Credit: Beth Roskilly
MISSOULA – Slow-growing ponderosa pines may have a better chance of surviving longer than fast-growing ones, especially as climate change increases the frequency and intensity of drought, according to new research from the University of Montana.
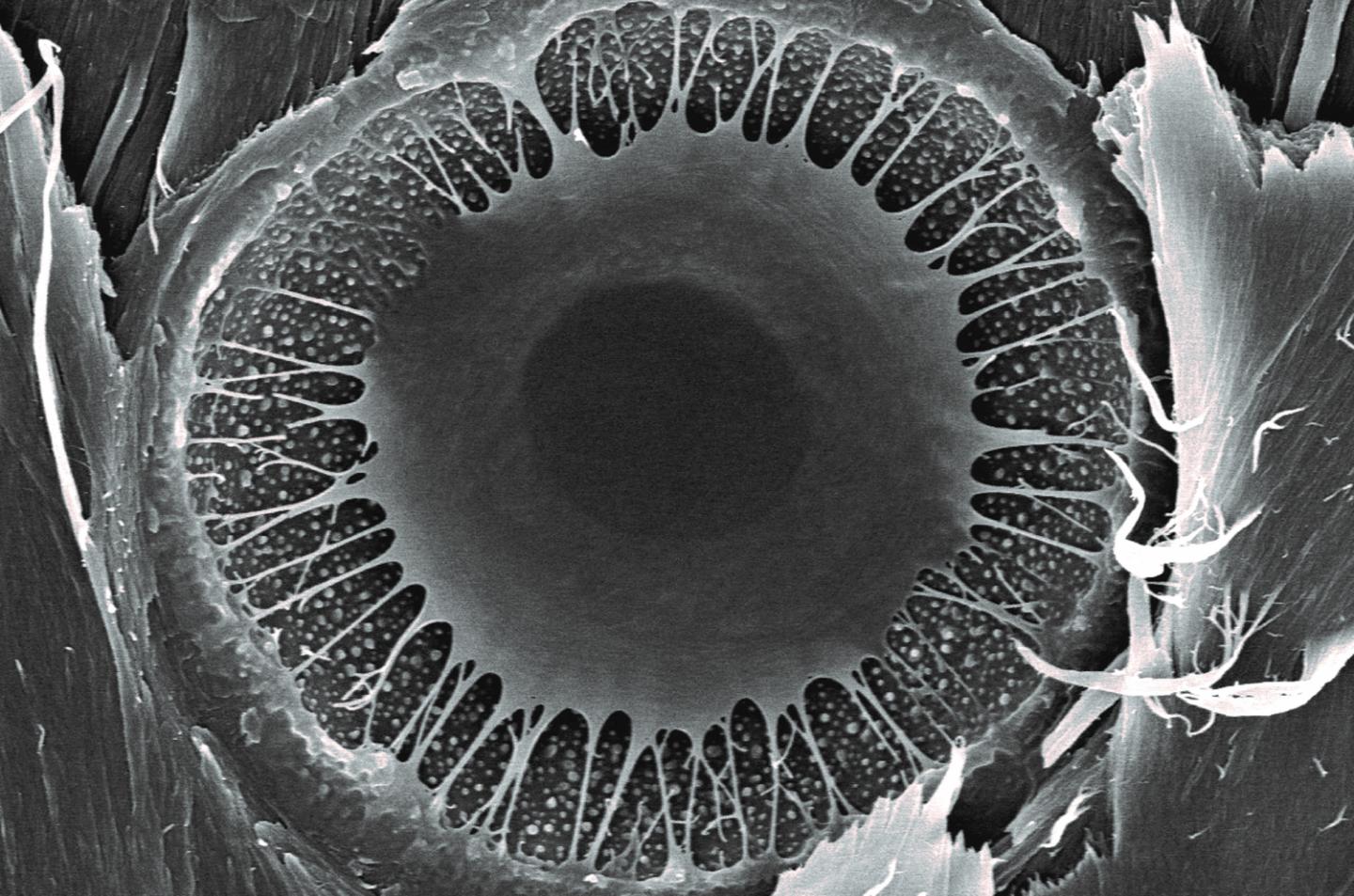
Researchers found that ponderosa longevity might hinge on the shape of microscopic valve-like structures between the cells that transport water through the tree.
The study, led by UM alumna Beth Roskilly and Professor Anna Sala, was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences this week. The researchers sampled growth rates of ponderosa pine trees of varying ages at two remote sites in Idaho. They also studied structural traits of the trees’ xylem – vascular tissue that transports water and minerals through the wood and provides structural support.
Their findings reveal that some young trees grow quickly while others grow slowly. But old ponderosa pine trees – those older than 350 years – are slow growers compared to younger trees, and these individual trees have always been slow growing, even when they were young.
In contrast to predictions, slow-growing trees, whether old or young, did not produce denser, tougher wood, which might have made the trees more resistant to disease or decay. Instead, a key difference between fast and slow growers resides in a microscopic valve-like structure between the cells that transport water in the wood, called the pit membrane. The unique shape of this valve in slow-growing trees provides greater safety against drought, but it slows down water transport, limiting growth rate.
“Ponderosa pines, like people, cannot have it all,” said Roskilly, the paper’s lead author. “Drought resistance contributes to longevity but also to slow growth. In other words, there is a fundamental tradeoff based on xylem structure. Our study suggests that trees with fast growth become large quickly, which can be beneficial for young trees competing for resources, but they are more vulnerable to drought and can die at earlier ages. On the other hand, trees that grow slowly are more drought resistant, which enhances longevity.”
Roskilly earned her UM master’s degree in organismal biology, ecology and evolution in 2018, and the study is a result of her degree work in UM’s College of Humanities and Sciences.
“Ancient trees are special for many reasons,” said Sala, a professor in UM’s Division of Biological Sciences and an adjunct professor in the W.A. Franke College of Forestry and Conservation. “They are beautiful, they make the highest quality musical instruments, they help maintain diversity, and they store atmospheric carbon in wood for a long time. But the results of this research also suggest they are special because forest managers cannot make just any ponderosa pine tree live for centuries no matter how hard they try. For ponderosa pines to become centennials, their wood must possess this unique structure.”
###
Other co-authors in the study include UM alumnus Eric Keeling, a professor at the State University of New York; UM alumna Sharon Hood, a research ecologist with the U.S. Forest Service; and Arnaud Giuggiola, a former visiting master’s student from the University of Bordeaux. This project built on dissertation work by Keeling and began as an undergraduate research project started by Roskilly.
The article, “Conflicting functional effects of xylem pit structure relate to the growth-longevity trade-off in a conifer species” can be accessed online at http://bit.
Media Contact
Anna Sala
[email protected]
Original Source
http://bit.




