University of Arizona doctoral degree candidate Jay Sanguinetti has authored a new study, published online in the journal Psychological Science, that indicates that the brain processes and understands visual input that we may never consciously perceive.
The finding challenges currently accepted models about how the brain processes visual information.
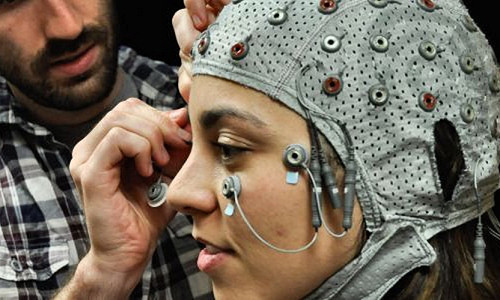
A doctoral candidate in the UA’s Department of Psychology in the College of Science, Sanguinetti showed study participants a series of black silhouettes, some of which contained meaningful, real-world objects hidden in the white spaces on the outsides. Saguinetti worked with his adviser Mary Peterson, a professor of psychology and director of the UA’s Cognitive Science Program, and with John Allen, a UA Distinguished Professor of psychology, cognitive science and neuroscience, to monitor subjects’ brainwaves with an electroencephalogram, or EEG, while they viewed the objects.
“We were asking the question of whether the brain was processing the meaning of the objects that are on the outside of these silhouettes,” Sanguinetti said. “The specific question was, ‘Does the brain process those hidden shapes to the level of meaning, even when the subject doesn’t consciously see them?”
The answer, Sanguinetti’s data indicates, is yes.
Study participants’ brainwaves indicated that even if a person never consciously recognized the shapes on the outside of the image, their brains still processed those shapes to the level of understanding their meaning.
“There’s a brain signature for meaningful processing,” Sanguinetti said. A peak in the averaged brainwaves called N400 indicates that the brain has recognized an object and associated it with a particular meaning.
“It happens about 400 milliseconds after the image is shown, less than a half a second,” said Peterson. “As one looks at brainwaves, they’re undulating above a baseline axis and below that axis. The negative ones below the axis are called N and positive ones above the axis are called P, so N400 means it’s a negative waveform that happens approximately 400 milliseconds after the image is shown.”
The presence of the N400 peak indicates that subjects’ brains recognize the meaning of the shapes on the outside of the figure.
“The participants in our experiments don’t see those shapes on the outside; nonetheless, the brain signature tells us that they have processed the meaning of those shapes,” said Peterson. “But the brain rejects them as interpretations, and if it rejects the shapes from conscious perception, then you won’t have any awareness of them.”
“We also have novel silhouettes as experimental controls,” Sanguinetti said. “These are novel black shapes in the middle and nothing meaningful on the outside.”
The N400 waveform does not appear on the EEG of subjects when they are seeing truly novel silhouettes, without images of any real-world objects, indicating that the brain does not recognize a meaningful object in the image.
“This is huge,” Peterson said. “We have neural evidence that the brain is processing the shape and its meaning of the hidden images in the silhouettes we showed to participants in our study.”
The finding leads to the question of why the brain would process the meaning of a shape when a person is ultimately not going to perceive it, Sanguinetti said.
“The traditional opinion in vision research is that this would be wasteful in terms of resources,” he explained. “If you’re not going to ultimately see the object on the outside why would the brain waste all these processing resources and process that image up to the level of meaning?”
“Many, many theorists assume that because it takes a lot of energy for brain processing, that the brain is only going to spend time processing what you’re ultimately going to perceive,” added Peterson. “But in fact the brain is deciding what you’re going to perceive, and it’s processing all of the information and then it’s determining what’s the best interpretation.”
“This is a window into what the brain is doing all the time,” Peterson said. “It’s always sifting through a variety of possibilities and finding the best interpretation for what’s out there. And the best interpretation may vary with the situation.”
Our brains may have evolved to sift through the barrage of visual input in our eyes and identify those things that are most important for us to consciously perceive, such as a threat or resources such as food, Peterson suggested.
In the future, Peterson and Sanguinetti plan to look for the specific regions in the brain where the processing of meaning occurs.
“We’re trying to look at exactly what brain regions are involved,” said Peterson. “The EEG tells us this processing is happening and it tells us when it’s happening, but it doesn’t tell us where it’s occurring in the brain.”
“We want to look inside the brain to understand where and how this meaning is processed,” said Peterson.
Images were shown to Sanguinetti’s study participants for only 170 milliseconds, yet their brains were able to complete the complex processes necessary to interpret the meaning of the hidden objects.
“There are a lot of processes that happen in the brain to help us interpret all the complexity that hits our eyeballs,” Sanguinetti said. “The brain is able to process and interpret this information very quickly.”
Sanguinetti’s study indicates that in our everyday life, as we walk down the street, for example, our brains may recognize many meaningful objects in the visual scene, but ultimately we are aware of only a handful of those objects. The brain is working to provide us with the best, most useful possible interpretation of the visual world, Sanguinetti said, an interpretation that does not necessarily include all the information in the visual input.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by University of Arizona.