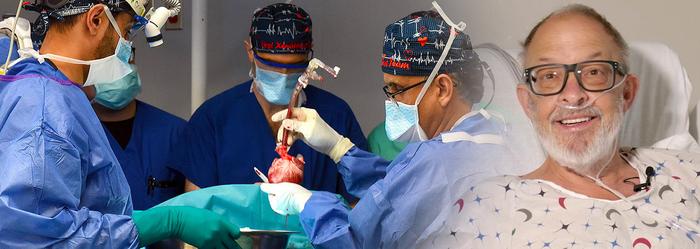
In a remarkable advancement for xenotransplantation, a surgical breakthrough at the University of Maryland Medical Center has showcased the potential for genetically-modified pig organs to save human lives. In 2023, Lawrence Faucette, a 58-year-old patient suffering from end-stage heart failure, became the second recipient globally of a pig heart, a groundbreaking procedure aimed at addressing the dire shortage of human organ donors. Despite the promising start and initial functionality of the transplant, Faucette lived for only 40 days post-surgery before the organ began to fail due to complications related to rejection.
The detailed report of Mr. Faucette’s case was recently published in the prestigious journal Nature Medicine. This study illuminated several critical insights gleaned from the xenotransplantation process and sets the stage for future clinical trials. Two weeks post-surgery, the medical team noticed initial signs of rejection in the 10 gene-edited pig heart during the first biopsy. This early detection is invaluable as it provides pivotal learning opportunities for researchers and surgeons working in this innovative area of medicine.
As the medical team monitored the performance of the pig heart, they recorded instances of excellent systolic and diastolic function during the initial weeks after the surgery, illustrating the organ’s capability to support human physiological needs well. However, the surge of anti-pig antibodies observed post-transplantation highlighted an area of concern, indicating the complexity of the immune response in xenotransplantation. This surge played a crucial role in the eventual graft failure, emphasizing the necessity for ongoing research focused on immunological compatibility and rejection mechanisms.
Researchers involved in the study acknowledge the significant hurdles presented by antibody-mediated rejection. The team’s findings suggest that even with a patient who presented low pre-existing anti-pig antibodies, unexpected immune reactions can lead to detrimental outcomes for the transplanted organ. This reality underlines the importance of exploring innovative strategies to manage and mitigate such immune responses in future xenotransplant procedures.
This case does not exist in isolation; rather, it is part of an expanding effort within the medical community to realize the potential of xenotransplantation as a realistic and effective solution to the organ shortage crisis impacting countless individuals worldwide. The team at the University of Maryland, alongside pharmaceutical partners and contributors, are steadfast in their commitment to refining xenotransplant methodologies, creating protocols that will improve outcomes for patients awaiting critical organ replacement.
In addition to the clinical insights gained, the emotional resilience displayed by patients such as Mr. Faucette carries significant weight in the world of xenotransplantation. The nobility of participating in such a transformative medical journey inspires hope and fosters a greater understanding of the human experience within the clinical landscape. This aspect of patient engagement is vital, as it not only drives motivation for scientific exploration but also fuels a collective aspiration towards enhancing the quality of life for individuals facing terminal medical conditions.
As research progresses, so too does the requirement for continued dialogue surrounding ethical considerations, patient selection processes, and the regulatory pathways necessary to bring these groundbreaking procedures to fruition on a larger scale. The shared mission among the scientific community is to ensure that advancements in xenotransplantation are met with both excitement and responsible oversight, prioritizing the welfare of patients while broadening the horizons of what modern medicine can achieve.
The overall assessment from the series of studies surrounding xenotransplantation, particularly those involving genetically-modified organs, reveals an optimistic yet cautious optimism for the future. While there is still a considerable journey ahead, the lessons learned from each patient case, including Mr. Faucette’s experience, are laying the groundwork for potential breakthroughs that could redefine organ transplantation on a global scale. The determination within the medical community to surmount the existing limitations is not just a professional endeavor but an ethical imperative driven by compassion for those in desperate need of life-sustaining treatments.
Thus, as the realm of xenotransplantation continues to evolve, it remains a beacon of hope for many, inviting not just scientific inquiry but also a deeper understanding of our interconnectedness as a society facing critical health challenges. Through continued innovation and shared purpose, the path forward may very well illuminate solutions that honor the essence of life itself.
Subject of Research: Xenotransplantation
Article Title: Transplantation of a genetically modified porcine heart into a live human
News Publication Date: 8-Jan-2025
Web References: Nature Medicine
References: 10.1038/s41591-024-03429-1
Image Credits: University of Maryland School of Medicine
Keywords: Xenotransplantation, organ donation, anti-pig antibodies, heart failure, genetically-modified organs, transplantation challenges.