Despite the effectiveness of vaccination campaigns worldwide, the threat posed by Covid-19 still exists. First of all, a new SARS-CoV-2 variant could very well emerge that may not respond to current vaccines. Secondly, the efficacy of the vaccines in the long term remains unknown. Lastly, cases of acute infection are continuing to be reported. And yet, there is no effective treatment to date.
Credit: University of Louvain (UCLouvain)
Despite the effectiveness of vaccination campaigns worldwide, the threat posed by Covid-19 still exists. First of all, a new SARS-CoV-2 variant could very well emerge that may not respond to current vaccines. Secondly, the efficacy of the vaccines in the long term remains unknown. Lastly, cases of acute infection are continuing to be reported. And yet, there is no effective treatment to date.
In order to develop an antiviral that prevents infection, it is first necessary to understand the exact mechanisms (at molecular level) used by the virus to infect a cell. This is the task that the team of David Alsteens, researcher at the Institute of Biomolecular Sciences and Technologies of University of Louvain (UCLouvain), Belgium, has been working on for the last two years. In a study published in Nature Communications, they investigated the interaction between sialic acids (SAs), which are sorts of sugar residues present on the surface of cells, and the spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2 (using atomic force microscopy). The purpose? To understand its role in the infection process.
What do we already know? That all cells are decorated with sugar residues. And what purpose do these sugars serve? To promote cell recognition, which allows viruses to identify their targets more easily. But, also, to facilitate their point of attachment to allow them to enter their host cell and thus initiate their infection.
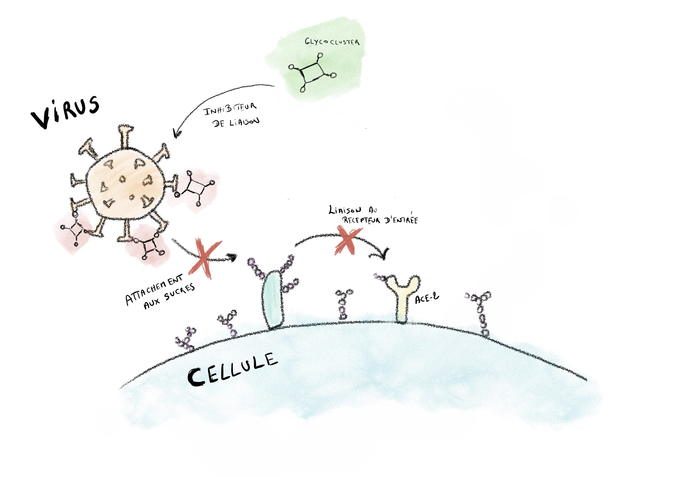
What did the UCLouvain researchers discover? They identified a variant of these sugars (9-O-acetylated) that interacted more strongly with the S protein than other sugars. In short, they found the set of keys that allows viruses to open the cell door. Why a set of keys? The virus is composed of a series of spike proteins with a suction cup effect that allows them to bind to the cell and ultimately enter. The more keys the virus finds, the better the interaction with the cell and the wider the door will open. Hence the importance of finding out how the virus manages to multiply the entry keys.
This is where the second discovery of the UCLouvain researchers comes in: they decided to catch the virus in its own trap, by preventing it from binding to its host cell. How? By blocking the S protein’s points of attachment and thus suppressing any interaction with the cell surface. As though a padlock had been attached to the lock of the cell’s front door. One of the conditions for this is that the interaction between the virus and the agent blocking it is stronger than the one between the virus and the cell. In this particular case, the scientists demonstrated that multivalent structures (or glycoclusters) with multiple 9-O-acetylated sialic acids on their surface (the famous sugar variant revealed by the UCLouvain team) are able to block both binding and infection by SARS-CoV-2. If the virus doesn’t attach to the cells, it can’t enter and therefore dies (lifetime 1 to 5 hours). This blocking action prevents infection.
Within the context of the Covid-19 pandemic, the various vaccines primarily addressed the SARS-CoV-2 mutations but not the virus as a whole. This UCLouvain discovery has the advantage of acting on the virus, independently of the mutations.
What’s next? The UCLouvain team will carry out tests on mice in order to apply this blocking of virus binding sites and observe whether this works on the organism. The results should be available soon, leading to the development of an antiviral based on these sugars, administered by aerosol, in case of infection or high-risk contact.
This discovery is also interesting for the future, to counter other viruses with similar attachment factors.
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-022-30313-8
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Multivalent 9-O-Acetylated-sialic acid glycoclusters as potent inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 infection
Article Publication Date
10-May-2022




