Sex differences exist in the regulation of energy homeostasis, the organism’s mechanism to keep a stable body weight. Current studies indicate for instance that female mammals, including humans, are better protected against metabolic diseases during reproductive age. This is particularly important with regard to obesity, a noncommunicable disease whose prevalence has tripled since 1975 according to the World Health Organization (WHO). However, it is still not fully understood how hormones, released by sex-specific reproductive glands, signal to the brain to regulate energy metabolism in females versus males. Researchers at Helmholtz Munich pursued the question and discovered a new protein called Cited1 within hypothalamic neurons that is involved in the regulation and sensitivity of satiety pathways. The results are now published in Cell Metabolism.
Credit: ©Cristina Garcia-Caceres
Sex differences exist in the regulation of energy homeostasis, the organism’s mechanism to keep a stable body weight. Current studies indicate for instance that female mammals, including humans, are better protected against metabolic diseases during reproductive age. This is particularly important with regard to obesity, a noncommunicable disease whose prevalence has tripled since 1975 according to the World Health Organization (WHO). However, it is still not fully understood how hormones, released by sex-specific reproductive glands, signal to the brain to regulate energy metabolism in females versus males. Researchers at Helmholtz Munich pursued the question and discovered a new protein called Cited1 within hypothalamic neurons that is involved in the regulation and sensitivity of satiety pathways. The results are now published in Cell Metabolism.
Obesity is a global health problem, due to its high prevalence and strong association with hypertension, coronary heart disease, stroke, and other metabolic disorders. In mammals, energy balance is maintained via a homeostatic system involving both peripheral and central systems – changes in body weight reflect an unbalanced energetic state. Studies confirmed that a clear sexual dimorphism exists in how the brain regulates energy homeostasis and in the resulting metabolic adaptation to diet-induced obesity.
Protective mechanisms of estrogens
There is growing evidence showing that postmenopausal females are more prone to develop obesity in comparison to premenopausal females. Multiple studies have established a link between the vulnerability to develop metabolic disturbances with reproductive decline. This suggests that estrogens, a category of sex hormones responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics, play a protective role in this context. The most important estrogen hormone in females, estradiol, thereby regulates energy homeostasis by altering feeding behavior. However, how this sex hormone mediates its anti-obesity actions is still largely unknown.
“Less satiety without Cited1”
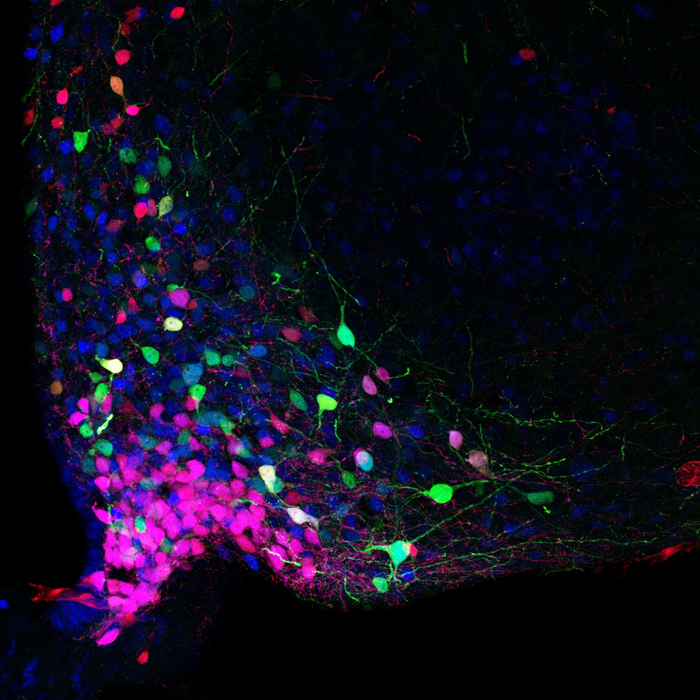
A research team led by Cristina García-Cáceres, Deputy Director and Head of the Astrocyte-Neuron Unit at the Institute for Diabetes and Obesity (IDO) of Helmholtz Munich, the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) and Professor at the Ludwig Maximilians University (LMU) Hospital Munich, has now discovered a novel protein named Cited1, that is highly enriched in estradiol-sensitive neurons of the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus, a part of the brain linking the endocrine and the nervous systems. The researchers discovered that this protein is essential for the integration of energy stores with reproductive signals for metabolic adaptation in diet-induced obesity. Using mouse models, the researchers observed that the absence of Cited1 in the hypothalamus of females weakens their capacity to respond adequately to satiety hormones such as leptin, to levels comparable with males, and thus increases their sensitivity to diet-induced obesity. This shows that Cited1 is involved in satiety signaling pathways of hypothalamic neurons, thereby contributing to the fine-tuning of food intake.
Sex differences in metabolic diseases
In this study, the researchers provide new insights that contribute to a better understanding of how neurons integrate endocrine inputs from gonadal and adipose axes via Cited1, thus contributing to the sexual dimorphism in diet-induced obesity. The study contributes to the understanding of sex differences in obesity pathogenesis and paves the way to new sex-specific anti-obesity drugs with fewer side effects to combat obesity. Further, it opens new avenues to study the role of Cited1 in the convergence of other potential neuroendocrine functions, such as puberty or growth.
Journal
Cell Metabolism
DOI
10.1016/j.cmet.2023.02.004
Article Title
Estradiol regulates leptin sensitivity to control feeding via hypothalamic Cited1
Article Publication Date
7-Mar-2023




