Credit: Illustration: Nils Wiedemann
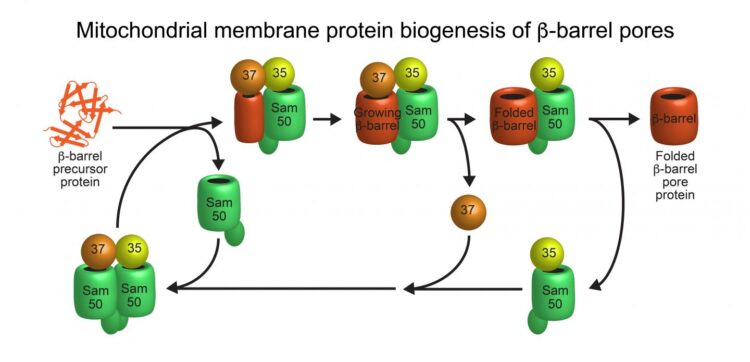
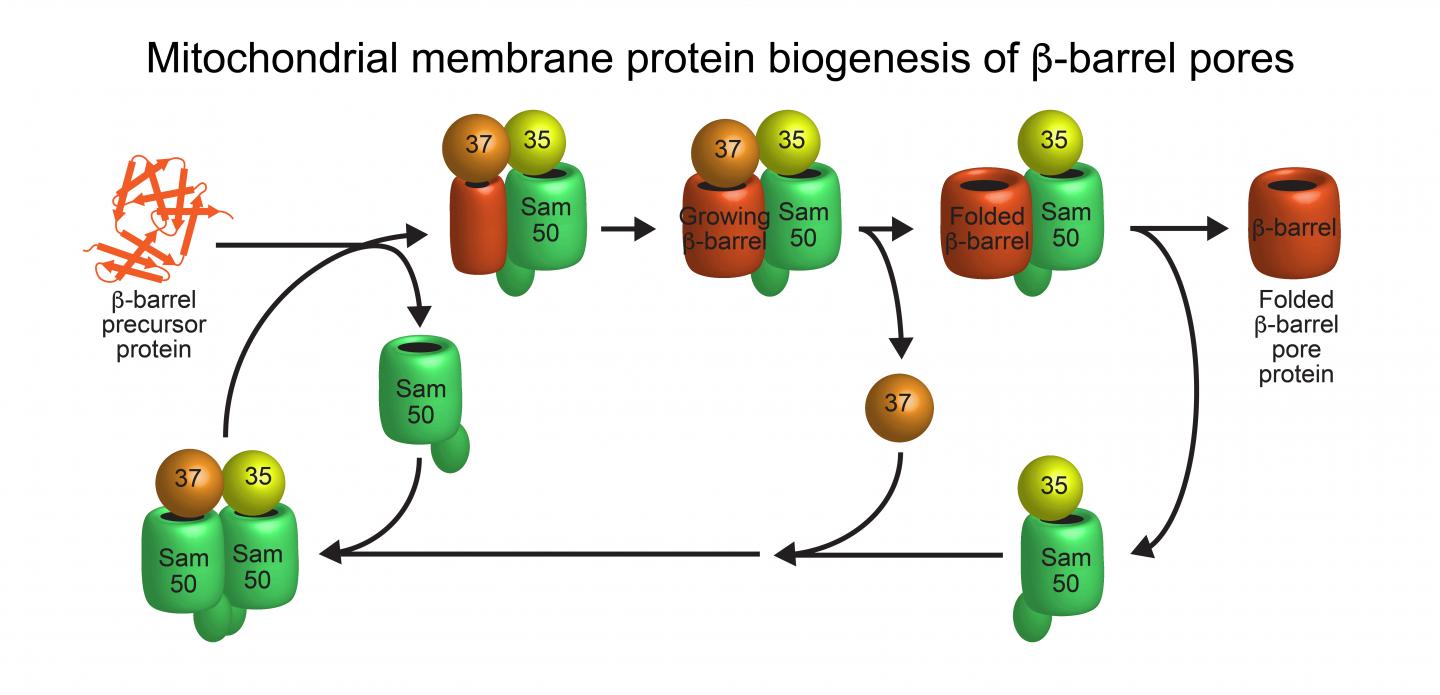
Mitochondria are vital for the human body as cellular powerhouses: They possess more than 1,000 different proteins, required for many central metabolic pathways. Disfunction of these lead to severe diseases, especially of the nervous system and the heart. In order to transport proteins and metabolites, mitochondria contain a special group of so-called beta-barrel membrane proteins, which form transport pores in the outer mitochondrial membrane. So far, scientists have not been able to explain the operating mode of the sorting and assembly machinery (SAM) for the biogenesis of these beta-barrel proteins. A team led by Prof. Dr. Toshiya Endo from Kyoto University/Japan, Prof. Dr. Nils Wiedemann and Prof. Dr. Nikolaus Pfanner from the University of Freiburg and Prof. Dr. Thomas Becker from the University of Bonn has now solved the structure and function of the SAM complex. The researchers have published their results in the journal Nature.
The SAM complex consists typically of two beta-barrel subunits named Sam50, which are capped on their outside by the two additional subunits Sam35 and Sam37. The researchers found that while the SAM complex forms a new beta-barrel protein, it contains only one Sam50. The second beta-barrel subunit functions as a flexible placeholder: it temporarily leaves the SAM complex, freeing the space for the new beta-barrel protein to form. This dynamic mechanism suggests how a new beta-barrel protein can mature to full size in the SAM complex and only be released as a completely folded protein. “This enabled us to identify a new principle for the formation of membrane proteins that perform vital functions in our cells,” explains Wiedemann.
###
Nils Wiedemann and Nikolaus Pfanner are group leaders at the Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology and project leaders in the clusters of excellence in biological signaling BIOSS and CIBSS as well as the Spemann Graduate School of Biology and Medicine at the University of Freiburg.
Original publication
Takeda, H., Tsutsumi, A., Nishizawa, T., Lindau, C., Busto, J.V., Wenz, L.S., Ellenrieder, L., Imai, K., Straub, S.P., Mossmann, W., Qiu, J., Yamamori, Y., Tomii, K., Suzuki, J., Murata, T., Ogasawara, S., Nureki, O., Becker, T., Pfanner, N., Wiedemann, N., Kikkawa, M., Endo, T. (2021): Mitochondrial sorting and assembly machinery operates by β-barrel switching. In: Nature. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-03113-7
Contact:
Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Faculty of Medicine
University of Freiburg
Media Contact
Prof. Dr. Nils Wiedemann
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.