New web application helps visualize climate changes in 540 North American cities
Credit: Matthew Fitzpatrick/University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science
FROSTBURG, MD (February 12, 2019)–In one generation, the climate experienced in many North American cities is projected to change to that of locations hundreds of miles away–or to a new climate unlike any found in North America today.
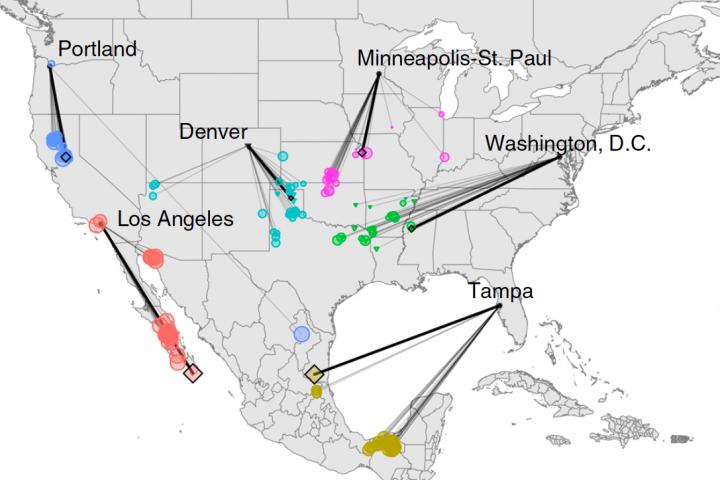
A new study and interactive web application aim to help the public understand how climate change will impact the lives of people who live in urban areas of the United States and Canada. These new climate analyses match the expected future climate in each city with the current climate of another location, providing a relatable picture of what is likely in store.
“Under current high emissions the average urban dweller is going to have to drive more than 500 miles to the south to find a climate like that expected in their home city by 2080,” said study author Matt Fitzpatrick of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science. “Not only is climate changing, but climates that don’t presently exist in North America will be prevalent in a lot of urban areas.”
The study found that by the 2080s, even if limits are placed on emissions, the climate of North American urban areas will feel substantially different, and in many cases completely unlike contemporary climates found anywhere in the western hemisphere north of the equator.
If emissions continue unabated throughout the 21st century, the climate of North American urban areas will become, on average, most like the contemporary climate of locations about 500 miles away and mainly to the south. In the eastern U.S., nearly all urban areas, including Boston, New York, and Philadelphia, will become most similar to contemporary climates to the south and southwest. Climates of most urban areas in the central and western U.S. will become most similar to contemporary climates found to the south or southeast.
“Within the lifetime of children living today, the climate of many regions is projected to change from the familiar to conditions unlike those experienced in the same place by their parents, grandparents, or perhaps any generation in millennia,” said Fitzpatrick. “Many cities could experience climates with no modern equivalent in North America.”
The climate of cities in the northeast will tend to feel more like the humid subtropical climates typical of parts of the Midwest or southeastern U.S. today–warmer and wetter in all seasons. For instance, unless we take action to mitigate emissions, Washington, D.C. will feel more like northern Mississippi. The climates of western cities are expected to become more like those of the desert Southwest or southern California–warmer in all seasons, with changes in the amount and seasonal distribution of precipitation. San Francisco’s climate will resemble that of Los Angeles. New York will feel more like northern Arkansas.
Scientists analyzed 540 urban areas that encompassed approximately 250 million inhabitants in the United States and Canada. For each urban area, they mapped the similarity between that city’s future climate expected by the 2080s and contemporary climate in the western hemisphere north of the equator using 12 measures of climate, including minimum and maximum temperature and precipitation during the four seasons.
The study also mapped climate differences under two emission trajectories: unmitigated emissions (RCP8.5), the scenario most in line with what might be expected given current policies and the speed of global action, and mitigated emissions (RCP4.5), which assumes policies are put in place to limit emissions, such as the Paris Agreement.
Climate-analog mapping is a statistical technique that matches the expected future climate at one location–your city of residence, for instance–with the current climate of another familiar location to provide a place-based understanding of climate change. Combining climate mapping with the interactive web application provides a powerful tool to communicate how climate change may impact the lives of a large portion of the population of the United States and Canada.
“We can use this technique to translate a future forecast into something we can better conceptualize and link to our own experiences,” said Fitzpatrick. “It’s my hope that people have that ‘wow’ moment, and it sinks in for the first time the scale of the changes we’re expecting in a single generation.”
Search the interactive climate map for your location at http://www.
The paper, “Contemporary climatic analogs for 540 North American urban areas in the late 21st century,” by Matt Fitzpatrick of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science and Robert Dunn of North Carolina State University, is published in Nature Communications on February 12.
###
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND CENTER FOR ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
The University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science leads the way toward better management of Maryland’s natural resources and the protection and restoration of the Chesapeake Bay. From a network of laboratories located across the state, UMCES scientists provide sound evidence and advice to help state and national leaders manage the environment, and prepare future scientists to meet the global challenges of the 21st century. http://www.
Media Contact
Amy Pelsinsky
[email protected]
410-330-1389
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




