Grown in labs, human brain organoids are cultivated from stem cells, feed on nutrient broth and serve as a model of human brain development in miniature. Their growth and structure mimic portions of real brains, allowing scientists to better investigate the origins and potential treatments of neural diseases. How similar are they to actual human brains, though? Are they close enough to be considered people in their own right?
Credit: LAIMAN-ARIGA/Kyoto University the Institute for the Advanced Study of Human Biology
Grown in labs, human brain organoids are cultivated from stem cells, feed on nutrient broth and serve as a model of human brain development in miniature. Their growth and structure mimic portions of real brains, allowing scientists to better investigate the origins and potential treatments of neural diseases. How similar are they to actual human brains, though? Are they close enough to be considered people in their own right?
The question is complicated in myriad ethical and moral ways, but researchers based in Japan and Taiwan propose that the legal lens may prove critical when understanding the potential personhood of human brain organoids.
They published their argument for a legal framework to guide the conversation on April 3 in the Journal of Law and Biosciences.
“The moral status of human brain organoids has often been discussed, but their legal status has rarely been discussed,” said corresponding author Tsutomu Sawai, associate professor in the Graduate School of Humanities and Social Sciences at Hiroshima University. “To clarify the legal status of human brain organoids will illuminate issues such as what information should be informed to the cell donor, to what extent the donor’s consent justifies the research, and what uses are acceptable.”
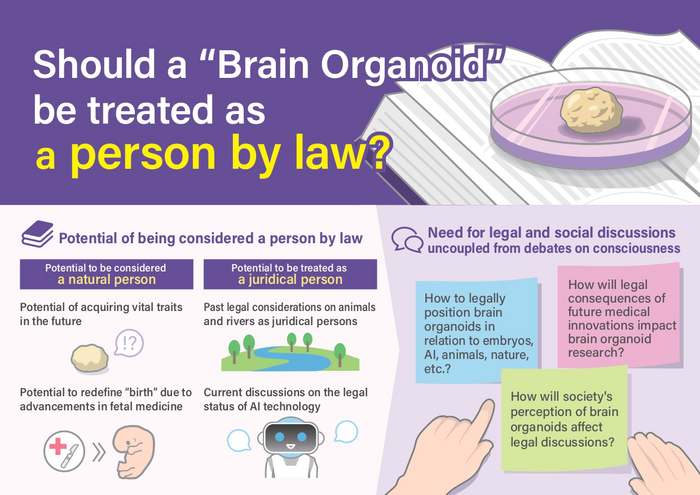
Legal person refers to any entity that holds legal rights and obligations — it can be human or not, according to Sawai. Human legal persons are called natural persons, and they are defined by being born of a womb and whether they can be considered legal dead once their heart or brain stops working. Nonhuman legal persons are called juridical persons and can include corporations and governmental agencies.
In their paper, Sawai and his team explore how the legal definition of what it means to be a natural or a juridical person applies to human brain organoids. Currently, the organoids do not fulfill basic requirements of what it means to be a natural person, Sawai said, but research may bridge the existing gaps.
“Although human brain organoids do not constitute natural persons at present, the likelihood of their potential to become natural persons in the near future requires more thorough consideration in advance of that reality occurring,” said first author Masanori Kataoka, researcher in Hiroshima University’s Graduate School of Humanities and Social Sciences. “Research on linking human brain organoids with bodies is expected to advance rapidly in the coming years, whereas the conditions of natural personhood, especially viability and birth are becoming increasingly flexible and contentious.”
The researchers noted that previous discussions on this topic have focused almost exclusively on natural personhood, overshadowing questions about the potential juridical personhood of human brain organoids. Corporations, for example, are considered juridical persons so that they can participate in legal matters, such as entering contracts. According to Kataoka, whether this applies to human brain organoids would depend on what legal purposes such consideration may have, and the matter should be considered separately from whether they are natural persons.
“Current brain organoid technology is in many ways quite limited, and it has not yet reached a stage where human brain organoids could become natural or juridical persons,” Sawai said. “However, as we have emphasized, this issue will soon become urgent once brain organoid technology has been further developed. In preparation for that time, it is essential to examine the accompanying questions thoroughly and in advance; we have taken the first step in that direction.”
##
Sawai is also affiliated with Kyoto University’s Institute for the Advanced Study of Human Biology. Tsung-Ling Lee with Taipei Medical University’s Graduate Institute of Health and Biotechnology Law also co-authored this paper.
The Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Uehiro Foundation, the Mitsubishi Foundation, the Japan Science and Technology’s Research Institute of Science and Technology for Society funded this work.
About Hiroshima University
Since its foundation in 1949, Hiroshima University has striven to become one of the most prominent and comprehensive universities in Japan for the promotion and development of scholarship and education. Consisting of 12 schools for undergraduate level and 5 graduate schools, ranging from natural sciences to humanities and social sciences, the university has grown into one of the most distinguished comprehensive research universities in Japan. English website: https://www.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/en
Journal
Journal of Law and the Biosciences
DOI
10.1093/jlb/lsad007
Article Title
The legal personhood of human brain organoids
Article Publication Date
3-Apr-2023




