A new method for sport and music training
Credit: National Institute of Information and Communications Technology
Highlights
- The dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) causes motor performance deterioration due to anxiety
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the dACC reduces the performance deterioration
- This method could potentially be used to help athletes and musicians overcome anxiety
Abstract
Researchers in the Center for Information and Neural Networks (CiNet), the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT, President: Hideyuki Tokuda, Ph.D.), Japan and the Centre national de la recherché scientifique (CNRS), France used fMRI to discover a new neural mechanism involving the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) to explain how anxiety deteriorates physical performance. Moreover, the performance deterioration was rescued by suppressing brain activity with transcranial magnetic stimulation to the dACC. The findings would provide a new therapeutic strategy for athletes, musicians and other performers susceptible to anxiety during performance. The paper was published online in Nature Communications on September 19, 2019.
Background
Athletes, musicians and other performers, be they professionals or amateurs, are required to conduct rapid complex movements that can be affected by anxiety. Influential self-focus theory postulates that the motor skills required for these actions become automatic and unconscious during learning, but anxiety causes an interference between conscious and unconscious processing that can negatively impact the performance. However, no behavioral or brain data has confirmed the theory. Such data would provide therapeutic targets that negate the effects of anxiety on motor performances.
Achievements
Principle Investigator Masahiko Haruno (NICT), with Dr. Gowrishankar Ganesh (CNRS) and Dr. Takehiro Minamoto (Shimane University) conducted fMRI by designing a novel behavioral task and found a correlation between activity in the dACC and the motor performance deterioration due to anxiety. The application of TMS to suppress dACC activity rescued the deterioration, providing the first direct evidence that suppressing anxiety-stimulated regions could reduce performance deterioration.
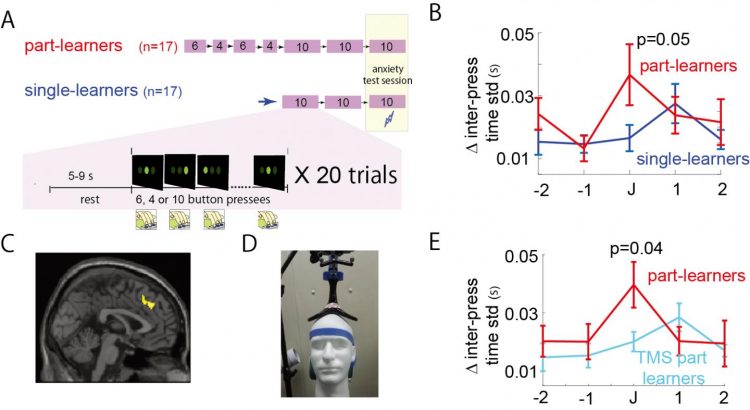
In general, specific motor skills, such as those used in tennis or playing the piano, require repeated practice to memorize the motions and their order. In the new study, the researchers simulated this practice on a computerized 10-step rapid button press task. Part-learners learned the task in two parts, one 6 steps long and the other 4 steps long. Finally, they practiced all 10 steps at once. Single-learners, on the other hand, learned the 10-step rapid button presses together without breaking them into parts. After the learning, both groups of learners were asked to conduct the entire 10-step task and given an electrical shock if they made a mistake during the performance (Fig. 1A, anxiety test session).
Part-learners proved more adept at learning the task in the training sessions based on the speed and number of errors with which they completed the task. However, when the anxiety test session started, their performance dropped noticeably to a level worse than single-learners (Fig. 1B, J represents the junction of the two parts). This finding is consistent with the self-focus theory, which would expect performance to decline with anxiety.
fMRI revealed that the part-learners showed increased activity of the dACC at the time of the junction in the test session (Fig. 1C). Applying TMS to this region for 5 minutes (1 Hz) prior to the test session (Fig. 1D) eliminated the performance degradation in part-learners (Fig. 1E). On the other hand, part-learners who received sham TMS did not show improvement.
These experiments show for the first time the brain region responsible for performance degradation caused by anxiety and a possible therapeutic strategy using TMS.
Future research
In addition to more study of the dACC neural circuits that connect anxiety to performance degradation, the group will investigate how TMS can enhance the performance of athletes, musicians and other performers.
###
Media Contact
Sachiko Hirota
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.