Credit: EPFL
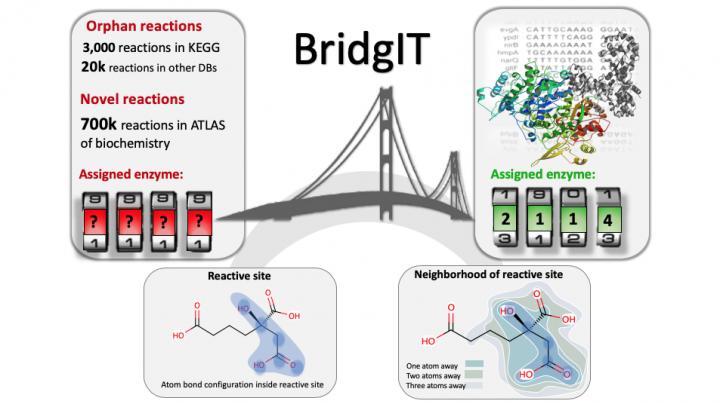
Effective protein engineering can give us control over the generated products inside a cell. However, for many of the biochemical reactions responsible for these products, we don’t we don’t know the specific protein- or enzyme-producing gene responsible. These reactions are called “orphan” and have become a big problem for protein engineers.
Moreover, software that predicts novel, hypothetical biochemical reactions – a common tool for modern biochemists and synthetic biologists – cannot assign potential genes to them, meaning that there are no recorded DNA sequences that scientists can tweak to change protein or enzyme production. And to further complicate matters, there are also many “orphan” metabolic enzymes whose particular reaction is unknown, thus leaving important gaps in our maps of metabolic networks and pathways.
In short, finding which gene(s) correspond to the enzyme/protein(s) that catalyze an orphan or novel, hypothetical reaction has grown into a critical issue for applications ranging from biotechnology to medicine.
Fortunately, chemical engineers from the lab of Vassily Hatzimanikatis at EPFL have found a solution. The group developed a new computational method and online tool, called “BridgIT”, to identify candidate genes and catalyzing proteins for orphan and novel, hypothetical reactions. All BridgIT needs to know is the four connecting bonds around the atoms of the reactive sites, and it can correctly annotate proteins for 93% of analyzed enzymatic reactions. This percentage rose to almost 100% when seven connecting bonds were included.
To test BridgIT’s accuracy, the researchers pitted it against databases of reactions that were once orphan but have now been assigned to genes and enzymes – basically, reactions that have become “non-orphan”. BridgIT predicted the exact or a highly related enzyme for 211 out of 234 reactions (>90%). And for hypothetical reactions that were once novel and have since been assigned enzymes, BridgIT found the exact enzymes for 334 out of 379 reactions (>88%).
The authors write: “BridgIT… will allow researchers to fill the knowledge gaps in metabolic networks and will act as a starting point for designing novel enzymes to catalyze non-natural transformations.”
###
Reference
Noushin Hadadi, Homa Mohammadi Peyhani, Ljubisa Miskovic, Marianne Seijo, Vassily Hatzimanikatis. PNAS 25 March 2019. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1818877116
Media Contact
Nik Papageorgiou
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




