Credit: Kanazawa University
[Background]
The environmental context in which addicts experience the rewarding effects of cocaine can readily elicit cocaine-associated memories. These memories persist long after abstinence and trigger cocaine-craving and consumption. Thus, understanding the neuronal mechanisms underlying the formation and retrieval of cocaine-associated memories is critical for developing treatment for cocaine addiction. The medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), a brain region associated with recognition, working memory and attention, has been suggested to play a critical role in drug addiction. Lesions to the mPFC disrupt cocaine-associated memories; however, it is unclear whether the mPFC is associated with the formation and/or retrieval of cocaine-associated memories. Thus, inactivation of the mPFC at specific times, either during the memory formation or retrieval phase, is necessary to address the distinct roles of the mPFC. Likewise, inactivation of specific mPFC cell types will permit elucidation of the role of discrete neuronal subpopulations (for example, mPFC glutamatergic pyramidal or GABAergic neurons) in the development of cocaine-associated memories. However, because of technical limitations, causal relationships between neuronal activity and memory formation/retrieval remain unclear.
[Results]
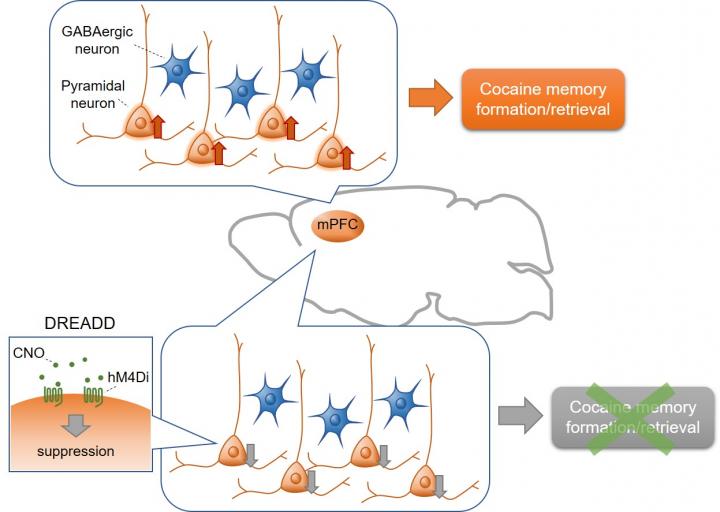
The present study was conducted by a collaboration of researchers from Kanazawa, Hokkaido, Okayama, Niigata, Nagoya, Tsukuba, and Kyoto Universities, Japan. The experiments were performed at Kanazawa University.The study employed a cocaine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) test, a Pavlovian conditioning paradigm, combined with ‘designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs’ (DREADD) technology. The CPP test involves administration of cocaine to animals in a specific context; the animals learn to associate the rewarding properties of cocaine with this context, resulting in the formation of cocaine-associated memories. In the test, the animals retrieve the cocaine-associated memory when placed in the cocaine-administered context and exhibit preference for the context. Wild-type C57BL/6J mice received bilateral intra-mPFC infusion of an adeno-associated virus (AAV) expressing inhibitory DREADD (hM4Di) under control of the CaMKII promotor to selectively suppress mPFC glutamatergic pyramidal neurons. GAD67-Cre mice received bilateral intra-mPFC infusion of a Cre-dependent AAV expressing hM4Di to specifically silence GABAergic neurons. hM4Di is an artificial receptor that is selectively activated by clozapine N-oxide (CNO), which leads to inhibition of neurons expressing hM4Di. Chemogenetic suppression of mPFC glutamatergic pyramidal neurons by injecting CNO significantly attenuated both the acquisition and expression of cocaine CPP. In contrast, suppression of mPFC GABAergic neurons affected neither the acquisition nor expression of cocaine CPP.
[Significance and future prospects]
The present study demonstrates that the chemogenetic suppression of mPFC glutamatergic, but not GABAergic, neurons inhibits both the acquisition and expression of cocaine CPP. To our knowledge, this is the first direct evidence showing that activation of glutamatergic pyramidal neurons in the mPFC is causally involved in both the formation and retrieval of cocaine-associated memories. Therefore, mPFC pyramidal neurons are a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of drug addiction.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




