Investigation of the complex mixture of chlorinated, brominated and mixed halogenated dibenzofurans and diphenyl ethers released from open e-waste burning in Ghana
Credit: Reprinted with permission from Environmental Science & Technology. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society.
A research team in Ehime University characterized the complex composition of chlorinated, brominated and mixed halogenated dioxins as well as their major precursors in soils from e-waste burning and dismantling areas in Agbogbloshie (Accra, Ghana), a major hub of informal e-waste processing in Africa. The findings were published on February 22, 2019 in Environmental Science & Technology.
E-waste, or Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE), refers to end-of-life products such as communication devices, consumer electronics and home appliances. E-waste contains substantial amounts of valuable metals to recycle, but is also considered as hazardous waste due to the presence of toxic substances such as heavy metals and many various plastic additives. A large volume of these hazardous waste materials has been recycled inappropriately, and treated informally in Asian and African developing countries using primitive methods such as circuit board heating and open burning of wires. These informal recycling activities have led to serious environmental pollution caused by the emission of not only contaminants contained in e-waste but also unintentionally formed secondary toxic chemicals.
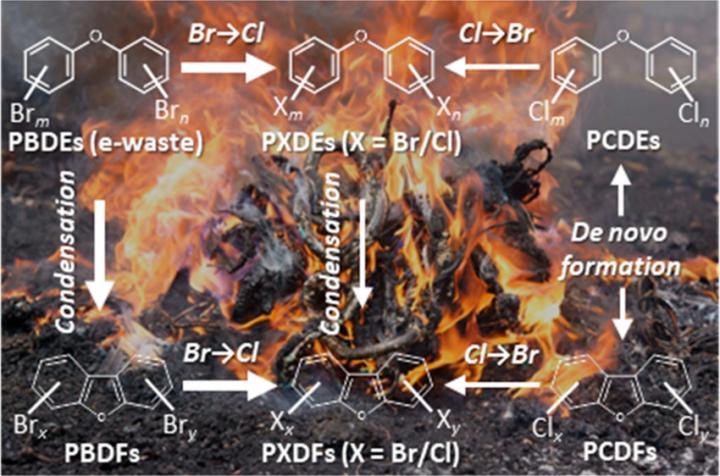
Dioxin-like compounds, or simply dioxins, are a group of unintentional contaminants generated during informal processing of e-waste with a wide range of potential toxic effects. However, assessment of the environmental and health impacts of dioxins from e-waste is challenging due to their complex composition. Chlorinated dioxins including polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans are combustion by-products of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) used in wire coating. Lesser-known brominated dioxins are thermal degradation products of brominated flame retardants (BFRs), which are plastic additives designed to prevent accidental fires. Mixed brominated/chlorinated dioxins are also generated during e-waste burning, but have not been well characterized because of the difficulties in analyzing their large number.
The research team in Ehime University used special analytical methods based on two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC×GC) and time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ToFMS) to conduct a comprehensive profiling of halogenated contaminants in the soils collected near e-waste burning and dismantling areas. Polybrominated and mixed halogenated dibenzofurans (PBDFs and PXDFs) were the major dioxins detected. Their composition profiles suggest that PBDFs were generated from polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), a group of flame retardants commonly found in e-waste plastics; and PXDFs mainly from PBDFs through successive bromine-to-clorine exchange. High concentrations of PXDFs in e-waste burning areas indicate that these “hidden” dioxins may contribute substantially to the total toxicity of the e-waste-derived dioxin mixture, and need to be included in future environmental and human exposure risk assessment.
###
Media Contact
Public Relations Division
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




