New method for generating the least accessible form of vicinal aminoalcohols; study published in ‘Nature Catalysis’
Credit: WWU – Glorius Group
Whether in beta-blockers to treat high blood pressure or in natural products: So-called vicinal aminoalcohols are high-quality organic compounds that are found in many everyday products. However, their production is difficult. For a long time, chemists are trying to develop efficient methods of synthesizing them. In their recent study published in the journal Nature Catalysis, scientists led by Prof. Dr. Frank Glorius of Münster University have found a solution for the production of a special variant of aminoalcohols. “The new method helps to study the properties of the substance and to find applications for these new compounds in the future”, emphasizes Frank Glorius from the Organic Chemistry Institute at Münster University.
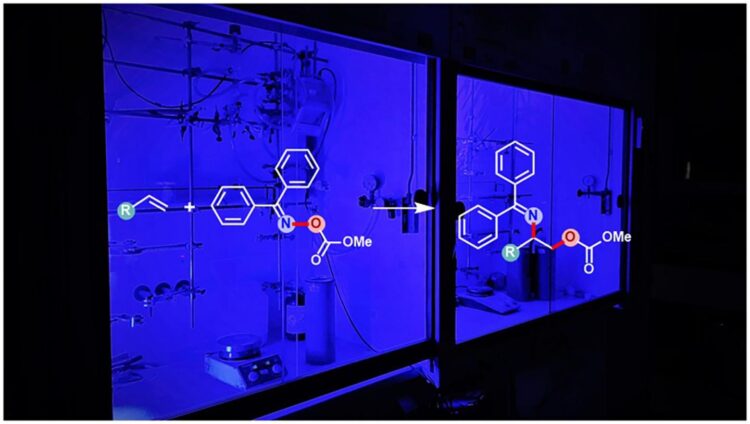
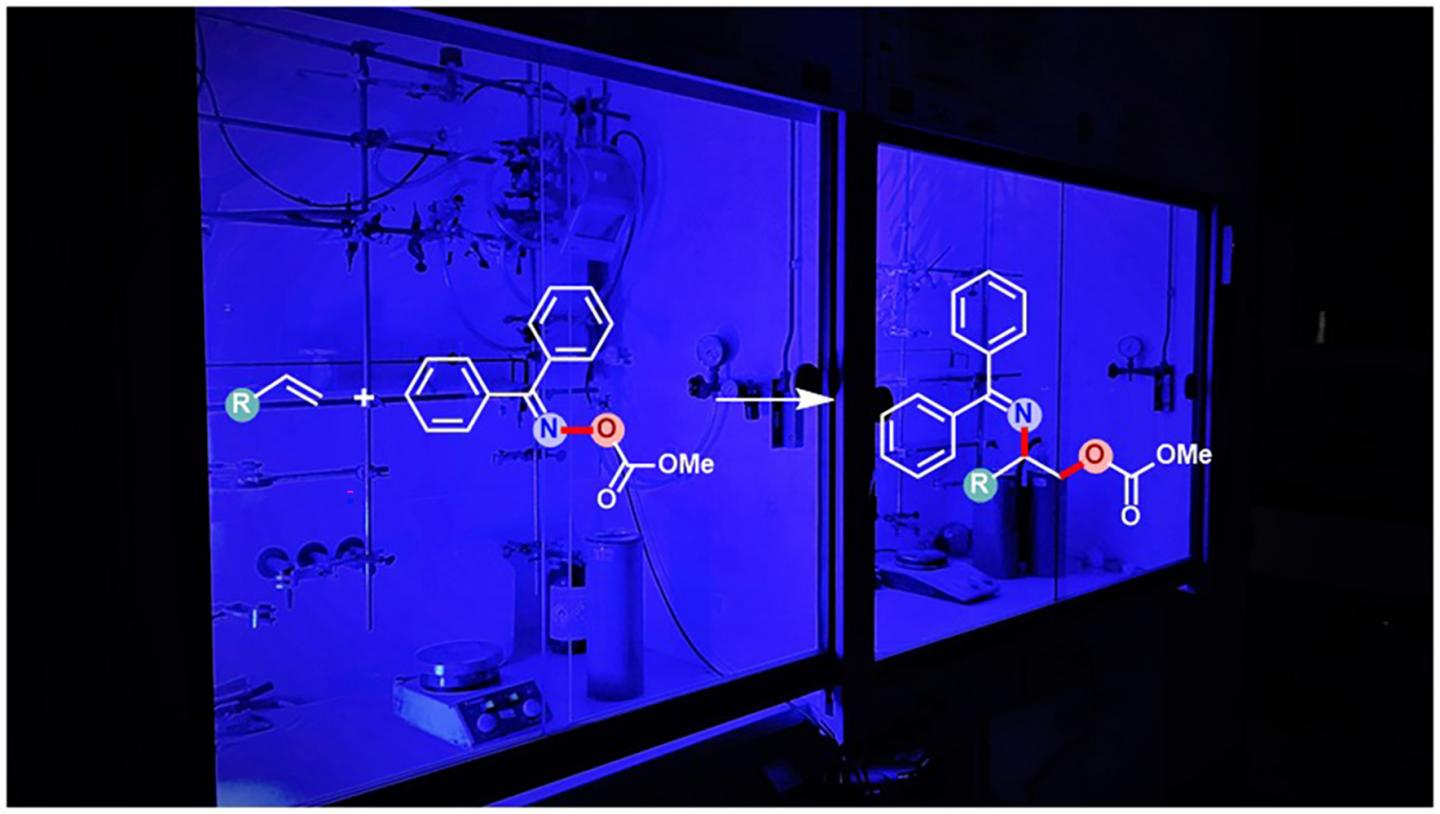
Vicinal aminoalcohols can occur in two different variants – called regioisomers – in which the amine and alcohol functional groups exchange positions. Although they are thus very similar, they often have different biochemical properties. Installation of both amine and alcohol groups in one step poses a major challenge. The discovery of the “Asymmetric Amino Hydroxylation Reaction” with which one of the regioisomers can be produced, even rewarded the chemist Barry Sharpless with a Nobel Prize in 2001. However, the other regioisomer cannot be synthesized by similar method and remained a long-standing problem – until now. With the help of the chemists’ new photo-initiated reaction method, the synthesis of the other regioisomer has now also become efficiently possible.
Background and method:
Unactivated alkenes containing a carbon-carbon double bond are known as feedstock chemicals for reaction processes due to their good availability. In general, the installation of both amine and alcohol groups in one step via this carbon-carbon double bond of unactivated alkene is at all times initiated by the