Tests showed that the animals were able to discern facial features and track images with their eyes.
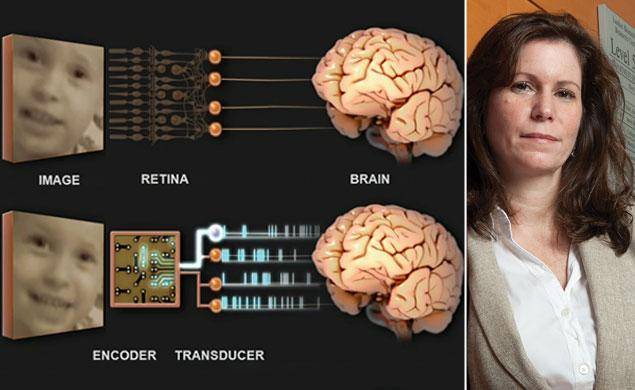
A reconstruction based on electrical signals from the implant showed recognisable features of a baby’s face. In contrast, a standard retinal implant without the new encoder produced a confused pattern of bright and dark spots.
The results, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could pave the way to life-changing retinal prosthetics, the scientists believe.
Even the best retinal implants currently restore only very limited vision, allowing patients to see spots of light and high-contrast edges. The US team led by Dr Sheila Nirenberg, from Cornell University in New York, wrote: “Our results show that incorporation of the code dramatically increases prosthetic performance, well beyond what can be achieved just by increasing resolution. “Moreover, they show that the combination of the code and high-resolution stimulation is able to bring prosthetic capabilities up to the level of normal or near-normal image presentation.”
Scientists around the world are exploring the potential of retinal implants to help people with degenerative blinding diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa.
More than 20 million people around the world are blind or at risk of blindness due to the diseases. Typically, they destroy the light-sensitive photoreceptors of the retina but leave nerve connections intact.
By replacing natural photoreceptors with artificial ones, it is hoped that some degree of sight can be restored. However, results to date have been disappointing. Although some sight can be restored, serious visual impairment remains.
The new study shows that boosting resolution – effectively the number of “pixels” the eye can see – is not enough on its own. For the image to be relayed successfully to the brain, the light signals must first be translated into the right patterns of electrical impulses.
Ganglion cells, a type of nerve cell within the retina, are responsible for communicating the visual messages. In congenitally blind mice fitted with the new implant, the ganglion cells fired correctly almost 90% of the time, said the scientists.
Behavioural and eye-tracking experiments suggested that a high level of vision had been restored to the mice. In one striking test, an image of a baby’s face was reconstructed from the “spike trains” – electrical signals – produced by blind mouse retinas with standard and encoder implants. Features that could not be seen at all in the “standard” reconstruction were clearly visible from the new implant. “Not only is it possible to discern that the image is a baby’s face, but also it is possible to tell that it is this particular baby,” the scientists wrote.
They concluded: “In sum, our results show that incorporating the code dramatically increases prosthetic capabilities. Although increasing resolution also improves performance, there is an inherent ceiling on the quality of image this can produce; adding the code breaks through this barrier. The coded output combined with high-resolution stimulation makes natural vision restoration possible.”
Source: businessinsider