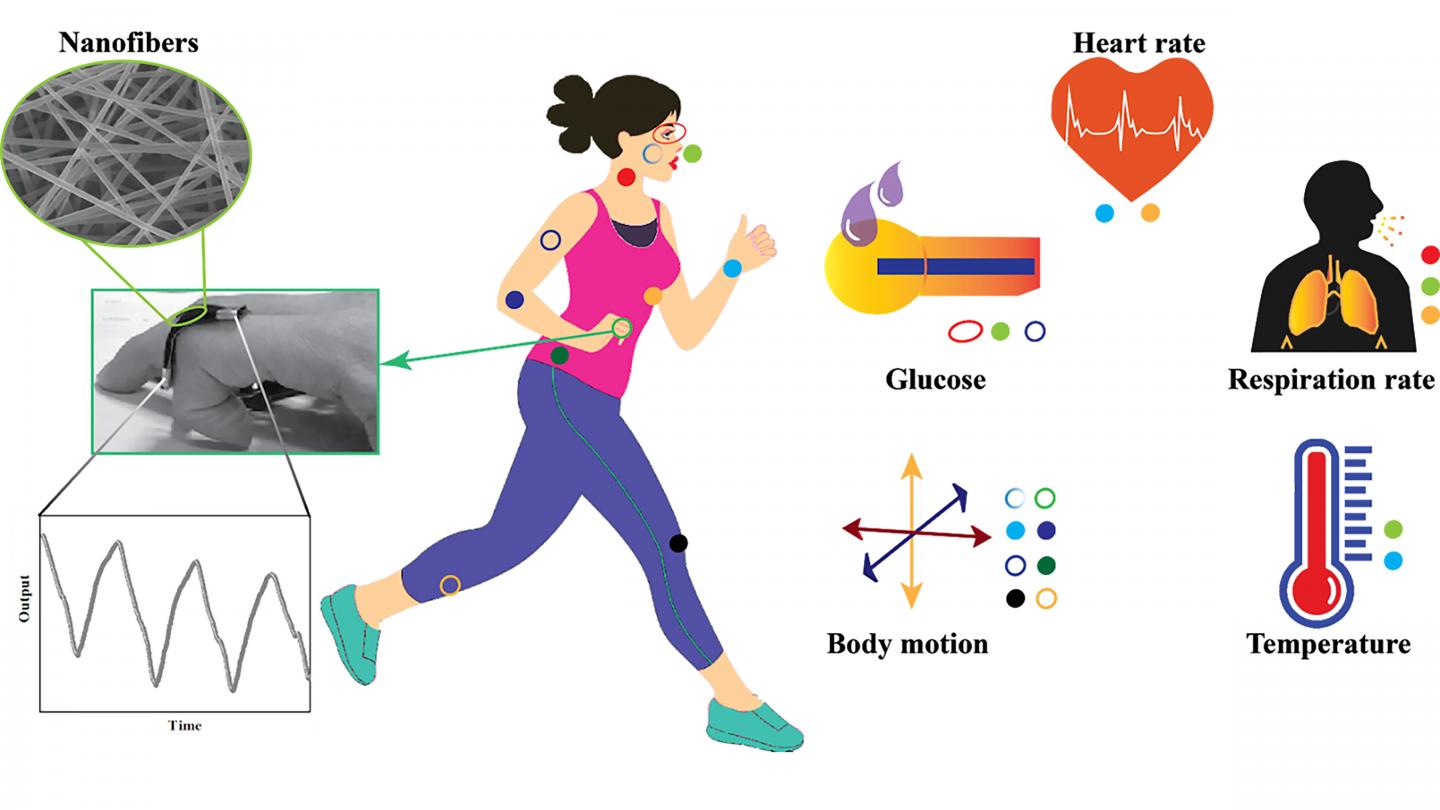
Credit: National University of Singapore
WASHINGTON, December 1, 2020 — A shirt that monitors your blood pressure or a pair of socks that can keep track of your cholesterol levels might be just a few years away from becoming reality.
In an article published in Applied Physics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers examine the use of microfibers, and even smaller nanofibers, as wearable monitors that could keep track of a patient’s vital signs.
The microfiber- and nanofiber-based technology addresses growing concerns in the medical community about monitoring chronic illnesses like diabetes, asthma, obesity, and high blood pressure as the population ages.
“Therefore, the demand for a personalized health care system which detects users’ bio-signals at any given location and time is rapidly growing,” said author Rituparna Ghosh.
The wearable fibers are highly sensitive and flexible and can be used to gauge blood pressure, heart rate, sleep quality, cholesterol levels, oxygen levels, and other vital signs. Because of their small size, they can be applied directly to the skin or woven into garments like shirts, socks, neckwear, or wristbands.
“You could have watches. You could have tattoos. It is usable in almost any form,” said Ghosh. “You could have something like a face mask. It could be a handkerchief which you put on your wrist and it starts giving data.”
Author Seeram Ramakrishna, from the National University of Singapore, said one of the most promising nanofiber technologies — piezoelectric sensors, which are powered by mechanical energy — could be ready to go to market in less than three years.
Other technologies, he said, may be ready for public use in anywhere from five to eight years.
Between now and then, Ramakrishna said more research needs to be done on making the fiber sensors more durable, so they can be used repeatedly, and coming up with a power source for them that is both reliable and portable. It also will take time, he said, to assure the medical community that the technology is accurate, and its data can be trusted for use with real-world patients.
“The medical community is always skeptical, while the wellness industry already is using these concepts,” he said. “We need a lot more cause-and-effect studies. We need to amass information so doctors will really accept that this is information they can rely on.”
The global market value of wearable technology was estimated to be more than $32 billion in 2019 and is expected to jump to as much as $74 billion by 2025 as new applications continue to emerge.
###
The article, “Micro/nano fiber-based non-invasive devices for health monitoring diagnosis and rehabilitation,” is authored by Rituparna Ghosh, Koh Yi Pin, Vundrala Sumedha Reddy, W.A.D.M. Jayathilaka, Dongxiao Ji, William Serrano-García, Suresh K. Bhargava, Seeram Ramakrishna, and Amutha Chinappan. The article will appear in Applied Physics Reviews on Dec. 1, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0010766). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Reviews features articles on significant and current topics in experimental or theoretical research in applied physics, or in applications of physics to other branches of science and engineering. The journal publishes both original research on pioneering studies of broad interest to the applied physics community, and reviews on established or emerging areas of applied physics. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.