amine group, followed by the addition of the alcohol group. As a result, always a particular regioisomer of the vicinal aminoalcohol is formed. Now the scientists have identified a particular class of amine-like compounds that are reactive yet stable enough to allow first the addition of the alcohol group to the carbon-carbon double bond, followed by the addition of the amine group to generate the previously inaccessible opposite regioisomer of the vicinal aminoalcohols.
“Like plants use chlorophyll to convert light into energy, we use what is called a photocatalyst”, explains Dr. Tuhin Patra, first author of this study. “This species can absorb the light from blue LEDs and transfer its energy into a molecule directly involved in the reaction. This simultaneously releases the amine and alcohol groups.” This process, in which the molecules transfer electrons to each other, is called energy transfer, the scientist explains.
Fascinatingly, the new method generates the least accessible regioisomer of the vicinal aminoalcohols in such a manner that both the alcohol and amine groups are protected from further reactions. Depending on the user’s needs, one of the two alcohol or amine groups can now be reactivated without affecting the other. However, even both groups can be enabled to react further at the same time, if that is necessary for the synthesis of further requirements. “Previous designs usually install only one group at a time in a complex multistep overall process. Our design not only allows the installation of two different groups in one step with desired protection, but also reliably generates the least accessible regioisomer, offering the chance to investigate future applications of this compound,” concludes Frank Glorius.
###
Original publication:
T. Patra, M. Das, C. Daniliuc, F. Glorius (2021): Metal-free, photosensitized oxyimination of unactivated alkenes with bifunctional oxime carbonates. Nature Catalysis; DOI: 10.1038/s41929-020-00553-2.
Media Contact
Prof. Dr. Frank Glorius
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.