Credit: Kanazawa University
Kanazawa, Japan – A team of scientists led by Kanazawa University proposed a new mathematical framework to understand the properties of the fundamental particles called neutrinos. This work may help cosmologists make progress on the apparent paradox of the existence of matter in the Universe.
The Standard Model of particle physics that outlines the basic constituents of matter and the forces that act between them has seen remarkable experimental success, culminating in the discovery of the last predicted particle, the Higgs boson, in 2012. However, the Standard Model does not resolve some of the long-standing issues in cosmology, such as the identity of “dark matter” that we know must be there but we cannot see, and why there is so much matter in the Universe compared with antimatter. Many scientists believe that the ghost-like particles called neutrinos may be an important part of the answer.
Neutrinos, which hardly interact with other matter, are created by nuclear reactions such as those that power our sun, and trillions of them pass through your body every second. Experiments have shown that, while not massless, neutrinos are much lighter than other particles. This has led physicists to hypothesize that neutrinos get their mass from a different process compared with other particles, called the “Seesaw mechanism.”
Now, a research team led by Kanazawa University has developed a new theory to explain the unusual properties of neutrinos.
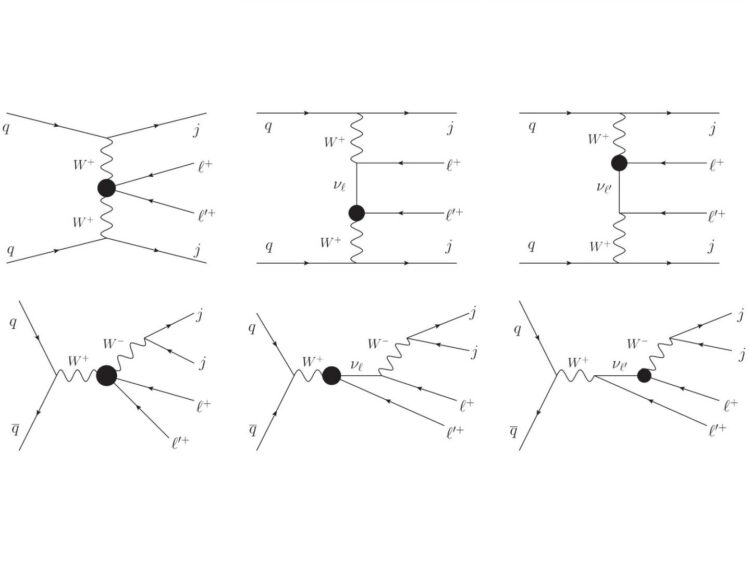
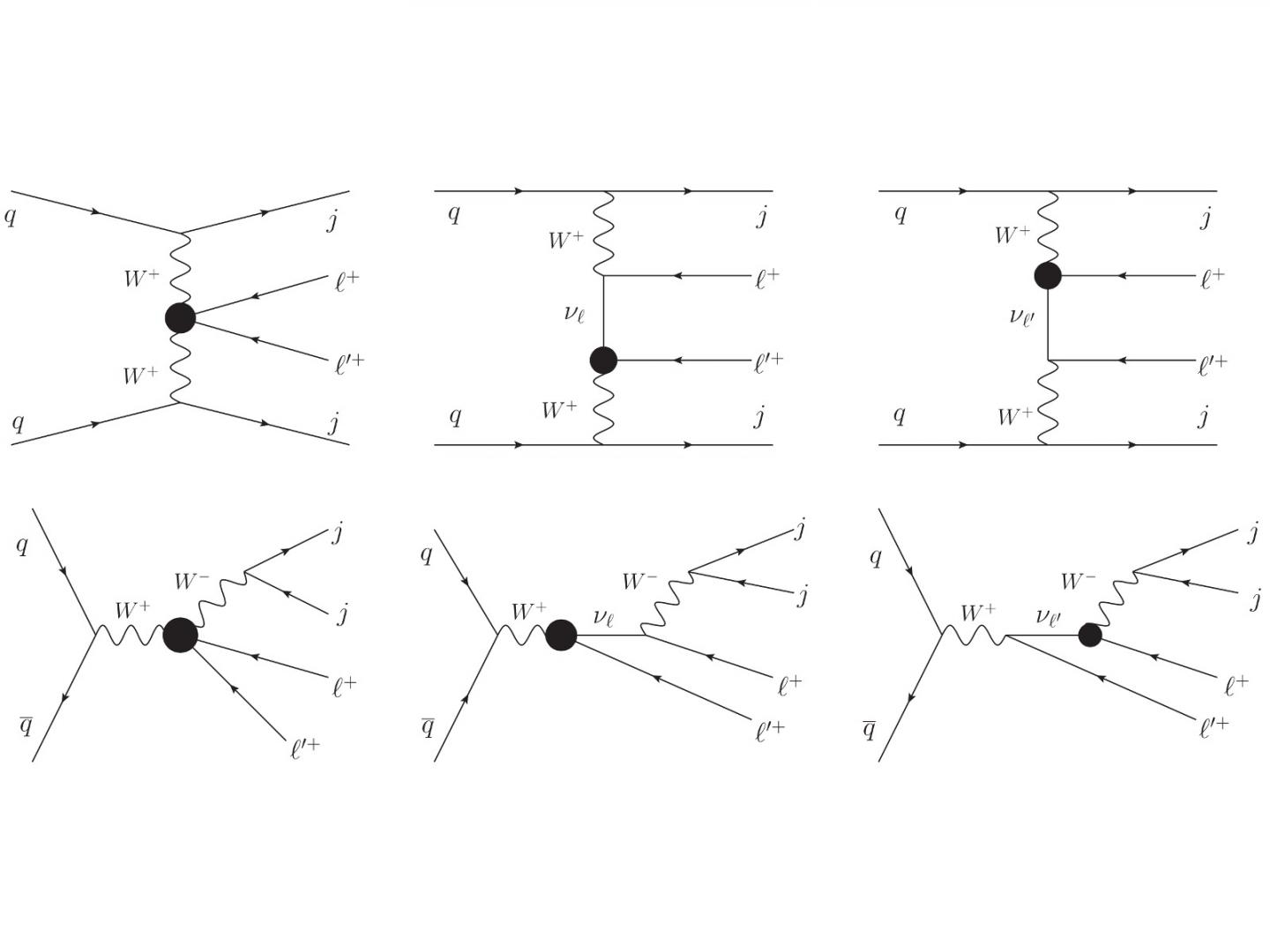
“We used the seesaw mechanisms with five- or seven-dimensional operators to describe the interaction of a neutrino with two lepton particles and two force-carrying W bosons,” explains Mayumi Aoki.
Leptons are a class of elementary particles that include neutrinos, electrons, and so on. Solving these equations showed violations of the Standard Model’s prediction that the number of leptons is always conserved.
“To move beyond the Standard Model, we have to explain why lepton conservation is sometimes violated, albeit to a very small degree,” says Aoki. “A tiny imbalance of one part in a trillion may explain the why all matter didn’t get annihilated by antimatter after the Big Bang.”
“Our work explains the origin of the neutrino mass and also provides predictions directly testable by the Large Hadron Collider,” says Aoki. The very light masses of neutrinos might hold the key to solving the big questions that have challenged humanity for millennia.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.