Current computing is based on binary logic – zeroes and ones – also called Boolean computing. A new type of computing architecture that stores information in the frequencies and phases of periodic signals could work more like the human brain to do computing using a fraction of the energy of today’s computers.
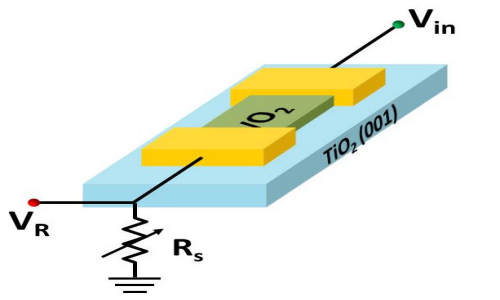
An illustration of an oscillating switch, the basis of a new type of low-power analog computing. Photo Credit: Nikhil Shukla, Penn State
Vanadium dioxide (VO2) is called a “wacky oxide” because it transitions from a conducting metal to an insulating semiconductor and vice versa with the addition of a small amount of heat or electrical current. A device created by electrical engineers at Penn State uses a thin film of VO2 on a titanium dioxide substrate to create an oscillating switch. Using a standard electrical engineering trick, Nikhil Shukla, a Ph.D. student in the group of Professor Suman Datta and co-advised by Professor Roman Engel-Herbert at Penn State, added a series resistor to the oxide device to stabilize their oscillations over billions of cycles. When Shukla added a second similar oscillating system, he discovered that over time the two devices would begin to oscillate in unison. This coupled system could provide the basis for non-Boolean computing. The results are reported in the May 14 online issue of Nature Publishing Group’s Scientific Reports.
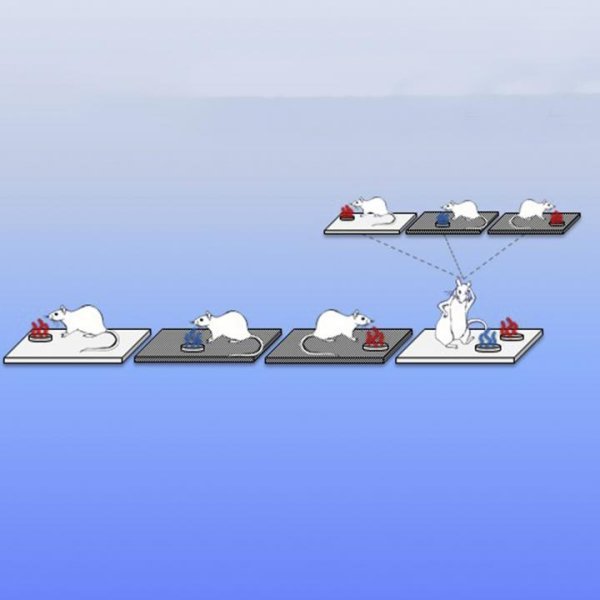
“It’s called a small-world network,” explained Shukla. “You see it in lots of biological systems, such as certain species of fireflies. The males will flash randomly, but then for some unknown reason the flashes synchronize over time.” The brain is also a small-world network of closely clustered nodes that evolved for more efficient information processing.
“Biological synchronization is everywhere,” added Datta, professor of electrical engineering at Penn State and formerly a Principal Engineer in the Advanced Transistor and Nanotechnology Group at Intel Corporation. “We wanted to use it for a different kind of computing called associative processing, which is an analog rather than digital way to compute.” An array of oscillators can store patterns, for instance, the color of someone’s hair, their height and skin texture. If a second area of oscillators has the same pattern, they will begin to synchronize, and the degree of match can be read out. “They are doing this sort of thing already digitally, but it consumes tons of energy and lots of transistors,” Datta said. Datta is collaborating with co-author and Professor of Computer Science and Engineering, Vijay Narayanan, in exploring the use of these coupled oscillations in solving visual recognition problems more efficiently than existing embedded vision processors as part of a National Science Foundation Expedition in Computing program.
Shukla and Datta called on the expertise of Cornell University materials scientist Darrell Schlom to make the VO2 thin film, which has extremely high quality similar to single crystal silicon. Georgia Tech computer engineer Arijit Raychowdhury and graduate student Abhinav Parihar mathematically simulated the nonlinear dynamics of coupled phase transitions in the VO2 devices. Parihar created a short video simulation of the transitions, which occur at a rate close to a million times per second, to show the way the oscillations synchronize. Penn State professor of materials science and engineering Venkatraman Gopalan used the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National laboratory to visually characterize the structural changes occurring in the oxide thin film in the midst of the oscillations.
Datta believes it will take seven to ten years to scale up from their current network of two-three coupled oscillators to the 100 million or so closely packed oscillators required to make a neuromorphic computer chip. One of the benefits of the novel device is that it will use only about one percent of the energy of digital computing, allowing for new ways to design computers. Much work remains to determine if VO2 can be integrated into current silicon wafer technology. “It’s a fundamental building block for a different computing paradigm that is analog rather than digital,” Shukla concluded.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by Penn State Materials Research Institute.