Climate change influences the likelihood and duration of armed conflicts in Africa. This is the result of a study carried out by a team from the INGENIO Institute, a joint centre of the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC), together with the University of Rome III and the University of Urbino Carlo Bo, published in the latest issue of the journal Economía Política.
Credit: UPV
Climate change influences the likelihood and duration of armed conflicts in Africa. This is the result of a study carried out by a team from the INGENIO Institute, a joint centre of the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC), together with the University of Rome III and the University of Urbino Carlo Bo, published in the latest issue of the journal Economía Política.
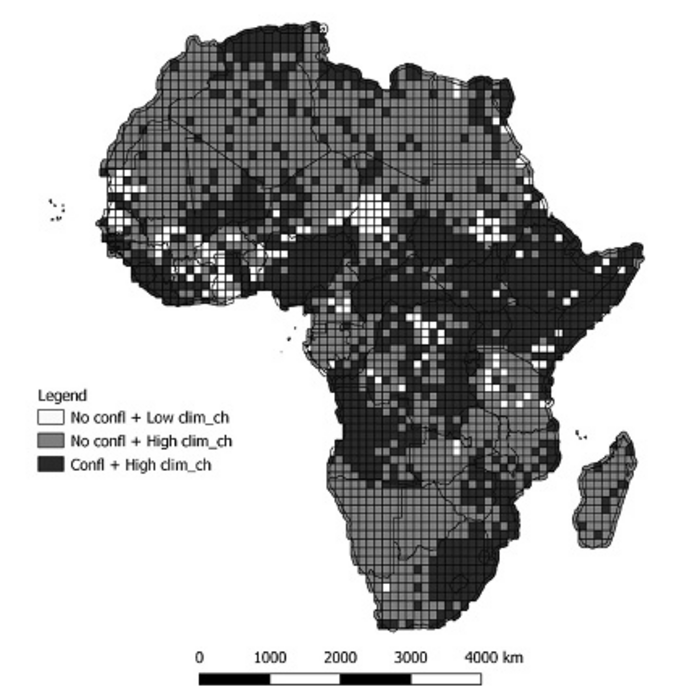
The team of researchers based their study on data from the African continent from 1990 to 2016. Using a negative binomial regression mathematical model, they assessed whether certain climatic phenomena, in combination with the socio-economic characteristics of the areas studied, affected the likelihood of a conflict breaking out and, if it did, its duration.
Among its findings, the study states that a prolonged increase in temperature and precipitation increases the probability of conflict beyond the affected area by four to five times, specifically in populations up to a radius of about 550 km.
The study also concludes that, in Africa, food shortages due to drought increase the possibility of conflict, especially if water shortages persist for at least three years. Conversely, excess rainfall triggers conflict, but in a very short period of time.
Implications for adaptative policies
“The results we have obtained have far-reaching implications for territorial policies on the African continent. For example, changes in climatic conditions influence the likelihood of conflict over large areas, which means that the design of climate adaptation policies must consider the particularities of each territory,” says Davide Consoli, a researcher at the INGENIO Institute and one of the authors of the study.
The INGENIO, University of Rome and University of Urbino team also points out that the persistence of violence requires the implementation of climate change adaptation strategies designed in combination with peacekeeping measures, especially in those areas most prone to armed conflict.
“These measures are essential in the design and implementation of adaptive strategies for climate resilience. In fact, poorly designed adaptation interventions can exacerbate existing inequalities and increase the risk of conflict,” concludes Consoli.
Journal
Economía y Política
DOI
10.1007/s40888-022-00271-x
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Climate change and armed conflicts in Africa: temporal persistence, non-linear climate impact and geographical spillovers
Article Publication Date
10-Jun-2022




