Autophagy disruption may be at the root of early cognitive changes in Huntington’s disease and is a potential target for disease-modifying therapies, report scientists in the Journal of Huntington’s Disease
Credit: Journal of Huntington’s Disease
Amsterdam, July 15, 2021 – Huntington’s Disease (HD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition characterized by motor, cognitive, and psychiatric symptoms, and motor symptoms are often preceded by cognitive changes. Recent evidence indicates that autophagy plays a central role in synaptic maintenance, and the disruption in autophagy may be at the root of these early cognitive changes. Understanding this mechanism better may help researchers develop treatments for patients with HD early in their disease progression, report scientists in a review article published in the Journal of Huntington’s Disease.
In this review, experts describe how autophagy, the cellular process responsible for clearing old or damaged parts of the cell, plays a critical role supporting synaptic maintenance in the healthy brain, and how autophagy dysfunction in HD may thereby lead to impaired synaptic maintenance and thus early manifestations of disease. The line of research discussed in this review represents a previously unexplored avenue for identifying potential disease-modifying therapies for HD.
“Like many neurodegenerative conditions affecting primarily cognition, such as Alzheimer’s disease, preclinical and clinical data indicate that synapses, the part of brain cells responsible for communication between cells, are affected early in HD,” explained Hilary Grosso Jasutkar, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, Columbia University, and Ai Yamamoto, PhD, Departments of Neurology and Pathology and Cell Biology, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA. “We have long thought that autophagy played a role in the pathophysiology of HD, but what this role is has been unclear until recently. Recent evidence indicates that autophagy may be important in maintaining the synapse. This line of research has the potential to lead to identification of a drug target to treat HD early in the disease process.”
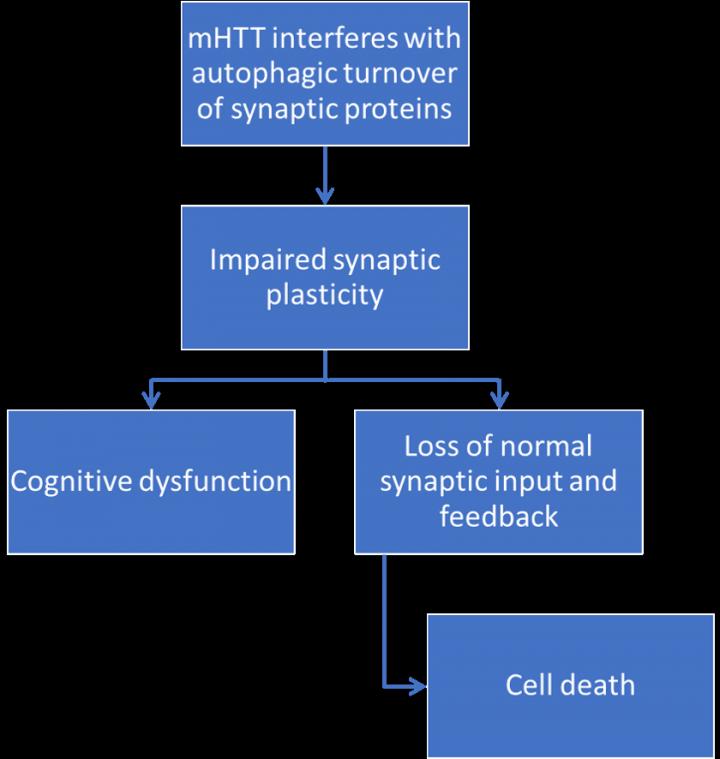
The authors first explore how cognitive dysfunction is an early manifestation of HD, and that similarly to other neurodegenerative diseases that primarily affect cognition, such as Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and frontotemporal dementia, early deficits in synaptic function may underlie these cognitive symptoms. Next, they review the growing evidence that the lysosome-mediated degradation pathway autophagy plays a central role in synaptic maintenance, and how the disruption in autophagy may contribute to early cognitive changes in HD.
The authors conclude that there are pathologic and imaging data in individuals with mutations in the Huntingtin protein (mHtt), as well as evidence from animal models with HD, that suggest that synapse dysfunction may occur early in HD, prior to cell death.
“Autophagy plays a specialized role in the maintenance and function of the synapse, and mHtt may disrupt this function, leading to the early synaptic changes seen in HD patients and model systems,” explained Dr. Grosso Jasutkar. “These synaptic changes may then manifest as impairments in synaptic plasticity and thus cognitive changes early in the disease course. Given that neurons rely on synaptic input and feedback for cell health, it is possible that this disruption in synaptic signaling in and of itself contributes to cell death in HD.”
“There is much work yet to be done in this field,” added Dr. Yamamoto. “Although various groups have demonstrated individual components of this pathway, a direct causal relationship of mutant Htt leading to synaptic dysfunction and, in turn, cognitive impairments, has yet to be demonstrated.”
“If the model described here is borne out, therapeutics aimed at enhancing the efficiency of synaptic autophagy early in the course of HD could be protective against early cognitive changes and potentially degeneration itself,” concluded the authors.
HD is a fatal genetic neurodegenerative disease that causes the progressive breakdown of nerve cells in the brain. An estimated 250,000 people in the United States are either diagnosed with, or at risk for, the disease. Symptoms include personality changes, mood swings and depression, forgetfulness and impaired judgment, unsteady gait, and involuntary movements (chorea). Every child of an HD parent has a 50% chance of inheriting the gene. Patients typically survive 10-20 years after diagnosis.
###
Media Contact
Diana Murray
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




