Credit: Ping-Hsiu Wu
Scientists have revealed the molecular mechanism regulating the trafficking of lysosomes that increases the invasiveness of radioresistant cancer cells following radiotherapy.
Radiotherapy is an effective and commonly used treatment for cancer. However, there are varieties of cancer that become resistant to these therapies, and in some cases, these radioresistant cancers can become more invasive following treatment, worsening the prognosis for the patient.
Scientists from the Global Center for Biomedical Science and Engineering, a collaboration between Hokkaido University, Japan, and Stanford University, USA, have revealed the mechanism by which molecules called Arl8b and BORC cause increased invasiveness and metastasis in radioresistant cancer cells following radiotherapy. Their results were published in the journal Communications Biology.
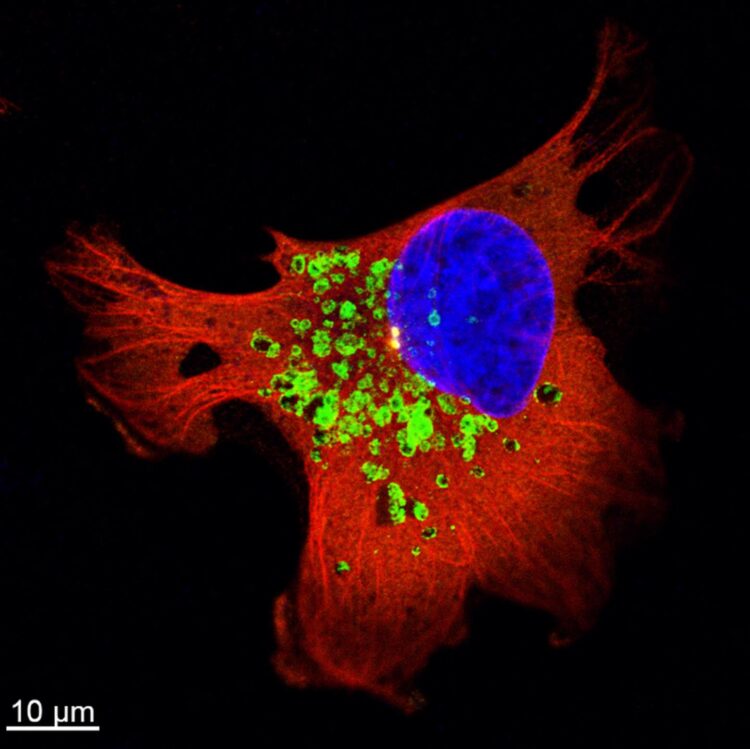
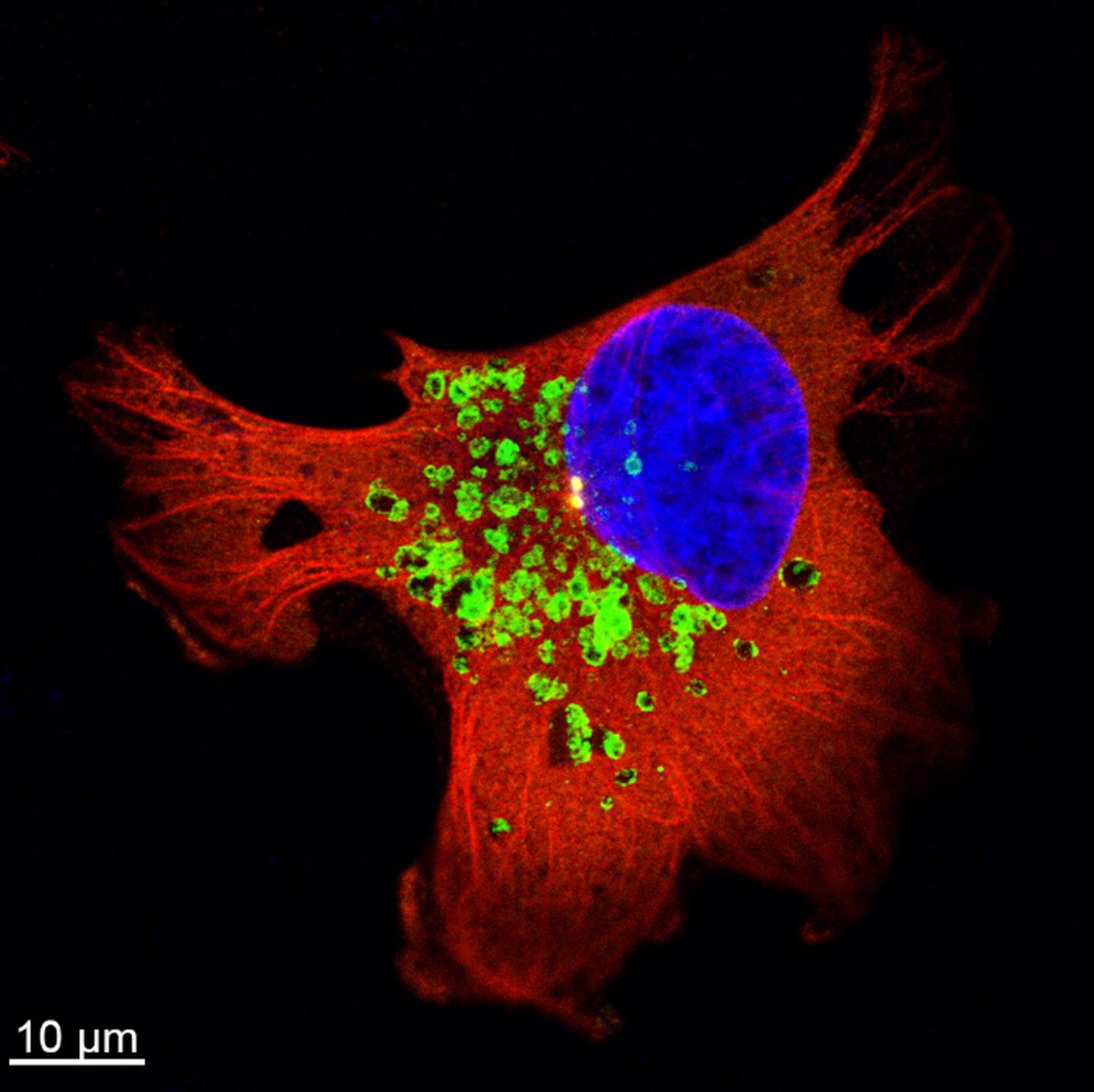
Previous work has shown that trafficking of vesicles inside cells plays an important role in cancer cell invasiveness. A type of vesicle called the lysosome is particularly significant. Lysosomes are renowned as the vesicles responsible for degradation of molecules, but they are also involved in secretion of molecules that work for cell adhesion, tumor invasion and metastasis. In the current work the scientists investigated the molecular basis for these roles in radioresistant breast cancer.
They first confirmed that the trafficking of lysosomes was upregulated in the cancer cells following radiotherapy, enhancing the secretion of enzymes that degrade the connective material surrounding them, and therefore increasing invasiveness of the cancer cells. They further investigated the molecular mechanisms behind this activity and determined that a regulatory molecule, Arl8b, is primarily responsible for this process.
