Credit: XIN Weiwen
Lithium is an energy-critical element that is considered to be a geopolitically significant resource. However, the supply of lithium may not be enough to meet continuously increasing demand. As a result, scientists are looking for new ways to extract lithium ions.
Ion selective membranes have already been used extensively for water treatment and ion sieving in electrodialysis technology. However, conventional membranes exhibit low and useless Li+ selectivity, making them insufficient for meeting industry requirements.
Chinese scientists have recently made progress in the preparation and application of a bioinspired material that is capable of achieving controlled ion transport and sieving, especially for lithium-ion extraction.
This work, published in Matter, was completed by Prof. WEN Liping’s team at the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. ZHANG Qianfan’s team from Beihang University.
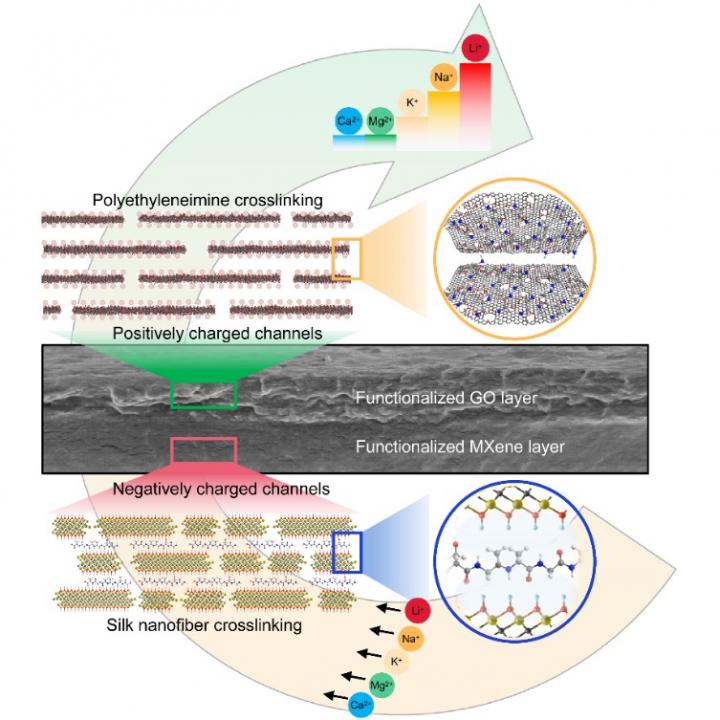
In this research, scientists utilized nanofibers, such as from natural silk and polyethyleneimine, to decorate 2D nanosheets. Inspired by the biological structure in nature, the 2D nanosheets are self-assembled layer-by-layer to form a nacre-like stacked structure. The composited membrane acts as an ion-gating heterojunction with opposite charges and asymmetrical nanochannels.
“To be more detailed, the composited membrane shows higher toughness than other reported materials and natural nacre structures. The membrane is also able to efficiently control interlayer spacing and achieve stable ordered nanostructures,” said Prof. WEN.
The typical brick-and-mortar structure formed by nanofibers and nanosheets exhibits a long-time use in solutions. Meanwhile, the confined dehydration and charge-exclusion effects conduct Li+ through composited channels rapidly.
Experimental and theoretical results indicate Li+ shows an excellent permeation rate that is far higher than Na+, K+, Mg2+ and Ca2+ due to its small radius and low charge.
Compared with mobilities in bulk, Li+ remains basically consistent with the bulk value. In stark contrast, other ions become less mobile than Li+ in bulk.
The methodology of using tailor-made 2D membranes with chemical, geometrical, and electrostatic heterostructures allows further exploration of nanofluidic phenomena inside nanochannel membranes for water treatment or power generation.
###
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Media Contact
HE Jianing
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




