“Macromolecules but also quantum dots, which often consist of thousands of atoms, can hardly be calculated in advance using conventional methods such as DFT,” says PD Dr. Annika Bande at HZB. With her team she has now investigated how the computing time can be shortened by using methods from artificial intelligence.
Credit: K. Singh, A. Bande/HZB
“Macromolecules but also quantum dots, which often consist of thousands of atoms, can hardly be calculated in advance using conventional methods such as DFT,” says PD Dr. Annika Bande at HZB. With her team she has now investigated how the computing time can be shortened by using methods from artificial intelligence.
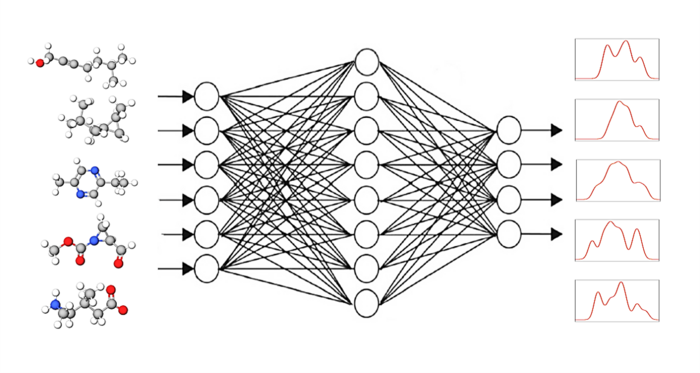
The idea: a computer programme from the group of “graphical neural networks” or GNN receives small molecules as input with the task of determining their spectral responses. In the next step, the GNN programme compares the calculated spectra with the known target spectra (DFT or experimental) and corrects the calculation path accordingly. Round after round, the result becomes better. The GNN programme thus learns on its own how to calculate spectra reliably with the help of known spectra.
“We have trained five newer GNNs and found that enormous improvements can be achieved with one of them, the SchNet model: The accuracy increases by 20% and this is done in a fraction of the computation time,” says first author Kanishka Singh. Singh participates in the HEIBRiDS graduate school and is supervised by two experts from different backgrounds: computer science expert Prof. Ulf Leser from Humboldt University Berlin and theoretical chemist Annika Bande.
“Recently developed GNN frameworks could do even better,” she says. “And the demand is very high. We therefore want to strengthen this line of research and are planning to create a new postdoctoral position for it from summer onwards as part of the Helmholtz project “eXplainable Artificial Intelligence for X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy”.”
Annotation:
The work was carried out within the framework of the HEIBRiDS graduate school and is being supported by the Helmholtz project “eXplainable Artificial Intelligence for X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy” (XAI-4-XAS).
The core of the project is to extend GNN, as used at HZB, to very large molecules in combination with the probabilistic analysis of molecular motifs developed at HEREON. It is used to capture only the relevant part of the configuration phase space of the molecules, which is necessary for the accurate prediction of X-ray spectra. The results of the ML predictions allow a rigorous interpretation of XAS experiments, so that characteristic parts of the spectrum of an extended material can be assigned 1:1 to its specific structural subgroups.
Journal
Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation
DOI
10.1021/acs.jctc.2c00255
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Graph Neural Networks for Learning Molecular Excitation Spectra
Article Publication Date
6-Jun-2022
COI Statement
none