The active form of Arl8b is normally responsible for the trafficking of lysosomes within a cell. The scientists observed that in radioresistant cancer cells, the active form of Arl8b increases following radiotherapy, allowing it to interact with other molecules to enhance lysosome trafficking. Further, by knockdown of Arl8b, the scientists showed that this molecule was required for the increase of invasiveness and metastasis.
The researchers analysed data on breast cancer patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to identify other molecules that may be involved. They found that, in addition to Arl8b levels, prognosis can be correlated with levels of a group of proteins called BORC complex, which is composed of eight subunits. High Arl8b levels correlated with poor prognosis; further, the prognosis could be stratified based on the levels of different BORC subunits. BORC is required for the association of Arl8b and lysosomes. The scientists showed that certain BORC subunits are required for the increased invasiveness of radioresistant cancer cells mediated by Arl8b; in addition, radiotherapy also upregulates genes responsible for the expression of certain BORC subunits.
In this study, the scientists uncovered the effect of radiotherapy on the lysosomal trafficking and some of the molecules controlling this process. Having elucidated the molecular basis for this mechanism, a larger dataset from human cancer patients must be analysed to validate the findings. Further, drugs that target this mechanism must be developed and evaluated as cancer therapies.
Dr. Jin-Min Nam and Dr. Yasuhito Onodera are part of the Radiation Biology group at the Global Center for Biomedical Science and Engineering (GCB), a collaboration between Hokkaido University, Japan, and Stanford University, USA. The group specializes in molecular and cellular oncology, and radiation biology.
###
Media Contact
Sohail Keegan Pinto
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.