The advance could lead to the development of stem cell-based therapies for muscle loss or damage due to injury, age or disease
Credit: UCLA Broad Stem Cell Research Center
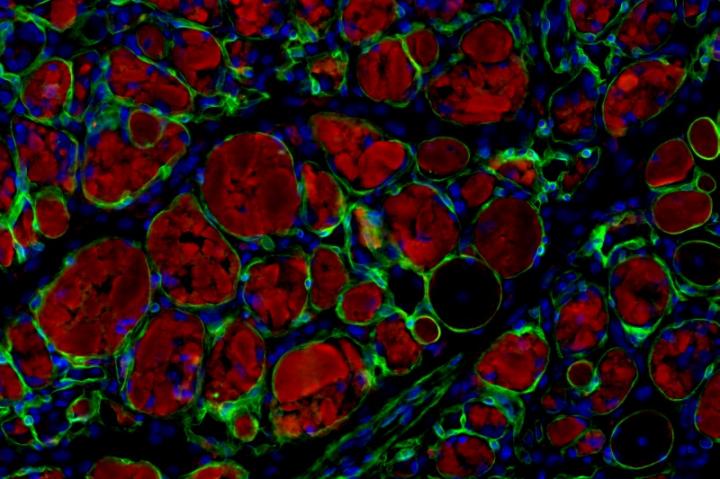
A UCLA-led research team has identified a chemical cocktail that enables the production of large numbers of muscle stem cells, which can self-renew and give rise to all types of skeletal muscle cells.
The advance could lead to the development of stem cell-based therapies for muscle loss or damage due to injury, age or disease. The research was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Muscle stem cells are responsible for muscle growth, repair and regeneration following injury throughout a person’s life. In fully grown adults, muscle stem cells are quiescent — they remain inactive until they are called to respond to injury by self-replicating and creating all of the cell types necessary to repair damaged tissue.
But that regenerative capacity decreases as people age; it also can be compromised by traumatic injuries and by genetic diseases such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
“Muscle stem cell-based therapies show a lot of promise for improving muscle regeneration, but current methods for generating patient-specific muscle stem cells can take months,” said Song Li, the study’s senior author and a member of the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA.
Li and his colleagues identified a chemical cocktail — a combination of the root extract forskolin and the small molecule RepSox — that can efficiently create large numbers of muscle stem cells within 10 days. In mouse studies, the researchers demonstrated two potential avenues by which the cocktail could be used as a therapy.
The first method uses cells found in the skin called dermal myogenic cells, which have the capacity to become muscle cells. The team discovered that treating dermal myogenic cells with the chemical cocktail drove them to produce large numbers of muscle stem cells, which could then be transplanted into injured tissue.
Li’s team tested that approach in three groups of mice with muscle injuries: adult (8-week-old) mice, elderly (18-month-old) mice and adult mice with a genetic mutation similar to the one that causes Duchenne in humans.
Four weeks after the cells were transplanted, the muscle stem cells had integrated into the damaged muscle and significantly improved muscle function in all three groups of mice.
For the second method, Li’s team used nanoparticles to deliver the chemical cocktail into damaged muscle tissue. The nanoparticles, which are about one one-hundredth the size of a grain of sand, are made of the same material as dissolvable surgical stitches, and they are designed to release the chemicals slowly as they break down.
The second approach also produced a robust repair response in all three types of mice. When injected into injured muscle, the nanoparticles migrated throughout the injured area and released the chemicals, which activated the quiescent muscle stem cells to begin dividing.
While both techniques were successful, the key benefit of the second one is that it eliminated the need for growing cells in the lab — all of the muscle stem cell activation and regeneration takes place inside the body.
The team was particularly surprised to find that the second method was effective even in elderly mice, in spite of the fact that as animals age, the environment that surrounds and supports muscle stem cells becomes less effective.
“Our chemical cocktail enabled muscle stem cells in elderly mice to overcome their adverse environment and launch a robust repair response,” said Li, who is also chair of bioengineering at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering and professor of medicine at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
In future studies, the research team will attempt to replicate the results in human cells and monitor the effects of the therapy in animals for a longer period. The experiments should help determine if either approach could be used as a one-time treatment for patients with serious injuries.
Li noted that neither approach would fix the genetic defect that causes Duchenne or other genetic muscular dystrophies. However, the team envisions that muscle stem cells generated from a healthy donor’s skin cells could be transplanted into a muscular dystrophy patient’s muscle — such as in the lungs — which could extend their lifespan and improve their quality of life.
###
In addition to Li, other UCLA contributors include assistant project scientist Jun Fang, professors James Tidball and Kym Faull, and research scientist Jennifer Soto. Scientists from UC Berkeley, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and National Cheng Kung University in Taiwan also contributed to the study.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the NIH under the Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award, the UCLA Broad Stem Cell Research Center Research Award Program and the UCLA Medical Scientist Training Program.
Media Contact
Tiare Dunlap
[email protected]




