Credit: Janak R. Joshi, Linxing Yao, Amy O. Charkowski, and Adam L. Heuberger
Potato is the most consumed vegetable crop worldwide. However, despite its importance, potato production is severely affected by high susceptibility to a wide range of microbial pathogens, such as bacteria from the genus Pectobacterium, which cause various devastating diseases in potato and produce important economic losses.
Even though resistance to Pectobacterium species is limited within cultivated potato varieties, it is known that a potato wild relative (S. chacoense) is resistant to them; however, until recently, the underlying mechanisms of this phenomenon remained unknown.
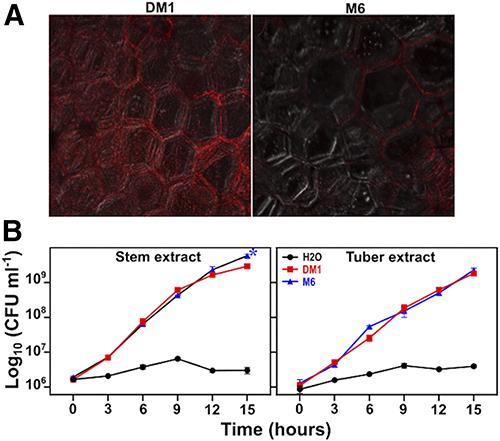
In a recent study published in the Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions (MPMI) journal, scientists from Colorado State University (CSU) revealed that metabolites from S. chacoense contribute to disease resistance by altering the pathogenic behavior of Pectobacterium brasiliense, rather than inhibiting its growth or killing it.
“We tested if chemicals extracted from the wild potato affect the behavior of the bacterium and found that these inhibited their ability to produce the enzymes that degrade plant cell walls. The chemicals also intercepted their ability to communicate with each other. To use a battle analogy, the wild potato plant chemicals intercepted the bacteria’s missiles, they cut off their radio communications, and together this encouraged the bacteria to remain friendly neighbors,” explained Adam Heuberger, a CSU Associate Professor involved in the research.
“This wild potato is also resistant to insects, viruses, and fungi. The question is always why, and then how, we can translate this information to improve society. There is much to learn by studying wild relatives of food and ornamental plants,” Heuberger added.
###
For more information about this research, read “Metabolites from Wild Potato Inhibit Virulence Factors of the Soft Rot and Blackleg Pathogen Pectobacterium brasiliense” published in MPMI in November.
Media Contact
Juan S. Ramirez-Prado
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




