Tumors are composed of rapidly multiplying cancer cells. Understanding which biochemical processes fuel their relentless growth can provide hints at therapeutic targets.
Credit: Patti lab, Washington University in St. Louis: Nature Communications
Tumors are composed of rapidly multiplying cancer cells. Understanding which biochemical processes fuel their relentless growth can provide hints at therapeutic targets.
Researchers from Washington University in St. Louis have developed a technology to study tumor growth in another dimension — literally. The scientists established a new method to watch what nutrients are used at which rates spatially throughout a tissue.
By using this multidimensional imaging approach, they identified pathways whose activities are uniquely elevated in brain cancer, offering clues for potential treatment strategies. The study was published May 19 in Nature Communications.
“We figured out how to infer the rate of biochemical reactions directly from discrete regions of tissue,” said Gary Patti, the Michael and Tana Powell Professor of Chemistry in Arts & Sciences and a professor of medicine at the School of Medicine. Patti, who is also a research member of the Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine, is senior author of the new study.
Human biology is intrinsically 3D in nature. The emerging field of spatial biology aims to capture this geometry by imaging the locations of genes, proteins and metabolites. The approach reported by Patti and colleagues extends spatial profiling to fluxes, the rates at which molecules are transformed inside of cells.
“Other technologies provide what is essentially a roadmap of biochemistry. Our goal was to add in a measurement of how fast traffic is flowing on the different roads,” Patti said.
By Patti’s analogy, the new method is akin to the feature in Google Maps that uses green and red colors to indicate the density of cars on a given street.
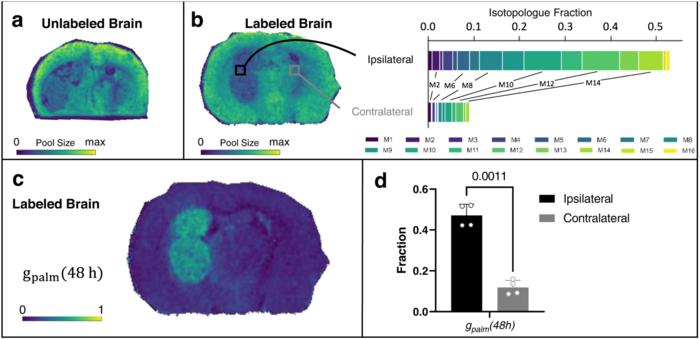
Using a mouse model of glioblastoma, a deadly form of brain cancer in humans, the researchers created a high-resolution map of the “tumor ecosystem.” This allowed them to tell which molecules were located in what parts of the brain and how quickly those molecules were turning into other things.
The results shed light on how cancer cells in a brain tumor get lipids, a basic component of fat.
Lipids are required to make the outermost covering of a cell, known as a membrane. As cancer cells multiply, they need lipids to encase the new cells. Previous work from Patti had shown that cancer cells prefer to scavenge lipids from their local environments. But that was when cancer cells were cultured in isolation with lipids present in the media.
The new study showed that cancer cells in the brain tend to make, rather than siphon off, the lipids that they need to multiply.
“The brain is a unique environment. The availability of lipids is more limited than in other tissues where tumors reside,” Patti explained.
The speed at which some lipids were synthesized was as much as 8-fold higher in brain tumors compared with surrounding healthy tissue. Although the exact magnitude of the increase varied, the pattern was surprisingly consistent in cancer cells throughout the tumor.
“A single tumor can span multiple different environments. The center might be hypoxic, while the outside is in contact with healthy tissue,” Patti said. “You might have predicted differences between these different regions, but we didn’t observe any patterns like that.”
This finding is important because knowing that cancer cells within brain tumors rely on the same biochemical pathway to fuel their growth means that scientists could target it to slow or stop disease progression.
“When a pathway is more active, its flux goes up. That makes it a good candidate for therapeutic intervention,” Patti said. “We are excited about testing whether impairment of fatty acid elongation will be effective in treating mouse models of disease.”
—
Schwaiger-Haber, M., Stancliffe, E., Anbukumar, D.S. et al. Using mass spectrometry imaging to map fluxes quantitatively in the tumor ecosystem. Nat Commun 14, 2876 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38403-x
This study was funded in part by the McDonnell Center for Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, as well as the National Institutes of Health grants R24 OD024624 and R35 ES2028365.
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-023-38403-x
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Using mass spectrometry imaging to map fluxes quantitatively in the tumor ecosystem
Article Publication Date
19-May-2023




